|
Antillatoxin
Antillatoxin (ATX) is a potent lipopeptide neurotoxin produced by the marine cyanobacterium ''Lyngbya majuscula''. ATX activates voltage-gated sodium channels, which can cause cell depolarisation, NMDA-receptor overactivity, excess calcium influx and neuronal necrosis. Sources Antillatoxin is found in the venom of the marine cyanobacterium ''Lyngbya majuscula''. The filamentous cyanobacterium grows on seagrass, macroalgae, and corals up to 30m deep in tropical and subtropical regions throughout the world. Structure The three dimensional NMR study of this toxin showed that it consists of a tripeptide glycine-''N''-methylvaline-alanine, a hydroxycarboxylic acid and a 9-''t''-butyl-6,8-dimethyl-6,8-diene attached to the C5 atom of the cyclic peptide backbone. Analogs There are three known analogous structures of ATX which have different toxicity: antillatoxin B (8-demethyl-antillatoxin) and DH-ATX (8-demethyl-8,9-dihydro-antillatoxin), and various stereoisomers of antillatoxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotoxin
Neurotoxins are toxins that are destructive to nerve tissue (causing neurotoxicity). Neurotoxins are an extensive class of exogenous chemical neurological insultsSpencer 2000 that can adversely affect function in both developing and mature nervous tissue.Olney 2002 The term can also be used to classify endogenous compounds, which, when abnormally contacted, can prove neurologically toxic. Though neurotoxins are often neurologically destructive, their ability to specifically target neural components is important in the study of nervous systems. Common examples of neurotoxins include lead, ethanol (drinking alcohol), glutamate,Choi 1987 nitric oxide, botulinum toxin (e.g. Botox), tetanus toxin,Simpson 1986 and tetrodotoxin. Some substances such as nitric oxide and glutamate are in fact essential for proper function of the body and only exert neurotoxic effects at excessive concentrations. Neurotoxins inhibit neuron control over ion concentrations across the cell memb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bleb (cell Biology)
In cell biology, a bleb is a bulge of the plasma membrane of a cell, characterized by a spherical, bulky morphology. It is characterized by the decoupling of the cytoskeleton from the plasma membrane, degrading the internal structure of the cell, allowing the flexibility required for the cell to separate into individual bulges or pockets of the intercellular matrix. Most commonly, blebs are seen in apoptosis (programmed cell death) but are also seen in other non-apoptotic functions. ''Blebbing'', or ''zeiosis'', is the formation of blebs. Formation Initiation and expansion Bleb growth is driven by intracellular pressure generated in the cytoplasm when the actin cortex undergoes actomyosin contractions. The disruption of the membrane-actin cortex interactions are dependent on the activity of myosin-ATPase Bleb initiation is affected by three main factors: high intracellular pressure, decreased amounts of cortex-membrane linker proteins, and deterioration of the actin cortex. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
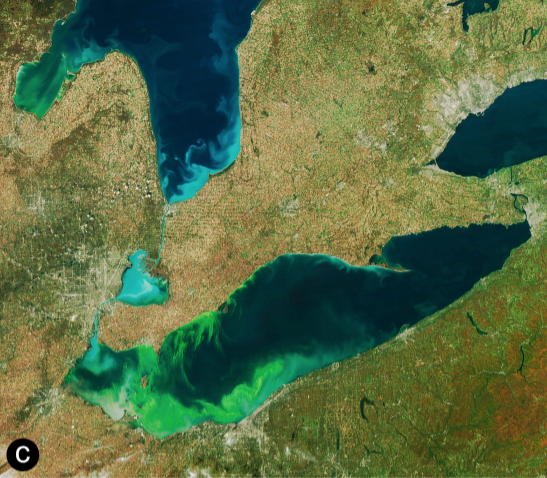
Cyanotoxins
Cyanotoxins are toxins produced by cyanobacteria (also known as blue-green algae). Cyanobacteria are found almost everywhere, but particularly in lakes and in the ocean where, under high concentration of phosphorus conditions, they reproduce exponentially to form blooms. Blooming cyanobacteria can produce cyanotoxins in such concentrations that they poison and even kill animals and humans. Cyanotoxins can also accumulate in other animals such as fish and shellfish, and cause poisonings such as shellfish poisoning. Some of the most powerful natural poisons known are cyanotoxins. They include potent neurotoxins, hepatotoxins, cytotoxins, and endotoxins. Despite the similarity in name, they are unrelated to cyanides. Exposure to cyanobacteria can result in gastro-intestinal and hayfever symptoms or pruritic skin rashes. Exposure to the cyanobacteria neurotoxin BMAA may be an environmental cause of neurodegenerative diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Parkinson's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Channel Toxins
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons. Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed atomic or monatomic ions, while two or more atoms form molecular ions or polyatomic ions. In the case of physical ionization in a fluid (gas or liquid), "ion pairs" are created by spontaneous molecule collisions, where each generated pair consists of a free electron and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotoxins
Neurotoxins are toxins that are destructive to nerve tissue (causing neurotoxicity). Neurotoxins are an extensive class of exogenous chemical neurological insultsSpencer 2000 that can adversely affect function in both developing and mature nervous tissue.Olney 2002 The term can also be used to classify endogenous compounds, which, when abnormally contacted, can prove neurologically toxic. Though neurotoxins are often neurologically destructive, their ability to specifically target neural components is important in the study of nervous systems. Common examples of neurotoxins include lead, ethanol (drinking alcohol), glutamate,Choi 1987 nitric oxide, botulinum toxin (e.g. Botox), tetanus toxin,Simpson 1986 and tetrodotoxin. Some substances such as nitric oxide and glutamate are in fact essential for proper function of the body and only exert neurotoxic effects at excessive concentrations. Neurotoxins inhibit neuron control over ion concentrations across the cell membrane, or commu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batrachotoxin
Batrachotoxin (BTX) is an extremely potent cardio- and neurotoxic steroidal alkaloid found in certain species of beetles, birds, and frogs. The name is from the Greek word grc, βάτραχος, bátrachos, frog, label=none. Structurally-related chemical compounds are often referred to collectively as batrachotoxins. It is an extremely poisonous alkaloid. In certain frogs, this alkaloid is present mostly on the skin. Such frogs are among those used for poisoning darts. Batrachotoxin binds to and irreversibly opens the sodium channels of nerve cells and prevents them from closing, resulting in paralysis and death. No antidote is known. History Batrachotoxin was discovered by Fritz Märki and Bernhard Witkop, at the National Institute of Arthritis and Metabolic Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, U.S.A. Märki and Witkop separated the potent toxic alkaloids fraction from '' Phyllobates bicolor'' and determined its chemical properties in 1963. They isola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riluzole
Riluzole is a medication used to treat amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and other motor neuron diseases. Riluzole delays the onset of ventilator-dependence or tracheostomy in some people and may increase survival by two to three months. Riluzole is available in tablet and liquid form. Medical use Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Riluzole was approved in the United States for the treatment of ALS by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1995. A Cochrane Library review states a 9% gain in the probability of surviving one year. Adverse effects * Very common (>10% frequency): nausea; weakness; decreased lung function * Common (1–10% frequency): headache; dizziness; drowsiness; vomiting; abdominal pain; increased aminotransferases * Uncommon (0.1-1% frequency): pancreatitis; interstitial lung disease * Rare (<0.1% frequency): |
Carbamazepine
Carbamazepine (CBZ), sold under the trade name Tegretol among others, is an anticonvulsant medication used primarily in the treatment of epilepsy and neuropathic pain. It is used as an adjunctive treatment in schizophrenia along with other medications and as a second-line agent in bipolar disorder. Carbamazepine appears to work as well as phenytoin and valproate for focal and generalized seizures. It is not effective for absence seizure, absence or myoclonic seizures. Carbamazepine was discovered in 1953 by Swiss chemist Walter Schindler. It was first marketed in 1962. It is available as a generic medication. It is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In 2020, it was the 185th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 2million prescriptions. Medical uses Carbamazepine is typically used for the treatment of seizure disorders and neuropathic pain. It is used off-label use, off-lab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenytoin
Phenytoin (PHT), sold under the brand name Dilantin among others, is an anti-seizure medication. It is useful for the prevention of tonic-clonic seizures (also known as grand mal seizures) and focal seizures, but not absence seizures. The intravenous form, fosphenytoin, is used for status epilepticus that does not improve with benzodiazepines. It may also be used for certain heart arrhythmias or neuropathic pain. It can be taken intravenously or by mouth. The intravenous form generally begins working within 30 minutes and is effective for roughly 24 hours. Blood levels can be measured to determine the proper dose. Common side effects include nausea, stomach pain, loss of appetite, poor coordination, increased hair growth, and enlargement of the gums. Potentially serious side effects include sleepiness, self harm, liver problems, bone marrow suppression, low blood pressure, and toxic epidermal necrolysis. There is evidence that use during pregnancy results in abnormalities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamotrigine
Lamotrigine, sold under the brand name Lamictal among others, is a medication used to treat epilepsy and stabilize mood in bipolar disorder. For epilepsy, this includes focal seizures, tonic-clonic seizures, and seizures in Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. In bipolar disorder, lamotrigine has not been shown to reliably treat acute depression; but for patients with bipolar disorder who are not currently symptomatic, it appears to be effective in reducing the risk of future episodes of depression. Common side effects include nausea, sleepiness, headache, vomiting, trouble with coordination, and rash. Serious side effects include lack of red blood cells, increased risk of suicide, Stevens–Johnson syndrome, and allergic reactions, which can be fatal. Concerns exist that use during pregnancy or breastfeeding may result in harm. Lamotrigine is a phenyltriazine, making it chemically different from other anticonvulsants. Its mechanism of action is not clear, but it appears to inhibit rele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |