|
Aplysioviolin
Aplysioviolin is a purple-colored molecule secreted by sea hares of the genera ''Aplysia'' and ''Dolabella (gastropod), Dolabella'' to deter predators. Aplysioviolin is a chemodeterrent, serving to dispel predators on Olfaction, olfactory and Taste, gustatory levels as well as by temporarily blinding predators with the molecule's dark color. Aplysioviolin is an important component of secreted ink and is strongly implicated in the sea hares' predatory escape mechanism. While the ink mixture as a whole may produce dangerous hydrogen peroxide and is relatively acidic, the aplysioviolin component alone has not been shown to produce human toxicity. Biosynthetic origin Aplysioviolin is a metabolic product of ''Aplysia californica'' species of sea hare, and is a major component to its ink mixture. Sea hares first consume red algae as nutriment, and extract from it the light-harvesting pigment phycoerythrin, cleaving it to separate the red-colored chromophore phycoerythrobilin from its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aplysia
''Aplysia'' () is a genus of medium-sized to extremely large sea slugs, specifically sea hares, which are a kind of marine gastropod mollusk. These benthic herbivorous creatures can become rather large compared with most other mollusks. They graze in tidal and subtidal zones of tropical waters, mostly in the Indo-Pacific Ocean (23 species); but they can also be found in the Atlantic Ocean (12 species), with a few species occurring in the Mediterranean. ''Aplysia'' species, when threatened, frequently release clouds of ink, it is believed in order to blind the attacker (though they are in fact considered edible by relatively few species). Following the lead of Eric R. Kandel, the genus has been studied as a model organism by neurobiologists, because its gill and siphon withdrawal reflex, as studied in ''Aplysia californica'', is mediated by electrical synapses, which allow several neurons to fire synchronously. This quick neural response is necessary for a speedy reaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aplysia Californica
The California sea hare (''Aplysia californica'') is a species of sea slug in the sea hare family, Aplysiidae.Rosenberg, G.; Bouchet, P. (2011). Aplysia californica J. G. Cooper, 1863. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=240765 on 2012-03-31 It is found in the Pacific Ocean, off the coast of California in the United States and northwestern Mexico. Distribution ''A. californica'' is found along the coast of California, United States, and northwestern Mexico (including the Gulf of California). ''Aplysia'' species inhabit the photic zone to graze on algae, mainly the intertidal, usually not deeper than . Description The maximum length recorded for the California sea hare is when crawling, thus fully extended, although most adult specimens are half this size or smaller. Adult animals can weigh up to . A closely related species, '' Aplysia vaccaria'', the black sea hare, can grow larger still. A California sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Textile
Textile is an Hyponymy and hypernymy, umbrella term that includes various Fiber, fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, Staple (textiles)#Filament fiber, filaments, Thread (yarn), threads, and different types of #Fabric, fabric. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the only manufacturing method, and many other methods were later developed to form textile structures based on their intended use. Knitting and Nonwoven, non-woven are other popular types of fabric manufacturing. In the contemporary world, textiles satisfy the material needs for versatile applications, from simple daily clothing to Bulletproof vest, bulletproof jackets, spacesuits, and Medical gown, doctor's gowns. Textiles are divided into two groups: consumer textiles for domestic purposes and technical textiles. In consumer textiles, Aesthetics (textile), aesthetics and Textile performance#Comfort, comfort are the most important factors, while in techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyeing
Dyeing is the application of dyes or pigments on textile materials such as fibers, yarns, and fabrics with the goal of achieving color with desired color fastness. Dyeing is normally done in a special solution containing dyes and particular chemical material. Dye molecules are fixed to the fiber by absorption, diffusion, or bonding with temperature and time being key controlling factors. The bond between the dye molecule and fiber may be strong or weak, depending on the dye used. Dyeing and printing are different applications; in printing, color is applied to a localized area with desired patterns. In dyeing, it is applied to the entire textile. The primary source of dye, historically, has been nature, with the dyes being extracted from plants or animals. Since the mid-19th century, however, humans have produced artificial dyes to achieve a broader range of colors and to render the dyes more stable for washing and general use. Different classes of dyes are used for different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APV Rudiger
APV may refer to: Science and technology * Advanced Power Virtualization, former name of PowerVM, an IBM software virtualization * APV (NMDAR antagonist), or AP5, a selective NMDA receptor antagonist * Advanced Professional Video, a video codec Transportation * Apple Valley Airport (California) (IATA airport code), US * Chevrolet Lumina APV, a minivan manufactured and marketed by General Motors * Suzuki APV, a microvan manufactured and marketed by Suzuki * Approach Procedure with Vertical guidance, a type of instrument approach in aviation Military * Armored protected vehicle, a kind of armoured fighting vehicle * Transport and aircraft ferry (US Navy hull classification symbol: APV); see List of auxiliaries of the United States Navy Other uses * Alavuden Peli-Veikot, a multi-sport club in Alavus, Finland * Allen Parkway Village, a housing development in Fourth Ward, Houston, US * Actuarial present value, a probability weighted present value often used in insurance * Adjusted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phycocyanobilin
Phycocyanobilin is a blue phycobilin, i.e., a tetrapyrrole chromophore found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of red algae, glaucophytes, and some cryptomonads. Phycocyanobilin is present only in the phycobiliproteins allophycocyanin and phycocyanin, of which it is the terminal acceptor of energy. It is covalently linked to these phycobiliproteins by a thioether bond. Phycocyanobilin (PCB), has the ability to bind to human serum albumin (HSA), protein found mainly in the blood of humans. This PCB-HCA complex benefits the structure of HSA, increasing the thermal stability of HSA, as well as increasing its ability to prevent against proteolytic activity of other proteins. Biosynthetic Pathway The biosynthetic pathway of phycocyanobilin begins with 5-Aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA). Two molecules of 5-ALA undergo a condensation reaction catalyzed by Porphobilinogen (PBG) Synthase to yield a molecule of Porphobilinogen (PBG) (not shown). Four molecules of PBG are polymerized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
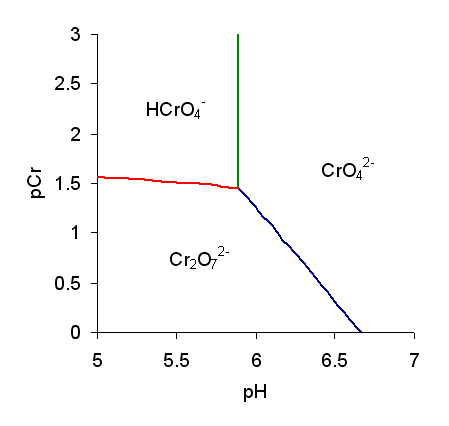
Chromic Acid
Chromic acid is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is also a jargon for a solution formed by the addition of sulfuric acid to aqueous solutions of dichromate. It consists at least in part of chromium trioxide. The term "chromic acid" is usually used for a mixture made by adding concentrated sulfuric acid to a dichromate, which may contain a variety of compounds, including solid chromium trioxide. This kind of chromic acid may be used as a cleaning mixture for glass. Chromic acid may also refer to the molecular species, of which the trioxide is the anhydride. Chromic acid features chromium in an oxidation state of +6 (and a valence of VI or 6). It is a strong and corrosive oxidizing agent and a moderate carcinogen. Molecular chromic acid Molecular chromic acid, , in principle, resembles sulfuric acid, . It would ionize accordingly: : The p''K''a for the equilibrium is not well characterized. Reported values vary between about −0.8 to 1.6. The structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean Civilization
The Mediterranean race (also Mediterranid race) is an Historical race concepts, obsolete racial classification of humans based on the now-disproven theory of biological race. According to writers of the late 19th to mid-20th centuries it was a sub-race of the Caucasian race. In various definitions it was said to be prevalent in the Mediterranean Basin and areas near the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and Black Sea, especially in Southern Europe, Eastern Europe, North Africa, most of West Asia, the Middle East or Near East; western Central Asia, parts of South Asia, and parts of the Horn of Africa. To a lesser extent, certain populations of people in Ireland, western parts of Great Britain, and Southern Germany, despite living far from the Mediterranean, were thought to have some minority Mediterranean elements in their population, such as Bavaria, Wales, and Cornwall.The Races of Europe by Carleton S. Coon, Carlton Stevens Coon. From Chapter XI: The Mediterranean World – Introd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrews
The Hebrews (; ) were an ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic-speaking people. Historians mostly consider the Hebrews as synonymous with the Israelites, with the term "Hebrew" denoting an Israelite from the nomadic era, which preceded the establishment of the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), Kingdom of Israel and Judah in the 11th century BCE. However, in some instances, the designation "Hebrew" may also be used historically in a wider sense, referring to the Phoenicians or other ancient Semitic-speaking civilizations, such as the Shasu on the eve of the Late Bronze Age collapse. It appears 34 times within 32 verses of the Hebrew Bible. Some scholars regard "Hebrews" as an ethnonym, while others do not, and others still hold that the multiple modern connotations of Ethnicity#Definitions and conceptual history , ethnicity may not all map well onto the sociology of Ancient Near East, ancient Near Eastern groups. By the time of the Roman Empire, the term () coul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
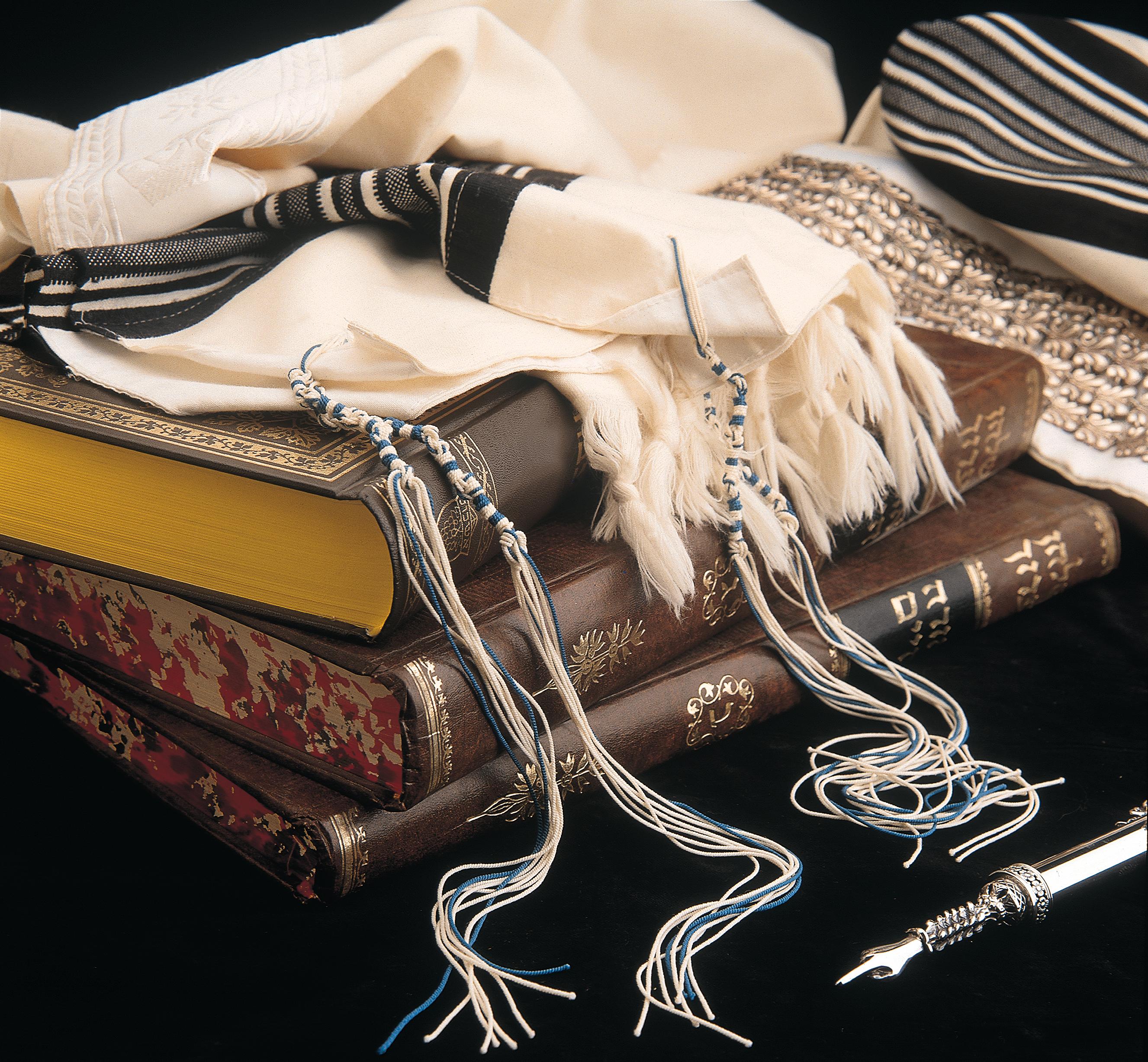
Tekhelet
''Tekhelet'' ( ''təḵēleṯ''; also transliterated ''tekheleth'', ''t'chelet'', ''techelet'', and ''techeiles'') is a highly valued blue dye that held great significance in history of the Mediterranean region, ancient Mediterranean civilizations. In the Hebrew Bible and Jewish tradition, tekhelet is used to color the ''tzitzit'' (fringe (trim), fringes) attached to the corners of four-cornered garments, including the tallit, and historically in the clothing of the High Priest of Israel and tapestries in the Tabernacle. The Bible does not specify the source or production method of tekhelet, but rabbinic literature records that it could only be derived from a marine animal known as the ''ḥillāzon'' (Hebrew: ). However, the knowledge of tekhelet production was lost during the Middle Ages, leading to the omission of tekhelet from tzitzit. In recent times, many Jews believe that experts have identified the ''ḥillāzon'' as the snail ''Hexaplex trunculus'' (historically cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural History of Europe, European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the interwoven civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, Rome known together as the Greco-Roman world, centered on the Mediterranean Basin. It is the period during which ancient Greece and Rome flourished and had major influence throughout much of Europe, North Africa, and West Asia. Classical antiquity was succeeded by the period now known as late antiquity. Conventionally, it is often considered to begin with the earliest recorded Homeric Greek, Epic Greek poetry of Homer (8th–7th centuries BC) and end with the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 AD. Such a wide span of history and territory covers many disparate cultures and periods. ''Classical antiquity'' may also refer to an idealized vision among later people of what was, in Ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |