|
Apus (genus)
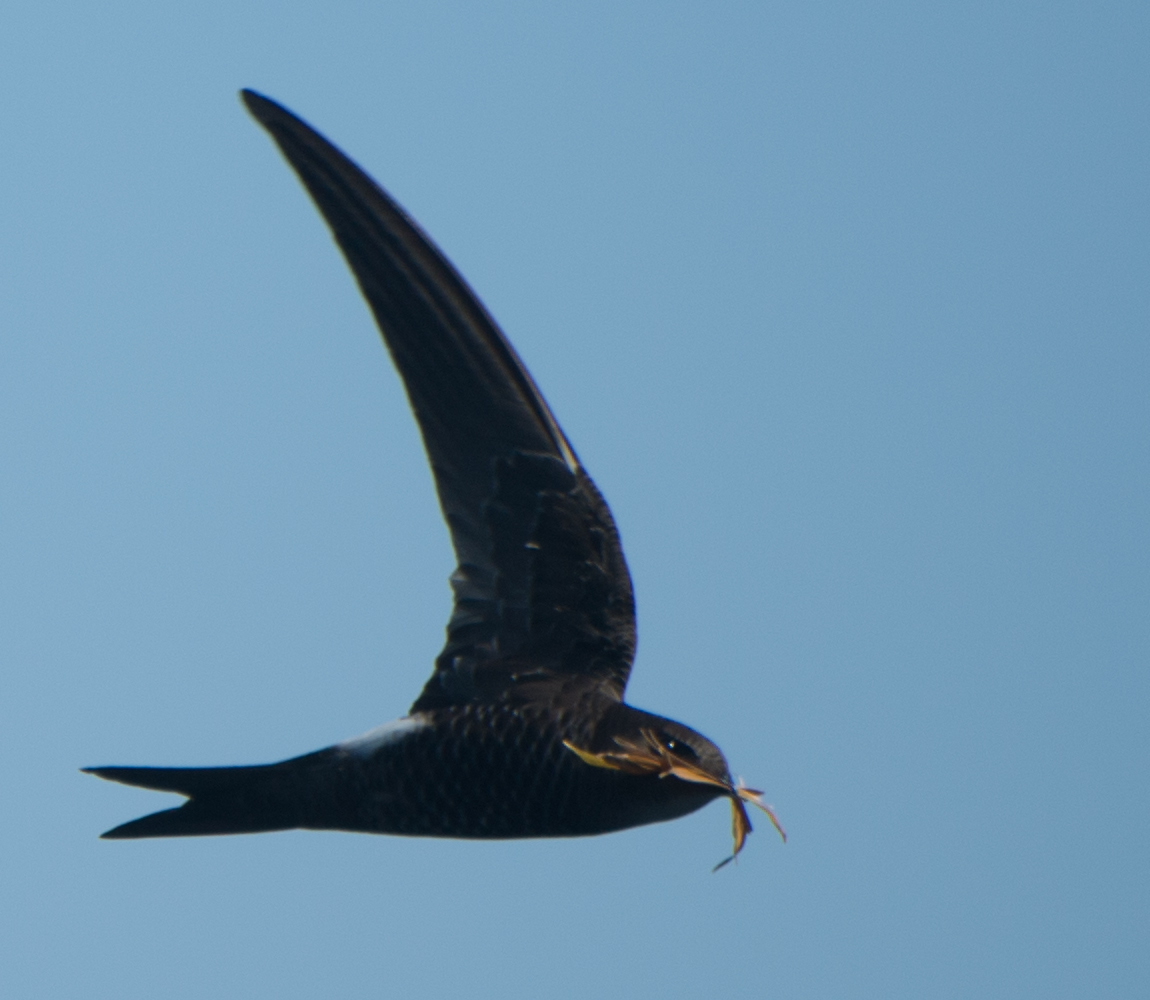
The bird genus ''Apus'' comprise some of the Old World members of the family Apodidae, commonly known as Swift (bird), swifts. They are among the fastest birds in the world. They resemble swallows, to which they are not related, but have shorter tails and sickle-shaped wings. Swifts spend most of their life aloft, have very short legs and use them mostly to cling to surfaces. Taxonomy The genus ''Apus'' was erected by the Italian naturalist Giovanni Antonio Scopoli in 1777 based on tautonymy and the common swift which had been given the binomial name ''Hirundo apus'' by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in 1758. The name ''Apus'' is Latin for a swift, thought by the ancients to be a type of swallow with no feet (from Ancient Greek α, ''a'', "without", and πούς, ''pous'', "foot"). Before the 1950s, there was some controversy over which group of organism should have the genus name ''Apus''. In 1801, Louis Augustin Guillaume Bosc, Bosc gave the genus name ''Apus'' to the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Swift
The common swift (''Apus apus'') is a medium-sized bird, superficially similar to the barn swallow or Common house martin, house martin but somewhat larger, though not stemming from those passerine species, being in the order Apodiformes. The resemblances between the groups are due to convergent evolution, reflecting similar contextual development. The swifts' nearest relatives are the New World hummingbirds and the Southeast Asian treeswifts. Its scientific name ''Apus'' is Latin for a swift, thought by the ancients to be a type of swallow with no feet (from Ancient Greek α, ''a'', "without", and πούς, ''pous'', "foot"). Swifts have very short legs which they use primarily for clinging to vertical surfaces (hence the German name ''Mauersegler'', literally meaning "wall-glider"). They never settle voluntarily on the ground where they would be vulnerable to accidents and predation, and non-breeding individuals may spend up to ten months in continuous flight. Taxonomy The co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blyth's Swift
Blyth's swift (''Apus leuconyx'') is a small species of bird. It is superficially similar to a house martin, but completely unrelated to those passerine species, as swifts are in the order Apodiformes. The resemblances between the groups are due to convergent evolution reflecting similar life styles. Taxonomy The common name commemorates Edward Blyth (1810–1873), English zoologist and Curator of the Museum of the Asiatic Society of Bengal. The scientific name comes from the Greek απους, ''apous'', meaning "without feet". A 2011 study has many taxonomists splitting this species from the fork-tailed swift complex. Description Blyth's swifts are similar in size to common swift, and they are black except for a white rump. They can be distinguished from a partially leucistic common swift by the deeper tail fork, longer wings, bigger head and larger white throat patch. Distribution and habitat Blyth's swifts breeds from the outer Himalayas through the Assam As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salim Ali's Swift
Salim Ali's swift (''Apus salimalii'') is a small bird, superficially similar to a house martin. It is, however, completely unrelated to those passerine species, since swifts are in the order Apodiformes. The resemblances between the groups are due to convergent evolution reflecting similar life styles. These birds have very short legs which they use only for clinging to vertical surfaces, almost never settling voluntarily on the ground. The scientific name of their genus comes from the Greek απους, ''apous'', meaning "without feet". Salim Ali's swifts spend most of their lives in the air, living on the insects they catch in their beaks. Salim Ali's swifts breed from the eastern Tibetan Plateau eastwards through western Sichuan province. This species is migratory; however, its wintering range is unknown. This swift is longer tailed and has a narrower white rump compared to other species in the complex. A 2011 study split this species from the fork-tailed swift complex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Swift
The Pacific swift (''Apus pacificus'') is a species of bird that is part of the Swift family. It breeds in eastern Asia. It is strongly migratory, spending the northern hemisphere's winter in Southeast Asia and Australia. The general shape and blackish plumage recall its relative, the common swift, from which it is distinguished by a white rump band and heavily marked underparts. The sexes are identical in appearance, although young birds can be identified by pale fringes to the wing feathers that are absent in adults. This swift's main call is a screech typical of its family. It is one of a group of closely related Asian swifts formerly regarded as one species. The Pacific swift is found in a wide range of climatic zones and habitats. It breeds in sheltered locations such as caves, natural rock crevices or under the roofs of houses. The nest is a half-cup of dry grass and other fine material that is gathered in flight, cemented with saliva and attached to a vertical surface. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bradfield's Swift
Bradfield's swift (''Apus bradfieldi'') is a species of swift in the family Apodidae. It is found in Angola, Botswana, Namibia, and South Africa South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O .... The common name and Latin binomial commemorate the South African naturalist R. D. Bradfield (1882–1949). References External links * Bradfield's swift Species text in The Atlas of Southern African Birds Bradfield's swift Birds of Southern Africa Fauna of Namibia Bradfield's swift Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{apodiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forbes-Watson's Swift
Forbes-Watson's swift (''Apus berliozi'') is a species of swift in the family Apodidae. It breeds in coastal areas of Somalia and the southern Arabian Peninsula and on the island of Socotra Socotra, locally known as Saqatri, is a Yemeni island in the Indian Ocean. Situated between the Guardafui Channel and the Arabian Sea, it lies near major shipping routes. Socotra is the largest of the six islands in the Socotra archipelago as .... In the non-breeding season it has been observed as far south as coastal Mozambique. References Apus (genus) Birds of the Horn of Africa Birds of the Arabian Peninsula Fauna of Socotra Birds described in 1965 Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{apodiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fernando Po Swift
The Fernando Po swift (''Apus sladeniae'') is a species of swift in the family Apodidae. It is found in Angola, Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, and Nigeria Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, .... The specific epithet is for Constance Sladen, who provided financial support for its discovery.Beolens, B., Watkins, M. and Grayson, M. (2020). The Eponym Dictionary of Birds: Bloomsbury Publishing, p. 516. References Apus (genus) Birds of Central Africa Birds described in 1904 Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{apodiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malagasy Black Swift
The Malagasy black swift (''Apus balstoni'') or Madagascar swift, is a species of swift in the family Apodidae. It is endemic to Madagascar and the Comoro Islands. Habitat Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests and subtropical or tropical moist montane forests. Subspecies * ''A. b. balstoni'' – Madagascar Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ... * ''A. b. mayottensis'' – Comoro Islands References Malagasy black swift Birds of the Comoros Birds of Madagascar Malagasy black swift Taxa named by Edward Bartlett Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{apodiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Black Swift
The African black swift (''Apus barbatus''), also known as the African swift or black swift, is a medium-sized bird in the swift family. It breeds in Africa discontinuously from Liberia, Cameroon, Zaire, Uganda and Kenya southwards to South Africa. The "black swifts" of Madagascar and the Comoros are either taken as two subspecies of the African black swift, or otherwise deemed a full species, the Malagasy black swift. Distinctive features The African black swift is long and bulky like a pallid swift; it appears entirely blackish-brown except for a small white or pale grey patch on the chin which is not visible from a distance. It has a short forked tail and very long swept-back wings that resemble a crescent or a boomerang. This species is very similar to the common swift but can be distinguished under optimum viewing conditions by the contrast between its black back and paler secondary wing feathers. The heavier build also gives it a distinctive flight action, which consisted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pallid Swift
The pallid swift (''Apus pallidus'') is a Swift (bird), swift (order Apodiformes). Swifts have very short legs which they use only for clinging to vertical surfaces. The genus name ''Apus'' is Latin for a swift, thought by the ancients to be a type of swallow with no feet (from Ancient Greek α, ''a'', "without", and πούς, ''pous'', "foot"), and ''pallidus'' is Latin for "pale". Like other swifts they never settle voluntarily on the ground, but spend most of their lives in the air, living on the insects they catch in their beaks. They drink on the wing. Taxonomy The pallid swift was first described by English naturalist George Ernest Shelley in 1870. Description This long species is very similar to the common swift, and separation is only possible with good views. Like its relative, it has a short forked tail and very long swept-back wings that resemble a crescent or a boomerang. It is entirely dark except for a large white throat patch which is frequently visible from a di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyanza Swift
The Nyanza swift (''Apus niansae'') is a species of swift in the family Apodidae. It is found in Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Somalia, South Sudan, Tanzania, and Uganda. Identification The Nyanza swift, also known as the brown swift, is a medium sized bird with sleek wings, along with a small and compact head. It has a short, forked tail, blunt rectrices, and small coverts. In contrast with its head and torso, the Nyanza swift’s outer wings are pale brown along with a pale throat. In the field, the Nyanza swift is commonly unseen and hard to identify without a good view or clear picture. It is commonly spotted in the rainy season and scarce during dry parts of the year. The anatomy of the Nyanza swift is not well known. Subspecies There are 2 subspecies * ''Apus niansae niansas'' * ''Apus niansa somalicus'' Habitat The Nyanza swift can be found in areas of high elevation, gorges, cliff faces, and human settlements like cities and towns. It has been spotted in places such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |