|
Aortic Valve
The aortic valve is a valve in the heart of humans and most other animals, located between the left ventricle and the aorta. It is one of the four valves of the heart and one of the two semilunar valves, the other being the pulmonary valve. The aortic valve normally has three cusps or leaflets, although in 1–2% of the population it is found to congenitally have two leaflets. The aortic valve is the last structure in the heart the blood travels through before stopping the flow through the systemic circulation. Structure The aortic valve normally has three cusps however there is some discrepancy in their naming. They may be called the left coronary, right coronary and non-coronary cusp. Some sources also advocate they be named as a left, right and posterior cusp. Anatomists have traditionally named them the left posterior (origin of left coronary), anterior (origin of the right coronary) and right posterior. The three cusps, when the valve is closed, contain a sinus called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Valve
A heart valve is a biological one-way valve that allows blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart. A mammalian heart usually has four valves. Together, the valves determine the direction of blood flow through the heart. Heart valves are opened or closed by a difference in blood pressure on each side. The mammalian heart has two atrioventricular valves separating the upper atria from the lower ventricles: the mitral valve in the left heart, and the tricuspid valve in the right heart. The two semilunar valves are at the entrance of the arteries leaving the heart. These are the aortic valve at the aorta, and the pulmonary valve at the pulmonary artery. The heart also has a coronary sinus valve and an inferior vena cava valve, not discussed here. Structure The heart valves and the chambers are lined with endocardium. Heart valves separate the atria from the ventricles, or the ventricles from a blood vessel. Heart valves are situated around the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
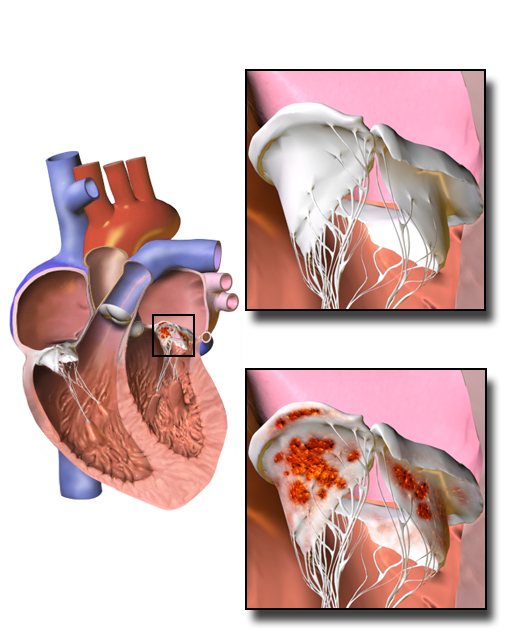
Calcific Aortic Valve Disease
Aortic stenosis (AS or AoS) is the narrowing of the exit of the left ventricle of the heart (where the aorta begins), such that problems result. It may occur at the aortic valve as well as above and below this level. It typically gets worse over time. Symptoms often come on gradually with a decreased ability to exercise often occurring first. If heart failure, loss of consciousness, or heart related chest pain occur due to AS the outcomes are worse. Loss of consciousness typically occurs with standing or exercising. Signs of heart failure include shortness of breath especially when lying down, at night, or with exercise, and swelling of the legs. Thickening of the valve without causing obstruction is known as aortic sclerosis. Causes include being born with a bicuspid aortic valve, and rheumatic fever; a normal valve may also harden over the decades due to calcification. A bicuspid aortic valve affects about one to two percent of the population. As of 2014 rheumatic heart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percutaneous Aortic Valve Replacement
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) is the implantation of the aortic valve of the heart through the blood vessels without actual removal of the native valve (as opposed to the aortic valve replacement by open heart surgery, surgical aortic valve replacement, AVR). The first TAVI was performed on 16 April 2002 by Alain Cribier, which became a new alternative in the management of high-risk patients with severe aortic stenosis. The implantated valve is delivered via one of several access methods: transfemoral (in the upper leg), transapical (through the wall of the heart), subclavian (beneath the collar bone), direct aortic (through a minimally invasive surgical incision into the aorta), and transcaval (from a temporary hole in the aorta near the navel through a vein in the upper leg), among others. Severe symptomatic aortic stenosis carries a poor prognosis. At present, there is no treatment via medication, making the timing of aortic valve replacement the most imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans-Joachim Schäfers
Hans-Joachim Schäfers (born 1957) is a German surgeon, as well as cardiac, thoracic, and vascular surgeon and university professor. He is director of the department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery at the Saarland University Medical Center in Homburg/Saar, Germany. He is known for his activities in aortic valve repair, aortic surgery, and pulmonary endarterectomy. Biography In 1995, he assumed as interim director the leadership of the Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular at the Saarland University Medical Center in Homburg/Saar. In April 1996, he was formally appointed director of the department and Professor of Surgery. He has assumed different obligations in academic committees, and he has initiated many research projects dealing with cardiac and thoracic surgical challenges. Apart from his wide surgical spectrum in cardiac and thoracic surgery his areas of core competence include operations for aortic aneurysms (especially thoracic aortic aneurysms), surgery f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turner Syndrome
Turner syndrome (TS), commonly known as 45,X, or 45,X0,Also written as 45,XO. is a chromosomal disorder in which cells of females have only one X chromosome instead of two, or are partially missing an X chromosome (sex chromosome monosomy) leading to the complete or partial deletion of the pseudoautosomal regions (PAR1, PAR2) in the affected X chromosome. Typically, people have two sex chromosomes (XX for females or XY for males). The chromosomal abnormality is often present in just some cells, in which case it is known as Turner syndrome with mosaicism. 45,X0 with mosaicism can occur in males or females, but Turner syndrome without mosaicism only occurs in females. Signs and symptoms vary among those affected but often include additional skin folds on the neck, arched palate, low-set ears, low hairline at the nape of the neck, short stature, and lymphedema of the hands and feet. Those affected do not normally develop menstrual periods or mammary glands without hormone trea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicuspid Aortic Valve
Bicuspid aortic valve (BAV) is a form of heart disease in which two of the leaflets of the aortic valve fuse during development in the womb resulting in a two-leaflet (bicuspid) valve instead of the normal three-leaflet (tricuspid) valve. BAV is the most common cause of heart disease present at birth and affects approximately 1.3% of adults. Normally, the mitral valve is the only bicuspid valve and this is situated between the heart's left atrium and left ventricle. Heart valves play a crucial role in ensuring the unidirectional flow of blood from the atria to the ventricles, or from the ventricle to the aorta or pulmonary trunk. BAV is normally inherited. Signs and symptoms In many cases, a bicuspid aortic valve will cause no problems. People with BAV may become tired more easily than those with normal valvular function and have difficulty maintaining stamina for cardio-intensive activities due to poor heart performance caused by stress on the aortic wall.Maredia A.K., G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Heart Defect
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly, congenital cardiovascular malformation, and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascular disease. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific type of defect. Symptoms can vary from none to life-threatening. When present, symptoms are variable and may include rapid breathing, bluish skin (cyanosis), poor weight gain, and feeling tired. CHD does not cause chest pain. Most congenital heart defects are not associated with other diseases. A complication of CHD is heart failure. Congenital heart defects are the most common birth defect. In 2015, they were present in 48.9 million people globally. They affect between 4 and 75 per 1,000 live births, depending upon how they are diagnosed. In about 6 to 19 per 1,000 they cause a moderate to severe degree of problems. Congenital heart defects are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcification
Calcification is the accumulation of calcium salts in a body tissue. It normally occurs in the formation of bone, but calcium can be deposited abnormally in soft tissue,Miller, J. D. Cardiovascular calcification: Orbicular origins. ''Nature Materials'' 12, 476-478 (2013). causing it to harden. Calcifications may be classified on whether there is mineral balance or not, and the location of the calcification. Calcification may also refer to the processes of normal mineral deposition in biological systems, such as the formation of stromatolites or mollusc shells (see Biomineralization). Signs and symptoms Calcification can manifest itself in many ways in the body depending on the location. In the pulpal structure of a tooth, calcification often presents asymptomatically, and is diagnosed as an incidental finding during radiographic interpretation. Individual teeth with calcified pulp will typically respond negatively to vitality testing; teeth with calcified pulp often lack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marfan's Syndrome
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with long arms, legs, fingers, and toes. They also typically have exceptionally flexible joints and abnormally curved spines. The most serious complications involve the heart and aorta, with an increased risk of mitral valve prolapse and aortic aneurysm. The lungs, eyes, bones, and the covering of the spinal cord are also commonly affected. The severity of the symptoms is variable. MFS is caused by a mutation in '' FBN1'', one of the genes that make fibrillin, which results in abnormal connective tissue. It is an autosomal dominant disorder. In about 75% of cases, it is inherited from a parent with the condition, while in about 25% it is a new mutation. Diagnosis is often based on the Ghent criteria, family history and genetic testing (DNA analysis). There is no known cure for MFS. Many of those with the disorder have a norma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infective Endocarditis
Infective endocarditis is an infection of the inner surface of the heart (endocardium), usually the heart valve, valves. Signs and symptoms may include fever, petechia, small areas of bleeding into the skin, heart murmur, feeling tired, and anemia, low red blood cell count. Complications may include valvular insufficiency, backward blood flow in the heart, heart failure – the heart struggling to pump a sufficient amount of blood to meet the body's needs, Heart block, abnormal electrical conduction in the heart, stroke, and kidney failure. The cause is typically a bacterial infection and less commonly a fungal infection. Risk factors include valvular heart disease, including rheumatic heart disease, rheumatic disease, congenital heart disease, artificial valves, hemodialysis, intravenous drug use, and electronic pacemakers. The bacteria most commonly involved are streptococci or staphylococci. Diagnosis is suspected based on symptoms and supported by blood cultures or Echocardi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheumatic Fever
Rheumatic fever (RF) is an inflammation#Disorders, inflammatory disease that can involve the heart, joints, skin, and brain. The disease typically develops two to four weeks after a Streptococcal pharyngitis, streptococcal throat infection. Signs and symptoms include fever, multiple arthralgia, painful joints, chorea, involuntary muscle movements, and occasionally a characteristic non-itchy rash known as erythema marginatum. The heart is involved in about half of the cases. Damage to the heart valves, known as valvular heart disease#Inflammatory disorders, rheumatic heart disease (RHD), usually occurs after repeated attacks but can sometimes occur after one. The damaged valves may result in heart failure, atrial fibrillation and infective endocarditis, infection of the valves. Rheumatic fever may occur following an infection of the throat by the bacterium ''Streptococcus pyogenes''. If the infection is left untreated, rheumatic fever occurs in up to three percent of people. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasodilation
Vasodilation, also known as vasorelaxation, is the widening of blood vessels. It results from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, in particular in the large veins, large arteries, and smaller arterioles. Blood vessel walls are composed of endothelial tissue and a basal membrane lining the lumen of the vessel, concentric smooth muscle layers on top of endothelial tissue, and an adventitia over the smooth muscle layers. Relaxation of the smooth muscle layer allows the blood vessel to dilate, as it is held in a semi-constricted state by sympathetic nervous system activity. Vasodilation is the opposite of vasoconstriction, which is the narrowing of blood vessels. When blood vessels dilate, the flow of blood is increased due to a decrease in vascular resistance and increase in cardiac output. Vascular resistance is the amount of force circulating blood must overcome in order to allow perfusion of body tissues. Narrow vessels create more vascular resista ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |