|
Apennine Colossus
The Apennine Colossus ( it, Colosso Appenninico) is a stone statue, approximately 30 m high,Morgan, Luke (2015), p.12 in the estate of the Villa Demidoff in Vaglia, Tuscany in Italy. Giambologna (Flemish sculptor Jean de Boulogne) created the colossal figure, a personification of the Apennine mountains, in the late 1580s. It was constructed on the grounds of the Villa di Pratolino, a Renaissance villa that fell into disrepair and was replaced by the Villa Demidoff in the 1800s. Description of the sculpture The colossus is about highMorgan, Luke (2015), p.12 and is meant as a personification of the Apennine Mountains. It was the water source for the Pratolino, its fountains and secret water plays. The colossus has the appearance of an elderly man crouched at the shore of a lake and is surrounded by other sculptures depicting mythological themes from Ovid's Metamorphoses including Pegasus, Parnassus or Jupiter. It is presumed that Giambologna was inspired by the description of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giambologna
Giambologna (1529 – 13 August 1608), also known as Jean de Boulogne (French), Jehan Boulongne (Flemish) and Giovanni da Bologna (Italian), was the last significant Italian Renaissance sculptor, with a large workshop producing large and small works in bronze and marble in a late Mannerist style. Biography Giambologna was born in Douai, Flanders (then and now in France), in 1529. After youthful studies in Antwerp with the architect-sculptor Jacques du Broeucq, he moved to Italy in 1550 and studied in Rome, making a detailed study of the sculpture of classical antiquity. He was also much influenced by Michelangelo, but developed his own Mannerist style, with perhaps less emphasis on emotion and more emphasis on refined surfaces, cool elegance, and beauty. Pope Pius IV gave Giambologna his first major commission, the colossal bronze Neptune and subsidiary figures for the Fountain of Neptune (the base designed by Tommaso Laureti, 1566) in Bologna. Giambologna spent hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
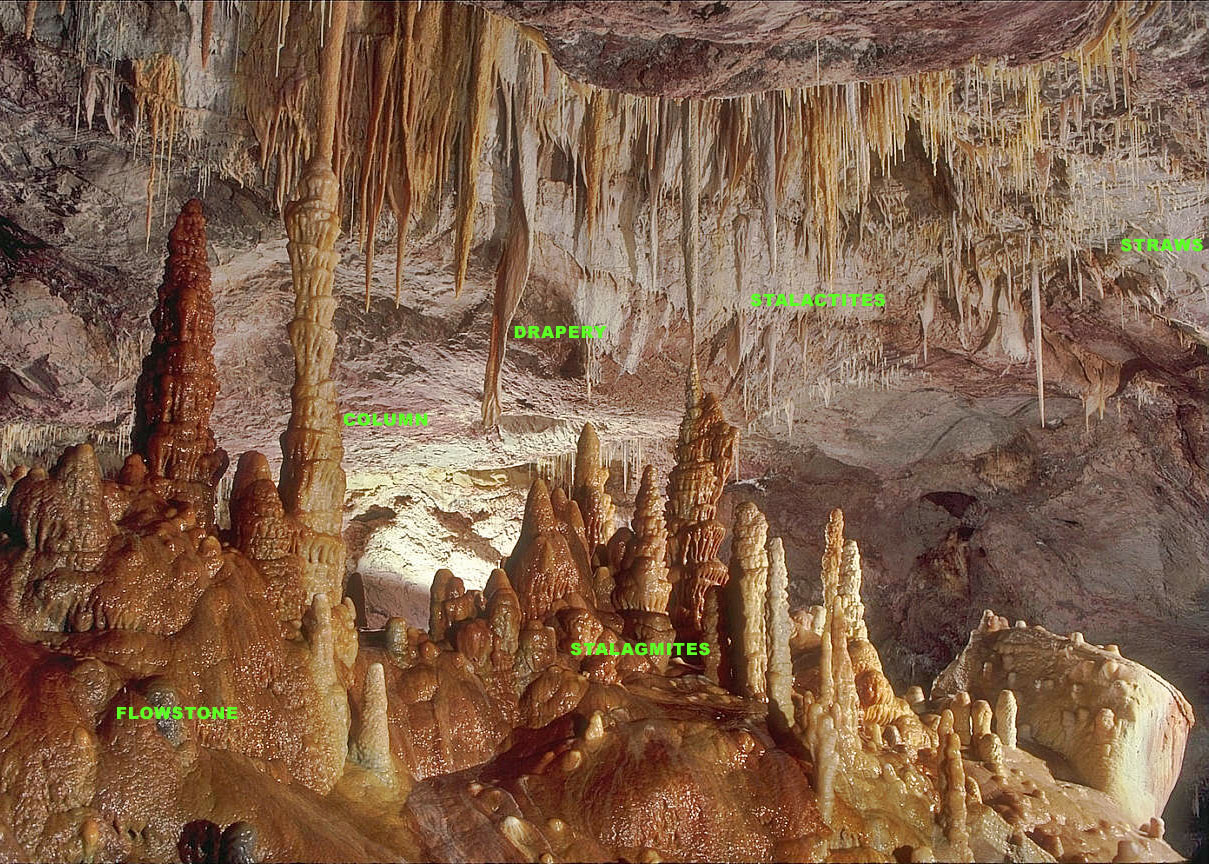
Stalactite
A stalactite (, ; from the Greek 'stalaktos' ('dripping') via ''stalassein'' ('to drip') is a mineral formation that hangs from the ceiling of caves, hot springs, or man-made structures such as bridges and mines. Any material that is soluble and that can be deposited as a colloid, or is in suspension, or is capable of being melted, may form a stalactite. Stalactites may be composed of lava, minerals, mud, peat, pitch, sand, sinter, and amberat (crystallized urine of pack rats). A stalactite is not necessarily a speleothem, though speleothems are the most common form of stalactite because of the abundance of limestone caves. The corresponding formation on the floor of the cave is known as a stalagmite. Mnemonics have been developed for which word refers to which type of formation; one is that ''stalactite'' has a C for "ceiling", and ''stalagmite'' has a G for "ground". Another example is that ''stalactites'' "hang on ''T''ight" and ''stalagmites'' "''M''ight grow up" � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non Finito
''Non finito'' is a sculpting technique meaning that the work is unfinished. Italian in etymology, it literally means "not finished". ''Non finito'' sculptures appear unfinished because the artist only sculpts part of the block, the figure sometimes appearing to be stuck within the block of material. It was pioneered by Donatello during the Renaissance and was also used by Michelangelo Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (; 6 March 1475 – 18 February 1564), known as Michelangelo (), was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work was in ... among others. The philosophic origins of ''non finito'' practice come from antiquity and the theories of Plato. Platonic philosophy states that any work of art, or otherwise, never completely resembles its heavenly counterpart. The act of leaving a work unfinished is sometimes a neo-Platonic homage to this. In the case of the ancient Romans, artists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michelangelo
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (; 6 March 1475 – 18 February 1564), known as Michelangelo (), was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work was inspired by models from classical antiquity and had a lasting influence on Western art. Michelangelo's creative abilities and mastery in a range of artistic arenas define him as an archetypal Renaissance man, along with his rival and elder contemporary, Leonardo da Vinci. Given the sheer volume of surviving correspondence, sketches, and reminiscences, Michelangelo is one of the best-documented artists of the 16th century. He was lauded by contemporary biographers as the most accomplished artist of his era. Michelangelo achieved fame early; two of his best-known works, the '' Pietà'' and ''David'', were sculpted before the age of thirty. Although he did not consider himself a painter, Michelangelo created two of the most influential fresc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Metropolitan Museum Of Art Bulletin
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 1000 Fifth Avenue, along the Museum Mile on the eastern edge of Central Park on Manhattan's Upper East Side, is by area one of the world's largest art museums. The first portion of the approximately building was built in 1880. A much smaller second location, The Cloisters at Fort Tryon Park in Upper Manhattan, contains an extensive collection of art, architecture, and artifacts from medieval Europe. The Metropolitan Museum of Art was founded in 1870 with its mission to bring art and art education to the American people. The museum's permanent collection consists of works of art from classical antiquity and ancient Egypt, paintings, and sculptures from nearly all the European masters, and an extensive collection of American and modern a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stefano Della Bella
Stefano della Bella (17 May 1610 – 12 July 1664) was an Italian draughtsman and printmaker known for etchings of a great variety of subjects, including military and court scenes, landscapes, and lively genre scenes. He left 1052 prints, and several thousand drawings, but only one known painting. He was born and died in Florence, Italy. Early life in Florence Della Bella was born at Florence to a family of artists, and was apprenticed to a goldsmith,Chishholm 1911. but became an engraver working briefly under Orazio Vanni and then Cesare Dandini.Massar 1996. He studied etching under Remigio Cantagallina, who had also been the instructor of Jacques Callot.Massar 1968, p. 160. Della Bella's early prints are very similar to those of Callot. When he was seventeen years of age, he presented an etching depicting a banquet in the Palazzo Pitti to the young Giancarlo de' Medici following which della Bella would receive official commissions by the Medici family. In 1630, at the age of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fishing Line
A fishing line is a flexible, high-tensile cord used in angling to tether and pull in fish, in conjunction with at least one hook. Fishing lines are usually pulled by and stored in a reel, but can also be retrieved by hand, with a fixed attachment to the end of a rod, or via a motor. Fishing lines generally resemble a long, ultra-thin rope, with important attributes including length, material, weight and thickness. Other factors relevant to certain fishing environments include breaking strength, knot strength, UV resistance, castability, limpness, stretch, abrasion resistance, and visibility. Traditional fishing lines are made of silk, while most modern lines are made from synthetic polymers such as nylon, polyethylene or polyvinylidene fluoride ("fluorocarbon") and may come in monofilament or braided ( multifilament) forms. Terminology Fishing with a hook-and-line setup is called angling. Fish are caught when one are drawn by the bait/ lure dressed on the hook int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgius Agricola
Georgius Agricola (; born Georg Pawer or Georg Bauer; 24 March 1494 – 21 November 1555) was a German Humanist scholar, mineralogist and metallurgist. Born in the small town of Glauchau, in the Electorate of Saxony of the Holy Roman Empire, he was broadly educated, but took a particular interest in the mining and refining of metals. For his groundbreaking work '' De Natura Fossilium'' published in 1546, he is generally referred to as the Father of Mineralogy.Rafferty, John P. (2012). ''Geological Sciences; Geology: Landforms, Minerals, and Rocks''. New York: Britannica Educational Publishing, p. 10. He is well known for his pioneering work '' De re metallica libri XII'', that was published in 1556, one year after his death. This 12-volume work is a comprehensive and systematic study, classification and methodical guide on all available factual and practical aspects, that are of concern for mining, the mining sciences and metallurgy, investigated and researched in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brill Publishers
Brill Academic Publishers (known as E. J. Brill, Koninklijke Brill, Brill ()) is a Dutch international academic publisher founded in 1683 in Leiden, Netherlands. With offices in Leiden, Boston, Paderborn and Singapore, Brill today publishes 275 journals and around 1200 new books and reference works each year all of which are "subject to external, single or double-blind peer review." In addition, Brill provides of primary source materials online and on microform for researchers in the humanities and social sciences. Areas of publication Brill publishes in the following subject areas: * Humanities: :* African Studies :* American Studies :* Ancient Near East and Egypt Studies :* Archaeology, Art & Architecture :* Asian Studies (Hotei Publishing and Global Oriental imprints) :* Classical Studies :* Education :* Jewish Studies :* Literature and Cultural Studies (under the Brill-Rodopi imprint) :* Media Studies :* Middle East and Islamic Studies :* Philosophy :* Religious ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacopo Ligozzi
Jacopo Ligozzi (1547–1627) was an Italian painter, illustrator, designer, and miniaturist. His art can be categorized as late-Renaissance and Mannerist styles. Biography Born in Verona, he was the son of the artist Giovanni Ermano Ligozzi, and part of a large family of painters and artisans. After a time in the Habsburg court in Vienna, where he displayed drawings of animal and botanical specimens, he was invited to come to Florence and became one of the court artists for the Medici. Upon the death of Giorgio Vasari in 1574, he became head of the '' Accademia e Compagnia delle Arti del Disegno'', the officially patronized guild of artists, which was often called to advise on diverse projects. He served Francesco I, Ferdinando I, Cosimo II and Ferdinando II, Grand Dukes of Tuscany. For the Medici, he adorned the Grotto of Thetys in the Colossus of the Apennine. He was named director of the grand-ducal ''Galleria dei Lavori'', a workshop providing designs for artworks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JSTOR
JSTOR (; short for ''Journal Storage'') is a digital library founded in 1995 in New York City. Originally containing digitized back issues of academic journals, it now encompasses books and other primary sources as well as current issues of journals in the humanities and social sciences. It provides full-text searches of almost 2,000 journals. , more than 8,000 institutions in more than 160 countries had access to JSTOR. Most access is by subscription but some of the site is public domain, and open access content is available free of charge. JSTOR's revenue was $86 million in 2015. History William G. Bowen, president of Princeton University from 1972 to 1988, founded JSTOR in 1994. JSTOR was originally conceived as a solution to one of the problems faced by libraries, especially research and university libraries, due to the increasing number of academic journals in existence. Most libraries found it prohibitively expensive in terms of cost and space to maintain a compre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_-_Fontana_del_Nettuno.jpg)