|
Anupam Mazumdar
Anupam Mazumdar is a theoretical physicist at the University of Groningen specializing in cosmology and quantum gravity. Together with Sougato Bose, Mazumdar has proposed a bonafide test for the existence of the graviton in a table-top experiment, via witnessing gravitationally-mediated entanglement between two macroscopic superpositions of masses. A positive test of this phenomenon would establish experimentally that gravity is quantum mechanical in nature, and establish the existence of the graviton. The test crucially depends on the quantum nature of gravity, creating non-classical states of matter, and local operation and quantum communication (LOQC). He has previously been affiliated to the Higgs Centre, at the University of Edinburgh, and the Discovery Center at the Niels Bohr Institute, Copenhagen. His work has focused on multi field theories of inflation, such as ''assisted inflation'', visible sector inflation such as ''MSSM inflation''. He has worked on the ghost-free ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Physical Society
The American Physical Society (APS) is a not-for-profit membership organization of professionals in physics and related disciplines, comprising nearly fifty divisions, sections, and other units. Its mission is the advancement and diffusion of knowledge of physics. The society publishes more than a dozen scientific journals, including the prestigious ''Physical Review'' and '' Physical Review Letters'', and organizes more than twenty science meetings each year. APS is a member society of the American Institute of Physics. Since January 2021 the organization has been led by chief executive officer Jonathan Bagger. History The American Physical Society was founded on May 20, 1899, when thirty-six physicists gathered at Columbia University for that purpose. They proclaimed the mission of the new Society to be "to advance and diffuse the knowledge of physics", and in one way or another the APS has been at that task ever since. In the early years, virtually the sole activity of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McGill University Alumni
McGill is a surname of Scottish and Irish origin, from which the names of many places and organizations are derived. It may refer to: People * McGill (surname) (including a list of individuals with the surname) * McGill family (Monrovia), a prominent early Americo-Liberian family * Anglicized variant for Clan Makgill, a Lowland Scottish clan * Donald McGillivray (botanist), botanical taxonomist whose standard author abbreviation is “McGill”. Organizations * McGill University, a research university located in Montreal, Quebec, Canada * McGill-Toolen Catholic High School, a private coeducational high school in Mobile, Alabama, United States * McGill Executive Institute, a business school within McGill University located in Montreal, Quebec, Canada * McGill Drug Store, a historical museum in McGill, Nevada * McGill's Bus Services, bus operating firm based in Greenock, Inverclyde, Scotland * McGill Motorsports, a NASCAR Busch Series team Places * McGill (Montreal Metro), a metr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Staff Of The University Of Groningen
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary education, secondary or tertiary education, tertiary higher education, higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 385 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and Skills, skill, north of Ancient Athens, Athens, Greece. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, ''Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the Gymnasium (ancient Greece), gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive Grove (nature), grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions into a method of teaching philosophy and in 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can deform spacetime to form a black hole. The boundary of no escape is called the event horizon. Although it has a great effect on the fate and circumstances of an object crossing it, it has no locally detectable features according to general relativity. In many ways, a black hole acts like an ideal black body, as it reflects no light. Moreover, quantum field theory in curved spacetime predicts that event horizons emit Hawking radiation, with the same spectrum as a black body of a temperature inversely proportional to its mass. This temperature is of the order of billionths of a kelvin for stellar black holes, making it essentially impossible to observe directly. Objects whose gravitational fields are too strong for light to escape were fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Condition
In relativistic classical field theories of gravitation, particularly general relativity, an energy condition is a generalization of the statement "the energy density of a region of space cannot be negative" in a relativistically-phrased mathematical formulation. There are multiple possible alternative ways to express such a condition such that can be applied to the matter content of the theory. The hope is then that any reasonable matter theory will satisfy this condition or at least will preserve the condition if it is satisfied by the starting conditions. Energy conditions are not physical constraints , but are rather mathematically imposed boundary conditions that attempt to capture a belief that "energy should be positive". Many energy conditions are known to not correspond to physical reality—for example, the observable effects of dark energy are well-known to violate the strong energy condition. In general relativity, energy conditions are often used (and required) in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmological Singularities
A gravitational singularity, spacetime singularity or simply singularity is a condition in which gravity is so intense that spacetime itself breaks down catastrophically. As such, a singularity is by definition no longer part of the regular spacetime and cannot be determined by "where" or "when". Gravitational singularities exist at a junction between general relativity and quantum mechanics; therefore, the properties of the singularity cannot be described without an established theory of quantum gravity. Trying to find a complete and precise definition of singularities in the theory of general relativity, the current best theory of gravity, remains a difficult problem. A singularity in general relativity can be defined by the scalar invariant curvature becoming infinite or, better, by a geodesic being incomplete. Gravitational singularities are mainly considered in the context of general relativity, where density apparently becomes infinite at the center of a black ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Event Horizon
In astrophysics, an event horizon is a boundary beyond which events cannot affect an observer. Wolfgang Rindler coined the term in the 1950s. In 1784, John Michell proposed that gravity can be strong enough in the vicinity of massive compact objects that even light cannot escape. At that time, the Newtonian theory of gravitation and the so-called corpuscular theory of light were dominant. In these theories, if the escape velocity of the gravitational influence of a massive object exceeds the speed of light, then light originating inside or from it can escape temporarily but will return. In 1958, David Finkelstein used general relativity to introduce a stricter definition of a local black hole event horizon as a boundary beyond which events of any kind cannot affect an outside observer, leading to information and firewall paradoxes, encouraging the re-examination of the concept of local event horizons and the notion of black holes. Several theories were subsequently developed, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micro Black Hole
Micro black holes, also called mini black holes or quantum mechanical black holes, are hypothetical tiny (<1 ) , for which effects play an important role. The concept that black holes may exist that are smaller than was introduced in 1971 by Stephen Hawking. It is possible that such black holes were created in the high-density environment o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
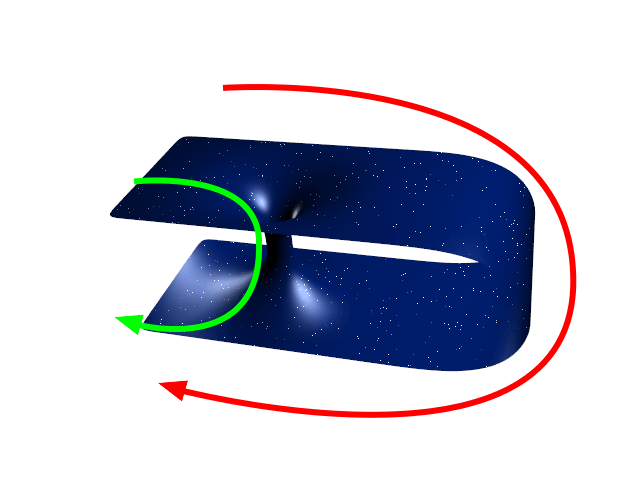
Wormhole
A wormhole ( Einstein-Rosen bridge) is a hypothetical structure connecting disparate points in spacetime, and is based on a special solution of the Einstein field equations. A wormhole can be visualized as a tunnel with two ends at separate points in spacetime (i.e., different locations, different points in time, or both). Wormholes are consistent with the general theory of relativity, but whether wormholes actually exist remains to be seen. Many scientists postulate that wormholes are merely projections of a fourth spatial dimension, analogous to how a two-dimensional (2D) being could experience only part of a three-dimensional (3D) object. Theoretically, a wormhole might connect extremely long distances such as a billion light years, or short distances such as a few meters, or different points in time, or even different universes. In 1995, Matt Visser suggested there may be many wormholes in the universe if cosmic strings with negative mass were generated in the ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infinite Derivative Gravity
Infinite derivative gravity is a theory of gravity which attempts to remove cosmological and black hole singularities by adding extra terms to the Einstein–Hilbert action, which weaken gravity at short distances. History In 1987, Krasnikov considered an infinite set of higher derivative terms acting on the curvature terms and showed that by choosing the coefficients wisely, the propagator would be ghost-free and exponentially suppressed in the ultraviolet regime. Tomboulis (1997) later extended this work. By looking at an equivalent scalar-tensor theory, Biswas, Mazumdar and Siegel (2005) looked at bouncing FRW solutions. In 2011, Biswas, Gerwick, Koivisto and Mazumdar demonstrated that the most general infinite derivative action in 4 dimensions, around constant curvature backgrounds, parity invariant and torsion free, can be expressed by: :S = \int \mathrm^4x \sqrt \left(M^2_P R+ R F_1 (\Box) R + R^ F_2 (\Box) R_ + C^ F_3 (\Box) C_ \right) where the F_i (\Box)=\sum^\infty_ f_ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |