|
Anura (elephant)
The is a zoo, owned by the government of Tokyo Metropolis, and located in Hino, Tokyo, Japan. The Tama Zoo was opened on May 5, 1958, originally as a of the Ueno Zoo. The zoo aims to use its large site – 52 ha, compared to the 14.3 ha of the Ueno Zoo – to show its animals moving in a more free and natural environment. Animals Animals in the zoo include: ;Insectarium * Blue glassy tiger * Common grass yellow *Flower mantis *Leafcutter ant ;Asian Zone *Amur tiger * Asiatic black bear *Asian elephant *Bar-headed goose * Black-faced spoonbill *Bornean orangutan *Eurasian eagle-owl *Eurasian otter *Golden eagle * Golden takin *Grey wolf *Himalayan tahr *Indian rhinoceros *Japanese badger * Japanese giant flying squirrel *Japanese hare *Japanese macaque * Japanese raccoon dog * Japanese serow * Lar gibbon *Malayan tapir *Masked palm civet *Mouflon * Oriental stork * Père David's deer * Pheasant pigeon *Przewalski's horse *Steller's sea eagle *Red-crowned crane *Red panda *Rein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hino, Tokyo
file:KongojiFudodo20130815.jpg, 250px, Takahata Fudō in Hino is a Cities of Japan, city located in the western Tokyo, western portion of the Tokyo Metropolis, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 187,048, and a population density of 6,800 persons per km². The total area of the city was . History The area of present-day Hino was part of ancient Musashi Province. During the Edo period, the village of Hino developed as a shukuba, post station on the Kōshū Kaidō. In the post-Meiji Restoration cadastral reform of 1871, Hino-juku became part of Kanagawa Prefecture. In the reorganization of districts in 1889, Hino-juku came under the jurisdiction of Minamitama District. The entire district was transferred to the control of Tokyo Prefecture on April 1, 1893, at which time Hino-juku was proclaimed Hino Town under the modern municipalities system. The area of the town expanded through annexation of neighboring villages in 1901 and 1958. On November 3, 1963, Hino was eleva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Eagle
The golden eagle (''Aquila chrysaetos'') is a bird of prey living in the Northern Hemisphere. It is the most widely distributed species of eagle. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family Accipitridae. They are one of the best-known bird of prey, birds of prey in the Northern Hemisphere. These birds are dark brown, with lighter golden-brown plumage on their napes. Immature eagles of this species typically have white on the tail and often have white markings on the wings. Golden eagles use their agility and speed combined with powerful feet and large, sharp talons to hunt a variety of prey, mainly hares, rabbits, and marmots and other ground squirrels. Golden eagles maintain home ranges or territories that may be as large as . They build large bird nest, nests in cliffs and other high places to which they may return for several breeding years. Most breeding activities take place in the spring; they are monogamous and may remain together for several years or possibly for life. Fem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
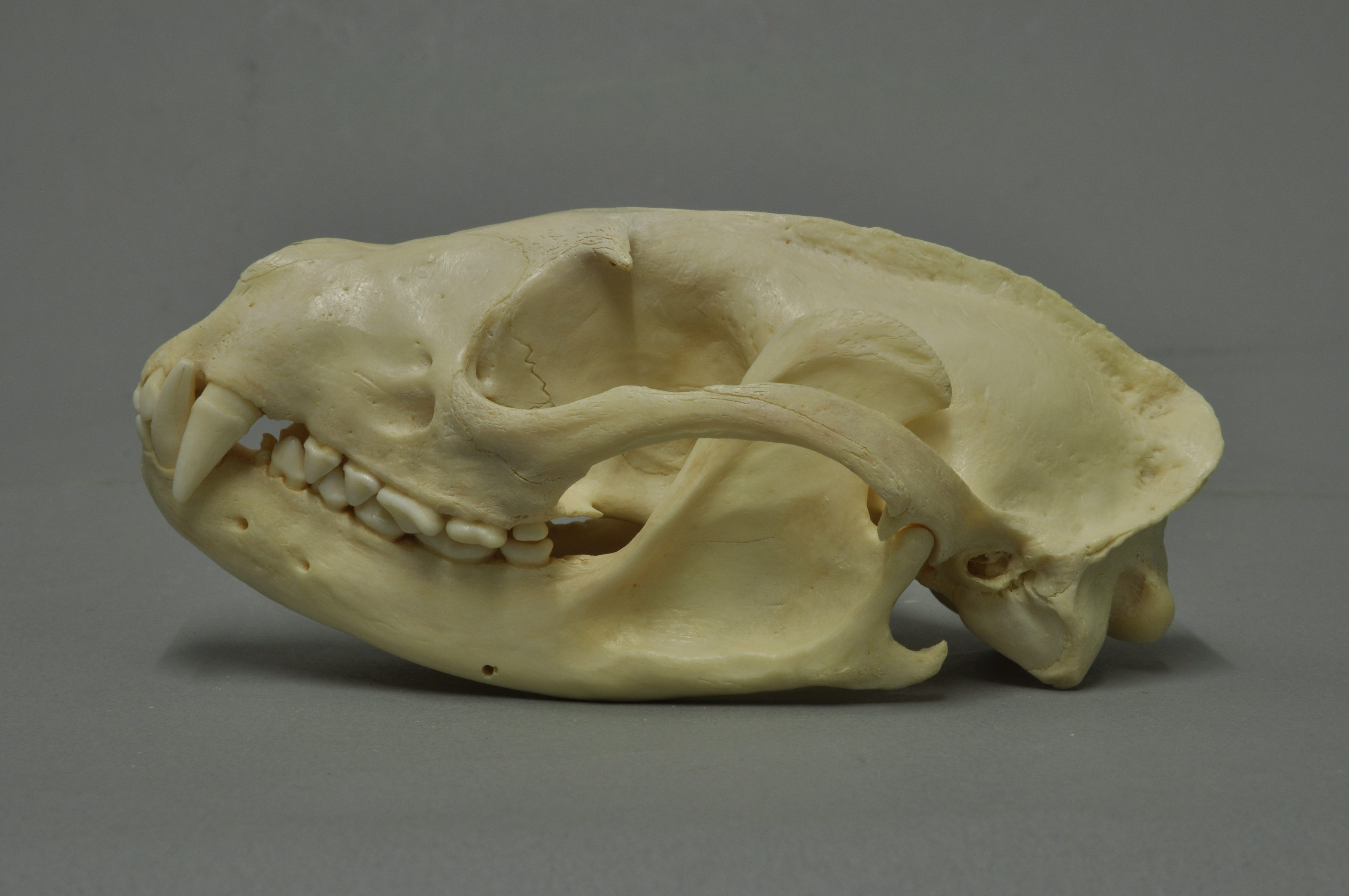
Masked Palm Civet
The masked palm civet (''Paguma larvata''), also called the gem-faced civet or Himalayan palm civet, is a viverrid species native to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. It has been listed as least concern on the IUCN Red List since 2008 as it occurs in many protected areas, is tolerant to some degree of habitat modification, and widely distributed with presumed large populations that are unlikely to be declining. The genus ''Paguma'' was first named and described by John Edward Gray in 1831. All described forms are regarded as a single species. In 2003, masked palm civets at a wildlife market in China were found to have been infected with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Characteristics The masked palm civet's fur is grayish to ochraceous, black on the head, shoulders and neck, and blackish brown on the tail and feet. It has a white blaze on the forehead; white marks above and below the eyes extend to the ears, forming a half-collar. In morpho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayan Tapir
The Malayan tapir (''Tapirus indicus''), also called Asian tapir, Asiatic tapir, oriental tapir, Indian tapir, piebald tapir, or black-and-white tapir, is the only living tapir species outside of the Americas. It is native to Southeast Asia from the Malay Peninsula to Sumatra. It has been listed as Endangered species, Endangered on the IUCN Red List since 2008, as the population is estimated to comprise fewer than 2,500 mature individuals. Taxonomy The scientific name ''Tapirus indicus'' was proposed by Anselme Gaëtan Desmarest in 1819 who referred to a tapir described by Pierre-Médard Diard. ''Tapirus indicus brevetianus'' was coined by a Dutch zoologist in 1926 who described a black Malayan tapir from Sumatra that had been sent to Rotterdam Zoo in the early 1920s. Phylogenetics, Phylogenetic analyses of 13 Malayan tapirs showed that the species is monophyletic. It was placed in the genus ''Acrocodia'' by Colin Groves and Peter Grubb (zoologist), Peter Grubb in 2011. However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Serow
The (''Capricornis crispus'') ( 羚羊) is a Japanese goat-antelope, an even-toed ungulate. It is found in dense woodland in Japan, primarily in northern and central Honshu. The serow is seen as a national symbol of Japan, and is subject to protection in conservation areas. Adult Japanese serow stand about tall and weigh . They are black to whitish, and colouring lightens in summer. The fur is very bushy, especially the tail. Both sexes have short, backwards-curving horns, and are difficult to distinguish by sight. Japanese serow are found in dense mountain forests where they eat leaves, shoots, and acorns. They are diurnal and feed in early mornings and late afternoons. Serows are solitary, or gather in couples or small family groups. The animal marks its territory with sweet-and-sour-smelling preorbital gland secretions, and males and females have separate territories that may overlap. In the mid-20th century, the Japanese serow was hunted to near-extinction. In 1955, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
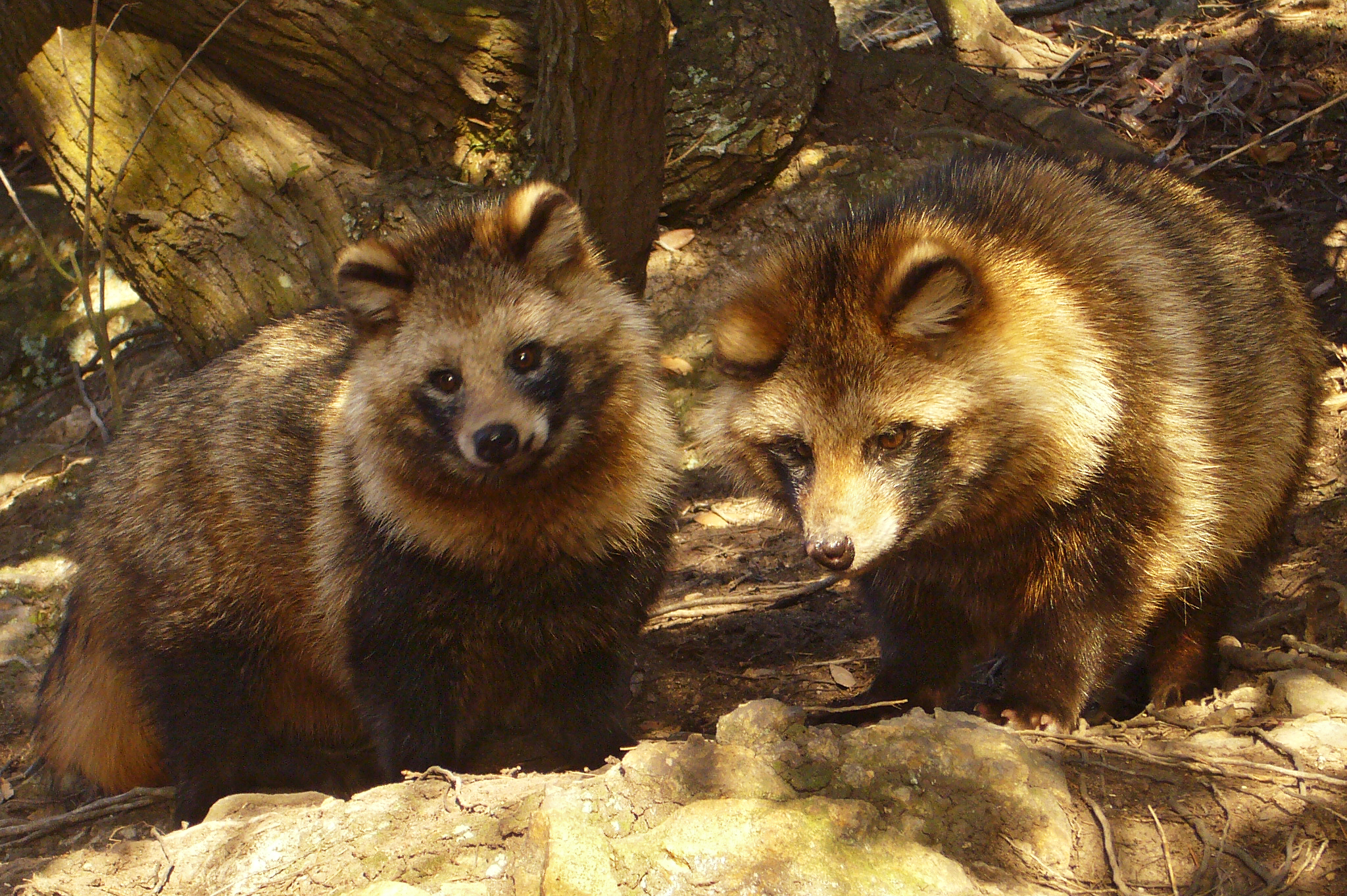
Japanese Raccoon Dog
The Japanese raccoon dog (''Nyctereutes viverrinus'', or ''tanuki'' ()) is a species of canid that is endemic to Japan. It is one of two species in the genus '' Nyctereutes'', alongside the common raccoon dog (''N. procyonoides''), of which it is considered to be a subspecies by some taxonomic authorities. Japanese raccoon dogs have had a significant role in Japanese folklore since ancient times. They are reputedly mischievous and jolly, masters of disguise and shapeshifting, but somewhat gullible and absent-minded. The animals are common in Japanese art, particularly as statues. Description The Japanese raccoon dog has a smaller stomach and shorter fur of lesser insulation value than mainland raccoon dogs. A white color type is rare. In mainland Japan, oculocutaneous albinism is caused by a mutation in the third and fifth exon of the TYR nucleotide sequence, which is responsible for melanin pigmentation. Behavior The Japanese raccoon dog is mainly nocturnal. It vocali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Macaque
The Japanese macaque (''Macaca fuscata''), also known as the snow monkey, is a terrestrial Old World monkey species that is native to Japan. Colloquially, they are referred to as "snow monkeys" because some live in areas where snow covers the ground for months each year – no other non-human primate lives farther north, nor in a colder climate. Individuals have brownish grey fur, pinkish-red faces, and short tails. Two subspecies are known. In Japan, the species is known as ''Nihonzaru'' (ニホンザル, a combination of ''Nihon'' 日本 "Japan" + ''saru'' 猿 "monkey") to distinguish it from other primates, but the Japanese macaque is very familiar in Japan—as it is the only species of monkey in Japan—so when Japanese people simply say ''saru'', they usually have the Japanese macaque in mind. Physical characteristics The Japanese macaque is sexual dimorphism, sexually dimorphic. Males weigh on average , while females average .Fooden J, Aimi M. (2005) "Systematic revie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Hare
The Japanese hare (''Lepus brachyurus'') is a species of hare endemic to Japan. In Japanese, it is called the ''Nousagi'' (Japanese: 野兎), meaning "field rabbit". Taxonomy Coenraad Jacob Temminck described the Japanese hare in 1845. The specific epithet (''brachyurus'') is derived from the Ancient Greek ''brachys'' meaning "short" and ''oura'' meaning "tail". The four subspecies of this hare are: *''L. b. angustidens'' *''L. b. brachyurus'' *''L. b. lyoni'' *''L. b. okiensis'' Description The Japanese hare is reddish-brown, with a body length that ranges from , and a body weight of . Its tail grows to lengths of . Its front legs can be from long and the back legs from long. The ears grow to be long, and the tail long. In areas of northern Japan, the west coast, and the island of Sado, where snowfall is heavy, the Japanese hare loses its coloration in the autumn, remaining white until the spring, when the reddish-brown fur returns. Habitat The Japanese hare is found acro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Giant Flying Squirrel
The is a species of flying squirrel, one of the giant flying squirrels in the genus ''Petaurista''. Description Like other flying squirrels, it has a web of skin between its legs which it uses to glide between trees. Glides of have been recorded. The tail is used for stability during flight. The body is about long, and the tail a further . It weighs between . It is much larger than the related Japanese dwarf flying squirrel which does not exceed . It eats fruit and nuts and lives in holes in large trees. The female has a home range of about a and the male about . Distribution and habitat It is native to Japan, where it inhabits sub-alpine forests and boreal evergreen forests on the islands of Honshu, Shikoku and Kyushu is the third-largest island of Japan's Japanese archipelago, four main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands (i.e. excluding Okinawa Island, Okinawa and the other Ryukyu Islands, Ryukyu (''Nansei'') Ryukyu Islands, Islands .... Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Badger
The Japanese badger (''Meles anakuma'') is a species of carnivoran of the family Mustelidae, the weasels and their kin. Endemic to Japan, it is found on Honshu, Kyushu, Shikoku, and Shōdoshima. It shares the genus '' Meles'' with its close relatives, the European (''M. meles''), Caucasian (''M. canescens'') and Asian (''M. leucurus'') badgers. In Japan, it is called by the name ''anaguma'' (穴熊) meaning "hole-bear", or ''mujina'' (むじな, 狢). Description Japanese badgers are generally smaller (average length in males, in females) and less sexually dimorphic (except in the size of the canine teeth) than their European counterparts. Tail length is between . This species is similar or mildly larger than the Asian badger. Adults usually weigh from . The average weight of female Japanese badgers in one study from the Tokyo area was found to be while that of males was . In Yamaguchi Prefecture, the average spring weight of female and male Japanese badgers was and . T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
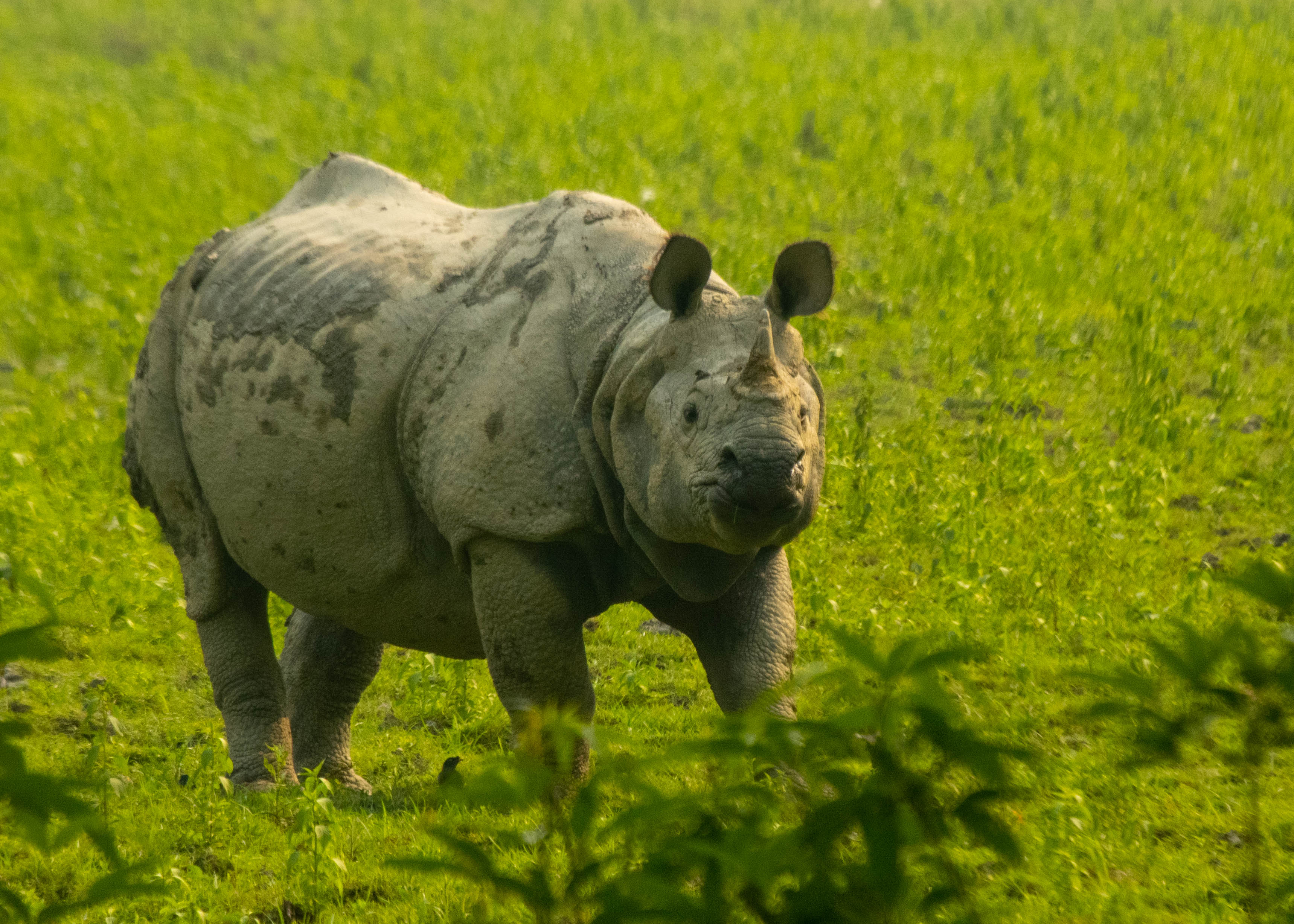
Indian Rhinoceros
The Indian rhinoceros (''Rhinoceros unicornis''), also known as the greater one-horned rhinoceros, great Indian rhinoceros or Indian rhino, is a species of rhinoceros found in the Indian subcontinent. It is the second largest living rhinoceros species, with adult males weighing and adult females . Its thick skin is grey-brown with pinkish skin folds. It has a single horn on its snout that grows up to long. Its upper legs and shoulders are covered in wart-like bumps, and it is nearly hairless aside from the eyelashes, ear fringes and tail brush. The Indian rhinoceros is native to the Indo-Gangetic Plain and occurs in 12 protected areas in northern India and southern Nepal. It is a Grazing (behaviour), grazer, eating mainly grass, but also twigs, leaves, branches, shrubs, flowers, fruits and aquatic plants. It is a largely solitary animal, only associating in the breeding season and when rearing calves. Females give birth to a single calf after a gestation of 15.7 months. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |