|
Aortic Valve Replacement
Aortic valve replacement is a cardiac surgery procedure whereby a failing aortic valve is replaced with an artificial heart valve. The aortic valve may need to be replaced because of aortic regurgitation (back flow), or if the valve is narrowed by stenosis. Current methods for aortic valve replacement include open-heart surgery, ''minimally invasive cardiac surgery (MICS)'', ''surgical aortic valve replacement'' (SAVR), percutaneous or transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR; also PAVR, PAVI, TAVI), and robotic aortic valve replacement (RAVR). A cardiologist can evaluate whether a heart valve repair or valve replacement would be of benefit. History During the late 1940s and early 1950s, the first surgical approaches towards treating aortic valve stenosis had limited success. The first attempts were valvotomies, (i.e. cutting the valve while the heart is pumping). A ball valve prosthesis placed on the descending thoracic aorta (heterotopically) was developed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aortic Sinus
An aortic sinus, also known as a sinus of Valsalva, is one of the anatomic dilations of the ascending aorta, which occurs just above the aortic valve. These widenings are between the wall of the aorta and each of the three cusps of the aortic valve. The aortic sinuses cause eddies which prevent the valve cusps from touching the internal surface of the aorta and obstructing the openings of the coronary arteries. Structure There are generally three aortic sinuses, one anterior and two posterior sinuses. These give rise to coronary arteries: * The left aortic or left posterior aortic sinus gives rise to the left coronary artery; * The right aortic or anterior aortic sinus gives rise to the right coronary artery; * The posterior aortic or right posterior aortic sinus usually gives rise to no vessels. It is often known as the ''non-coronary'' sinus. The aortic sinuses are typically more prominent than the pulmonary sinuses. Clinical significance If the coronary arteries aris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homograft
Allotransplant (''allo-'' meaning "other" in Greek) is the transplantation of cells, tissues, or organs to a recipient from a genetically non-identical donor of the same species. The transplant is called an allograft, allogeneic transplant, or homograft. Most human tissue and organ transplants are allografts. It is contrasted with autotransplantation (from one part of the body to another in the same person), syngenic transplantation of isografts (grafts transplanted between two genetically identical individuals) and xenotransplantation (from other species). Allografts can be referred to as "homostatic" if they are biologically inert when transplanted, such as bone and cartilage.(W. P. Longmire, ''J. National Cancer Institute'' 14, 669: ''The term ''homostatic graft'' might be applied to inert tissues such as bone and cartilage when transferred from one individual to another of the same species; and the term ''homovital graft'' might be used in reference to grafts whose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shortness Of Breath
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that consists of qualitatively distinct sensations that vary in intensity", and recommends evaluating dyspnea by assessing the intensity of its distinct sensations, the degree of distress and discomfort involved, and its burden or impact on the patient's activities of daily living. Distinct sensations include effort/work to breathe, chest tightness or pain, and "air hunger" (the feeling of not enough oxygen). The tripod position is often assumed to be a sign. Dyspnea is a normal symptom of heavy physical exertion but becomes disease, pathological if it occurs in unexpected situations, when resting or during light exertion. In 85% of cases it is due to asthma, pneumonia, cardiac ischemia, reflux/LPR, cardiac ischemia, COVID-19, interstitial lung di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aortic Insufficiency
Aortic regurgitation (AR), also known as aortic insufficiency (AI), is the leaking of the aortic valve of the heart that causes blood to flow in the reverse direction during ventricular diastole, from the aorta into the left ventricle. As a consequence, the cardiac muscle is forced to work harder than normal. Signs and symptoms Symptoms of aortic regurgitation are similar to those of heart failure and include the following: * Dyspnea on exertion * Orthopnea * Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea * Palpitations * Angina pectoris * Cyanosis (in acute cases) Causes In terms of the cause of aortic regurgitation, is often due to the aortic root dilation ('' annuloaortic ectasia''), which is idiopathic in over 80% of cases, but otherwise may result from aging, syphilitic aortitis, osteogenesis imperfecta, aortic dissection, Behçet's disease, reactive arthritis and systemic hypertension.Chapter 1: Diseases of the Cardiovascular system > Section: Valvular Heart Disease in: Aortic root d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echocardiography
Echocardiography, also known as cardiac ultrasound, is the use of ultrasound to examine the heart. It is a type of medical imaging, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. The visual image formed using this technique is called an echocardiogram, a cardiac echo, or simply an echo. Echocardiography is routinely used in the diagnosis, management, and follow-up of patients with any suspected or known heart diseases. It is one of the most widely used diagnostic imaging modalities in cardiology. It can provide a wealth of helpful information, including the size and shape of the heart (internal chamber size quantification), pumping capacity, location and extent of any tissue damage, and assessment of valves. An echocardiogram can also give physicians other estimates of heart function, such as a calculation of the cardiac output, ejection fraction, and diastolic function (how well the heart relaxes). Echocardiography is an important tool in assessing wall motion abnorma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery
Coronary artery bypass surgery, also known as coronary artery bypass graft (CABG, pronounced "cabbage"), is a surgical procedure to treat coronary artery disease (CAD), the buildup of plaques in the arteries of the heart. It can relieve chest pain caused by CAD, slow the progression of CAD, and increase life expectancy. It aims to bypass narrowings in heart arteries by using arteries or veins harvested from other parts of the body, thus restoring adequate blood supply to the previously ischemic (deprived of blood) heart. There are two main approaches. The first uses a cardiopulmonary bypass machine, a machine which takes over the functions of the heart and lungs during surgery by circulating blood and oxygen. With the heart in cardioplegic arrest, harvested arteries and veins are used to connect across problematic regions—a construction known as surgical anastomosis. In the second approach, called the off-pump coronary artery bypass (OPCAB), these anastomoses are cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
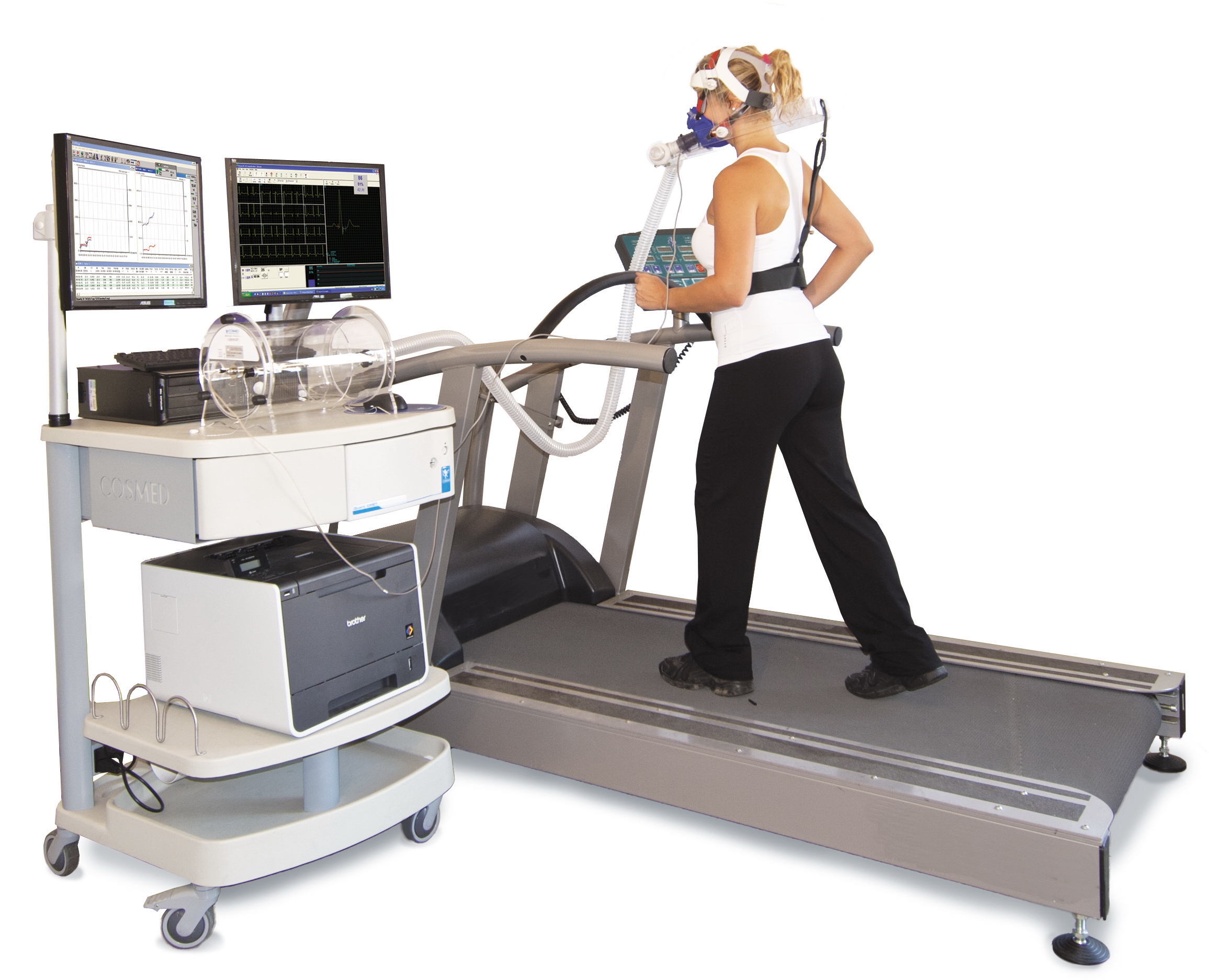
Cardiac Stress Test
A cardiac stress test is a cardiological examination that evaluates the cardiovascular system's response to external stress within a controlled clinical setting. This stress response can be induced through physical exercise (usually a treadmill) or intravenous pharmacological stimulation of heart rate. As the heart works progressively harder (stressed) it is monitored using an electrocardiogram (ECG) monitor. This measures the heart's electrical rhythms and broader electrophysiology. Pulse rate, blood pressure and symptoms such as chest discomfort or fatigue are simultaneously monitored by attending clinical staff. Clinical staff will question the patient throughout the procedure asking questions that relate to pain and perceived discomfort. Abnormalities in blood pressure, heart rate, ECG or worsening physical symptoms could be indicative of coronary artery disease. Stress testing does not accurately diagnose all cases of coronary artery disease, and can often indicate that it e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to Cardiac cycle, fill with and pump blood. Although symptoms vary based on which side of the heart is affected, HF typically presents with shortness of breath, Fatigue (medical), excessive fatigue, and bilateral peripheral edema, leg swelling. The severity of the heart failure is mainly decided based on ejection fraction and also measured by the severity of symptoms. Other conditions that have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver disease, anemia, and thyroid disease. Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease, heart attack, hypertension, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, alcohol use disorder, excessive alcohol consumption, infection, and cardiomyopathy. These cause heart failure by altering the structure or the function of the heart or in some cases both. There are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syncope (medicine)
Syncope , commonly known as fainting or passing out, is a loss of consciousness and muscle strength characterized by a fast onset, short duration, and spontaneous recovery. It is caused by a decrease in blood flow to the brain, typically from low blood pressure. There are sometimes symptoms before the loss of consciousness such as lightheadedness, sweating, pale skin, blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, or feeling warm. Syncope may also be associated with a short episode of muscle twitching. Psychiatric causes can also be determined when a patient experiences fear, anxiety, or panic; particularly before a stressful event, usually medical in nature. When consciousness and muscle strength are not completely lost, it is called presyncope. It is recommended that presyncope be treated the same as syncope. Causes range from non-serious to potentially fatal. There are three broad categories of causes: heart or blood vessel related; reflex, also known as neurally mediated; and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angina
Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease. Angina is typically the result of partial obstruction or spasm of the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle. The main mechanism of coronary artery obstruction is atherosclerosis as part of coronary artery disease. Other causes of angina include abnormal heart rhythms, heart failure and, less commonly, anemia. The term derives , and can therefore be translated as "a strangling feeling in the chest". An urgent medical assessment is suggested to rule out serious medical conditions. There is a relationship between severity of angina and degree of oxygen deprivation in the heart muscle. However, the severity of angina does not always match the degree of oxygen deprivation to the heart or the risk of a heart attack (myocardial infarction). Some people may experience sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aortic Stenosis
Aortic stenosis (AS or AoS) is the narrowing of the exit of the left ventricle of the heart (where the aorta begins), such that problems result. It may occur at the aortic valve as well as above and below this level. It typically gets worse over time. Symptoms often come on gradually with a decreased ability to exercise often occurring first. If heart failure, loss of consciousness, or heart related chest pain occur due to AS the outcomes are worse. Loss of consciousness typically occurs with standing or exercising. Signs of heart failure include shortness of breath especially when lying down, at night, or with exercise, and swelling of the legs. Thickening of the valve without causing obstruction is known as aortic sclerosis. Causes include being born with a bicuspid aortic valve, and rheumatic fever; a normal valve may also harden over the decades due to calcification. A bicuspid aortic valve affects about one to two percent of the population. As of 2014 rheumatic heart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |