|
Antoine Gazet
Antoine Gazet (active 1595–1610) was a physician and translator in the Habsburg Netherlands. He was born in Aire-sur-la-Lys around the middle of the 16th century and was educated at least in part in Italy. After returning from Italy he lived for several years in Aire, where his presence is attested in the parish records of Aire-sur-la-Lys#Collegiate Church of Saint-Pierre, Saint-Pierre d'Aire up to 1610. He was the brother of the poet and ecclesiastical historian Guillaume Gazet. Translations * Bernardino da Balbano, ''Le sacre mystere de la flagellation de nostre sauveur'' (Arras, Jean Bourgeois, 1595) * Fulvio Androzzi, ''Devot memorial des saints mysteres de la mort et passion de nostre sauveur et redempteur Jesus Christ'' (Arras, Jean Bourgeois, 1595) * Fulvio Androzzi, ''Traictè de la frequente communion et des fruicts qui en procedent'' (Douai, Jan Bogard, 1599)Andrew Pettegree and Malcolm Walsby (eds), ''Netherlandish Books: Books Published in the Low Countries and Dutch Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
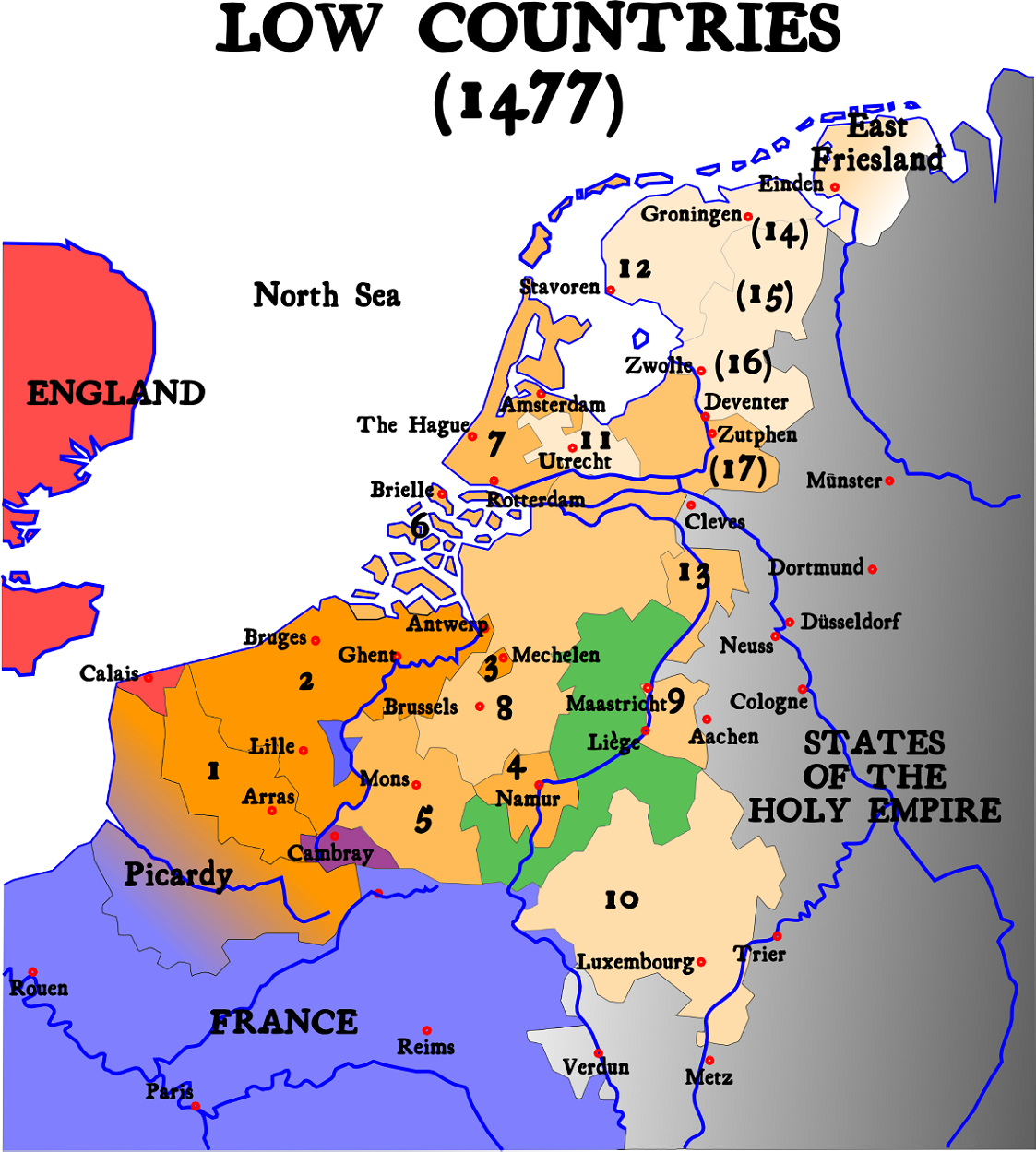
Habsburg Netherlands
Habsburg Netherlands were the parts of the Low Countries that were ruled by sovereigns of the Holy Roman Empire's House of Habsburg. This rule began in 1482 and ended for the Northern Netherlands in 1581 and for the Southern Netherlands in 1797. The rule began with the death in 1482 of Mary of Burgundy of the House of Valois-Burgundy who was the ruler of the Low Countries and the wife of Holy Roman Emperor Maximilian I of Austria. Their grandson, Emperor Charles V, was born in the Habsburg Netherlands and made Brussels one of his capitals. Becoming known as the Seventeen Provinces in 1549, they were held by the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs from 1556, known as the Spanish Netherlands from that time on. In 1581, in the midst of the Dutch Revolt, the Seven United Provinces seceded from the rest of this territory to form the Dutch Republic. The remaining Spanish Southern Netherlands became the Austrian Netherlands in 1714, after Austrian acquisition under the Treaty of Rastatt. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aire-sur-la-Lys
Aire-sur-la-Lys (; ; literally "Aire on the Lys (river), Lys") is a Communes of France, commune in the Pas-de-Calais Departments of France, department in northern France. Geography The commune is located 16 kilometres (10 mi) southeast of Saint-Omer, at the junction of the N43 with several departmental roads, by the banks of the Leie (French language, French: ''Lys'') and the Laquette rivers. History Aire-sur-la-Lys is mentioned for the first time in 857. It developed around a fort or castrum built by Baldwin II, Count of Flanders in response to the Normans, Norman invasions. More growth followed with the establishment of the Collegiate church of Saint-Pierre by Baldwin V, Count of Flanders. The town was laid siege ten times between 1127 and 1710. It was separated from the County of Flanders and attached to the County of Artois in 1196. Subsequently, ruled by the Burgundy (region), Burgundians then by the Spanish and Austrian Habsburgs. The town was besieged in 1676 by S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guillaume Gazet
Guillaume Gazet, Latinized Gulielmus Gazaeus (1554–1612) was a poet and ecclesiastical historian in the Spanish Netherlands. His brother, Antoine Gazet, was a physician and translator. Life Gazet was born in Arras, then part of the Habsburg Netherlands (now in France), in 1554. Around 1580 he was appointed parish priest of the church of Sainte-Marie-Madeleine in Arras, and later became a canon of the collegiate church of Saint-Pierre in Aire-sur-la-Lys while retaining his position as parish priest. He died in Arras on 25 August 1612 and was buried in his parish church there.Jean-Pierre Niceron, ''Mémoires pour servir à lʹhistoire des homme illustres dans la Republique des Lettres'', vol. 43 (Paris, 1745), pp. 271-276. Works As author * ''Magdalis. Comoedia sacra'' (Douai, Jan Bogard, 1589) * ''Chanson nouvelle pour l'heureux succez de l'armée catholicque ensemble, de la prinse des ville et chasteau de Calais'' (Arras, Robert Maudhuy, 1596) * ''L'ordre et suite des evesque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernardino Da Balbano
Bernardino da Balbano (active 1543–1558) was a Capuchin friar from Balvano in Southern Italy who served as provincial superior in Apulia and Basilicata, and as guardian of the convent in Potenza. He was reputed as a preacher, and was active in combatting the teachings of the Waldensians, which had received new impetus from the Protestant Reformation. After he had preached in Messina in 1552, the archbishop, Cardinal Giovanni Andrea Mercurio, sought papal intervention to have him return in 1554. Although some biographers date his death to 1558, he probably died in 1570. From around 1600, his writings were being promoted north of the Alps by the Capuchin community in Paris.Henri-Jean Martin, ''Livre, pouvoirs et société à Paris au XVIIe siècle (1598-1701)'', vol. 1 (Geneva, Droz, 1999), pp. 135-136. Writings Balbano produced a number of works both in Italian and in Latin. His best known were: * ''Specchio d'orazione'' (Rome and Parma, 1537), many times reprinted to 1605 **Fren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fulvio Androzzi
Fulvio Androzzi or Androzio (1523–1575) was an Italian Jesuit and author of devotional literature. Life Androzzi was born in 1523 in Montecchio (since renamed Treia), in the province of Macerata. He bore the title doctor of both laws, probably having graduated from the University of Camerino, and became vicar general to Berardo Bongiovanni, Bishop of Camerino, and was appointed to a canonry in the Basilica della Santa Casa in Loreto.Alberto Merola,Androzi, Fulvio, ''Dizionario Biografico degli Italiani'', vol. 3 (1961). In December 1555 he joined the Society of Jesus, founded just 15 years previously, and returned to Marche as an itinerant missionary. From late 1557 he was rector of the Jesuit college in Florence, and from 1561 of the college in Ferrara. He was professed of the fourth vow in Ferrara on 14 September 1562. He was active helping victims of the plague in 1570–1571, and began the extension of the college buildings (completed in 1580). He died in Ferrara on 27 Aug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Bogard
Jean Bogard (died around 1634) was a printer in Leuven and Douai in the 16th and 17th centuries. Life Bogard was born in Leuven around the mid-16th century and from 1564 was working as a printer in the city. E.-H.-J. Reusens, "Bogard (Jean)", ''Biographie Nationale de Belgique'', vol. 2 (Brussels, 1868), 615-616. Not long after the foundation of Douai University Bogard began publishing in Douai, while continuing to maintain his printing house in Leuven until around 1600. Bogard died in Douai around 1634, and his business was continued by his heirs. Publications * Vincent of Lerins, ''Petit traicté ... pour la vérité et antiquité de la Foy Catholique'' (Leuven, 1564) * Arnold Mermannus, ''De Fugienda Consuetudine Haereticorum Oratio Paraenetica Ad Catholicos'' (Leuven, 1564) * Petrus Bacherius, ''Hortulus precationum'' (Leuven, 1566) * François Richardot, ''Quatre sermons du sacrement de l'autel'' (Leuven, 1567) *Petrus Bacherius, ''In Omnes Epistolas Quadragesimales Homiliae' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Pettegree
Andrew David Mark Pettegree (born 1957) is a British historian and an expert on the European Reformation, the history of the book and media transformations. he holds a professorship at St Andrews University, where he is the director of the Universal Short Title Catalogue Project. He is the founding director of the St Andrews Reformation Studies Institute. Life and work His schooling took place at Oundle School. Educated at Merton College, Oxford, Pettegree held research fellowships at the University of Hamburg and Peterhouse, Cambridge before moving to St Andrews in 1986. In 1991 he was named the founding director of the St Andrews Reformation Studies Institute. His early work was mostly concentrated on the subject of sixteenth-century immigrant communities. In 2010 he published an interpretative work reassessing the early impact of the printing press, ''The Book in the Renaissance''. In this he suggests that to understand the impact of print we must look beyond the most n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malcolm Walsby
Malcolm, Malcom, Máel Coluim, or Maol Choluim may refer to: People * Malcolm (given name), includes a list of people and fictional characters * Malcom (footballer) (born 1997), Brazilian football forward * Clan Malcolm * Maol Choluim de Innerpeffray, 14th-century bishop-elect of Dunkeld Nobility * Máel Coluim, Earl of Atholl, Mormaer of Atholl between 1153/9 and the 1190s * Máel Coluim, King of Strathclyde, 10th century * Máel Coluim of Moray, Mormaer of Moray 1020–1029 * Máel Coluim (son of the king of the Cumbrians), possible King of Strathclyde or King of Alba around 1054 * Malcolm I of Scotland (died 954), King of Scots * Malcolm II of Scotland, King of Scots from 1005 until his death * Malcolm III of Scotland, King of Scots * Malcolm IV of Scotland, King of Scots * Máel Coluim, Earl of Angus, the fifth attested post 10th-century Mormaer of Angus * Máel Coluim I, Earl of Fife, one of the more obscure Mormaers of Fife * Maol Choluim I, Earl of Lennox, Mormaer * Máel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16th-century Births
The 16th century began with the Julian calendar, Julian year 1501 (represented by the Roman numerals MDI) and ended with either the Julian or the Gregorian calendar, Gregorian year 1600 (MDC), depending on the reckoning used (the Gregorian calendar introduced a lapse of 10 days in October 1582). The Renaissance in Italy and Europe saw the emergence of important artists, authors and scientists, and led to the foundation of important subjects which include accounting and political science. Copernicus proposed the Copernican heliocentrism, heliocentric universe, which was met with strong resistance, and Tycho Brahe refuted the theory of celestial spheres through observational measurement of the SN 1572, 1572 appearance of a Milky Way supernova. These events directly challenged the long-held notion of an immutable universe supported by Ptolemy and Aristotle, and led to major revolutions in astronomy and science. Galileo Galilei became a champion of the new sciences, invented the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th-century Deaths
The 17th century lasted from January 1, 1601 (represented by the Roman numerals MDCI), to December 31, 1700 (MDCC). It falls into the early modern period of Europe and in that continent (whose impact on the world was increasing) was characterized by the Baroque cultural movement, the latter part of the Spanish Golden Age, the Dutch Golden Age, the French ''Grand Siècle'' dominated by Louis XIV, the Scientific Revolution, the world's first public company and megacorporation known as the Dutch East India Company, and according to some historians, the General Crisis. From the mid-17th century, European politics were increasingly dominated by the Kingdom of France of Louis XIV, where royal power was solidified domestically in the civil war of the Fronde. The semi-feudal territorial French nobility was weakened and subjugated to the power of an absolute monarchy through the reinvention of the Palace of Versailles from a hunting lodge to a gilded prison, in which a greatly expanded ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physicians From The Habsburg Netherlands
A physician, medical practitioner (British English), medical doctor, or simply doctor is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through the study, diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of disease, injury, and other physical and mental impairments. Physicians may focus their practice on certain disease categories, types of patients, and methods of treatment—known as specialities—or they may assume responsibility for the provision of continuing and comprehensive medical care to individuals, families, and communities—known as general practice. Medical practice properly requires both a detailed knowledge of the academic disciplines, such as anatomy and physiology, underlying diseases, and their treatment, which is the science of medicine, and a decent competence in its applied practice, which is the art or craft of the profession. Both the role of the physician and the meaning of the word itself vary ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |