|
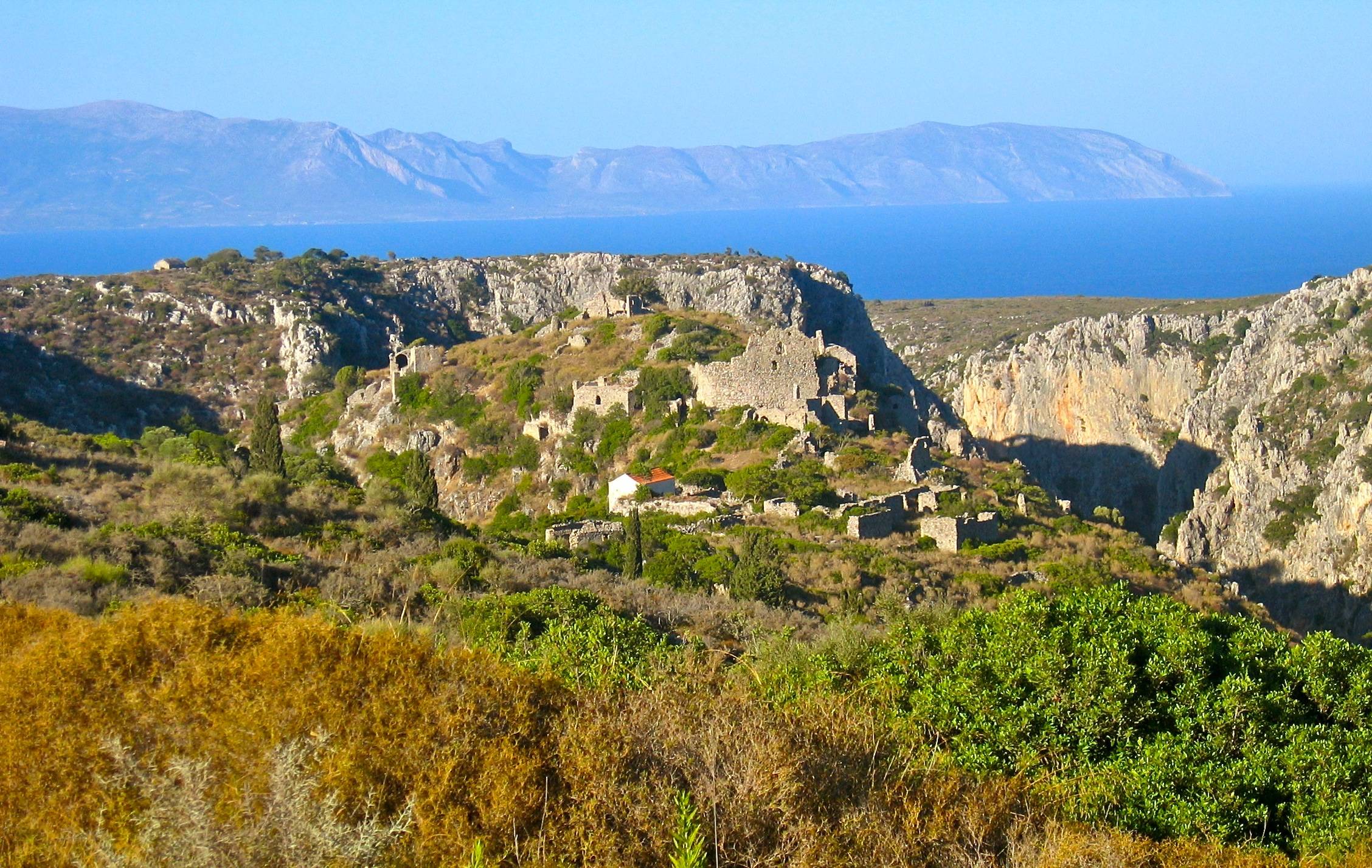
Antikythera
Antikythera or Anticythera ( ) is a Greek island lying on the edge of the Aegean Sea, between Crete and Peloponnese. In antiquity the island was known as (). Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality of Kythira island. Antikythera may also refer to the Kythira-Antikythira Strait, through which Mediterranean water enters the Sea of Crete. Its land area is , and it lies south-east of Kythira. It is the most distant part of the Attica region from its heart in the Athens metropolitan area. It is lozenge-shaped, NNW to SSE by ENE to WSW. It is notable for being the location of the discovery of the Antikythera mechanism and for the historical Antikythera wreck. Its main settlement and port is Potamós (pop. 34 inhabitants in the 2011 census). The only other settlements are Galanianá (pop. 15), and Charchalianá (pop. 19). Antikythera is periodically visited by the Ablemon Nautical Company ferry ''F/B Ionis'' on its route between Piraeus (Athens) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
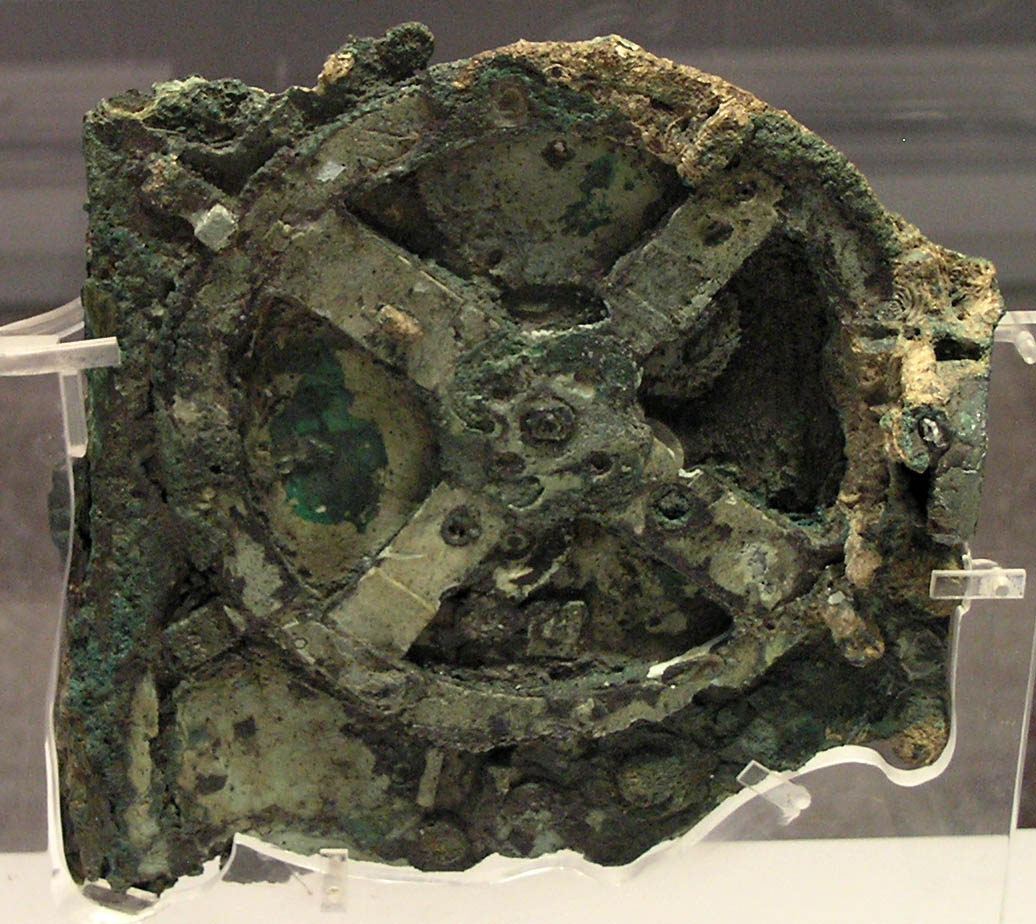
Antikythera Mechanism
The Antikythera mechanism ( ) is an Ancient Greek hand-powered orrery, described as the oldest example of an analogue computer used to predict astronomical positions and eclipses decades in advance. It could also be used to track the four-year cycle of athletic games which was similar to an Olympiad, the cycle of the ancient Olympic Games. This artefact was among wreckage retrieved from a shipwreck off the coast of the Greek island Antikythera in 1901. On 17 May 1902, it was identified as containing a gear by archaeologist Valerios Stais. The device, housed in the remains of a wooden-framed case of (uncertain) overall size , was found as one lump, later separated into three main fragments which are now divided into 82 separate fragments after conservation efforts. Four of these fragments contain gears, while inscriptions are found on many others. The largest gear is approximately in diameter and originally had 223 teeth. In 2008, a team led by Mike Edmunds and Tony Free ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antikythera Wreck
The Antikythera wreck ( gr, Ναυάγιο των Αντικυθήρων) is a Roman-era shipwreck dating from the second quarter of the first century BC."''The Antikythera Shipwreck. The Ship, The Treasures, The Mechanism. National Archaeological Museum, April 2012 – April 2013''". Hellenic Ministry of Culture and Tourism; National Archaeological Museum. Editors Nikolaos Kaltsas & Elena Vlachogianni & Polyxeni Bouyia. Athens: Kapon, 2012, . It was discovered by sponge divers off Point Glyphadia on the Greek island of Antikythera in 1900. The wreck yielded numerous statues, coins, and other artifacts dating back to the fourth century BC, as well as the severely corroded remnants of a device many regard as the world's oldest known analog computer, the Antikythera mechanism. These ancient artifacts, works of art, and elements of the ship are now on display at the National Archaeological Museum of Athens. Discovery Around Easter 1900, Captain Dimitrios Kondos and his crew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antikythera Ephebe
The Antikythera Ephebe, registered as: ''Bronze statue of a youth'' in the museum collections, is a bronze statue of a young man of languorous grace that was found in 1900 by sponge-divers in the area of the ancient Antikythera shipwreck off the island of Antikythera, Greece. It was the first of the series of Greek bronze sculptures that the Aegean and Mediterranean yielded up in the twentieth century which have fundamentally altered the modern view of ancient Greek sculpture. The wreck site, which is dated about 70–60 BC, also yielded the Antikythera mechanism (an astronomical calculating device), a characterful head of a Stoic philosopher, and a hoard of coins. The coins included a disproportionate quantity of Pergamene cistophoric tetradrachms and Ephesian coins, leading scholars to surmise that it had begun its journey on the Ionian coast, perhaps at Ephesus; none of its recovered cargo has been identified as from mainland Greece.Svoronos 1911, Myers 1999, Dafas 2019 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kythira
Kythira (, ; el, Κύθηρα, , also transliterated as Cythera, Kythera and Kithira) is an island in Greece lying opposite the south-eastern tip of the Peloponnese peninsula. It is traditionally listed as one of the seven main Ionian Islands, although it is distant from the main group. Administratively, it belongs to the Islands regional unit, which is part of the Attica region, despite its distance from the Saronic Islands, around which the rest of Attica is centered. As a municipality, it includes the island of Antikythera to the south. The island is strategically located between the Greek mainland and Crete, and from ancient times until the mid 19th century was a crossroads of merchants, sailors, and conquerors. As such, it has had a long and varied history and has been influenced by many civilizations and cultures. This is reflected in its architecture (a blend of traditional, Aegean and Venetian elements), as well as the traditions and customs, influenced by centuries o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andreas Anagnostakis
Andreas Anagnostakis (Ανδρέας Αναγνωστάκης; 11 August 1826 — 27 March 1897) was a Greek ophthalmologist, physician, and educator. He is best known for inventing the ophthalmoscope, a handheld tool used in diagnostics and still relevant today. He is credited as the first ophthalmologist in Greece. Biography Early life Anagostakis was born 11 August 1826 on the Greek island of Antikythera. His parents were from the village of Anopolis in Sfakia, Crete and possibly from one of the original founding Sfakiote families. They fled Cretan Turks on the island and settled in Syra, where Andreas attended school. He later went to the Medical School at the University of Athens, then continued his studies, funded by Queen Amalia, in Vienna, Berlin, and Paris. He graduated from Athens in 1849 with his doctorate in medicine. He was initially a general physician before deciding to specialize in ophthalmology. Career While studying in France, he came up with the idea to add a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
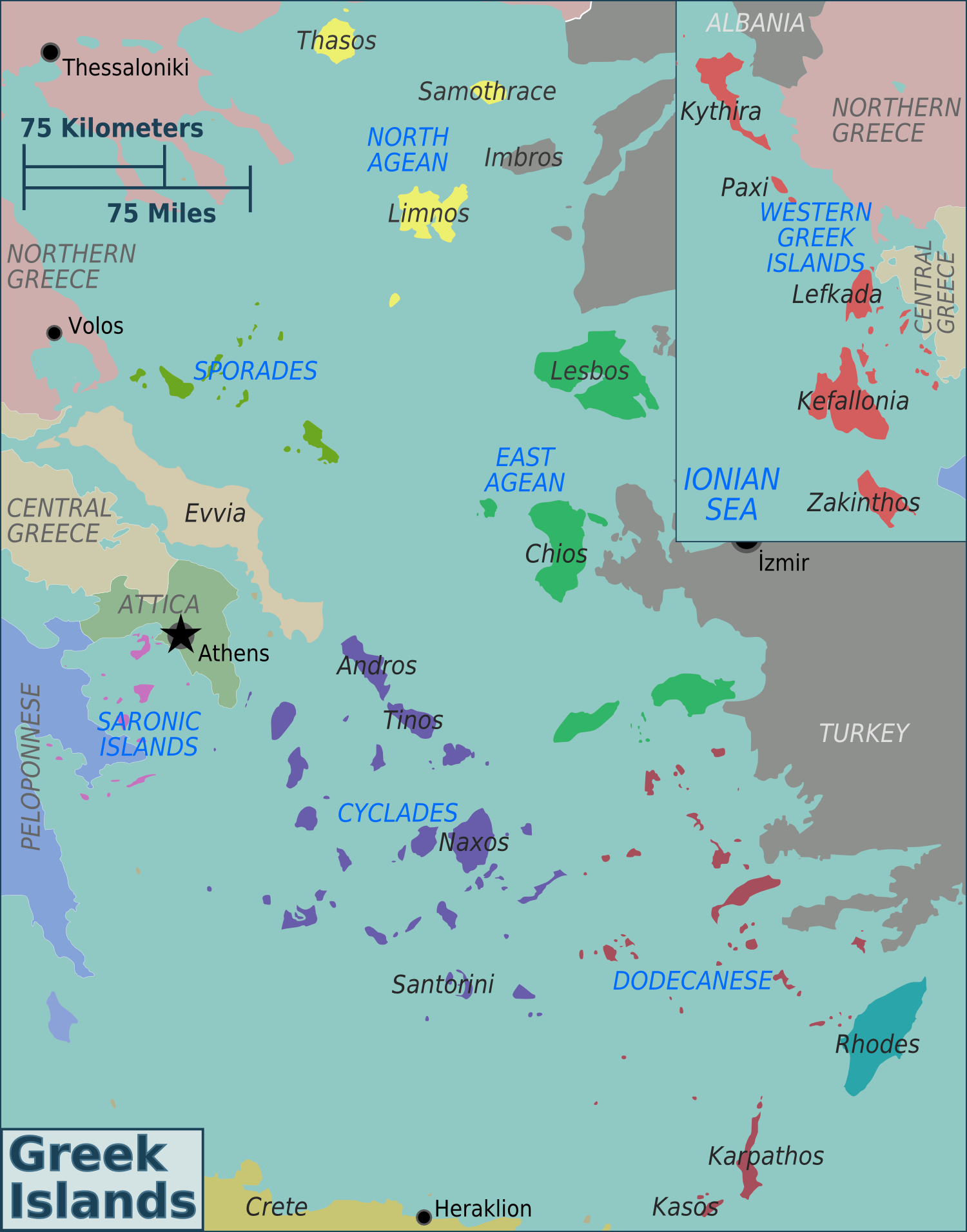
Greek Island
Greece has many islands, with estimates ranging from somewhere around 1,200 to 6,000, depending on the minimum size to take into account. The number of inhabited islands is variously cited as between 166 and 227. The largest Greek island by area is Crete, located at the southern edge of the Aegean Sea. The second largest island is Euboea or Evvia, which is separated from the mainland by the 60m-wide Euripus Strait, and is administered as part of the Central Greece region. After the third and fourth largest Greek islands, Lesbos and Rhodes, the rest of the islands are two-thirds of the area of Rhodes, or smaller. The Greek islands are traditionally grouped into the following clusters: the Argo-Saronic Islands in the Saronic Gulf near Athens; the Cyclades, a large but dense collection occupying the central part of the Aegean Sea; the North Aegean islands, a loose grouping off the west coast of Turkey; the Dodecanese, another loose collection in the southeast between Crete and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some 215,000 square kilometres. In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea and the Black Sea by the straits of the Dardanelles and the Bosphorus. The Aegean Islands are located within the sea and some bound it on its southern periphery, including Crete and Rhodes. The sea reaches a maximum depth of 2,639m to the west of Karpathos. The Thracian Sea and the Sea of Crete are main subdivisions of the Aegean Sea. The Aegean Islands can be divided into several island groups, including the Dodecanese, the Cyclades, the Sporades, the Saronic islands and the North Aegean Islands, as well as Crete and its surrounding islands. The Dodecanese, located to the southeast, includes the islands of R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antikythira Bird Observatory
The Antikythera Bird Observatory, ABO (Greek ''Ορνιθολογικός Σταθμός Αντικυθήρων, ΟΣΑ'') in Antikythira is the only bird observatory in Greece, developing a constant effort ringing activity during bird migration periods. It is run by the Hellenic Ornithological Society HOS (''Ελληνική Ορνιθολογική Εταιρία ΕΟΕ''), the Greek partner of BirdLife International BirdLife International is a global partnership of non-governmental organizations that strives to conserve birds and their habitats. BirdLife International's priorities include preventing extinction of bird species, identifying and safeguarding .... The ABO operates both on the island and the wider maritime area around it, as well as on the two adjacent islets of Pouri and Lagouvardos. Ornithological research on Antikythira has been carried out by the HOS since 1997, but the Antikythira Bird Observatory was established only three years later, in 2000. Researc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
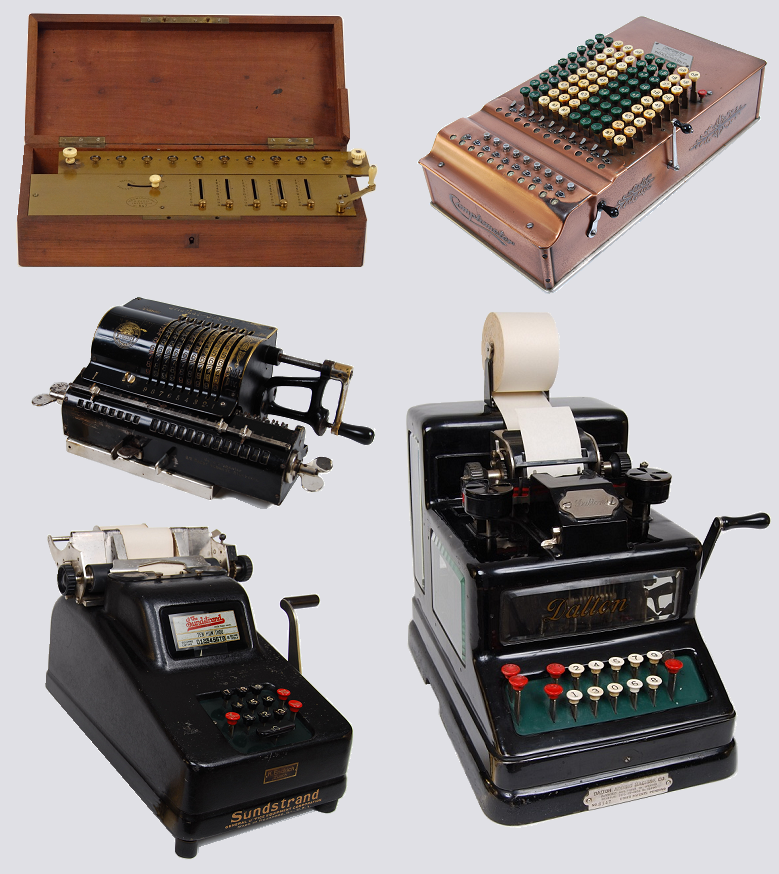
Mechanical Calculator
A mechanical calculator, or calculating machine, is a mechanical device used to perform the basic operations of arithmetic automatically, or (historically) a simulation such as an analog computer or a slide rule. Most mechanical calculators were comparable in size to small desktop computers and have been rendered obsolete by the advent of the electronic calculator and the digital computer. Surviving notes from Wilhelm Schickard in 1623 reveal that he designed and had built the earliest of the modern attempts at mechanizing calculation. His machine was composed of two sets of technologies: first an abacus made of Napier's bones, to simplify multiplications and divisions first described six years earlier in 1617, and for the mechanical part, it had a dialed pedometer to perform additions and subtractions. A study of the surviving notes shows a machine that would have jammed after a few entries on the same dial, and that it could be damaged if a carry had to be propagated over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attica (region)
Attica ( el, Περιφέρεια Αττικής, translit=Periféria Attikís, ) is an administrative region of Greece, that encompasses the entire metropolitan area of Athens, the country's capital and largest city. The region is coextensive with the former Attica Prefecture of Central Greece. It covers a greater area than the historical region of Attica. Overview Located on the eastern edge of Central Greece, Attica covers about 3,808 square kilometers. In addition to Athens, it contains within its area the cities of Elefsina, Megara, Laurium, and Marathon, as well as a small part of the Peloponnese peninsula and the islands of Salamis, Aegina, Angistri, Poros, Hydra, Spetses, Kythira, and Antikythera. About 3,800,000 people live in the region, of whom more than 95% are inhabitants of the Athens metropolitan area. In 2019, Attica had the HDI of 0.912, the highest in Greece. Administration The region was established in the 1987 administrative reform, and until 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolitan Area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban area, urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing Industry (economics), industries, commercial areas, Transport infrastructure, transport network, infrastructures and housing. A metro area usually comprises multiple Principal city, principal cities, jurisdictions and Municipality, municipalities: Neighbourhood, neighborhoods, townships, boroughs, City, cities, towns, exurbs, suburbs, County, counties, districts, as well as even State (polity), states and nations like the eurodistricts. As social, economic and political institutions have changed, metropolitan areas have become key economic and political regions. Metropolitan areas typically include Satellite city, satellite cities, towns and intervening rural areas that are socioeconomically tied to the Principal city, principal cities or urban core, often measured by commuting patterns. Metropolitan areas are sometimes anchored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleonic France
The First French Empire, officially the French Republic, then the French Empire (; Latin: ) after 1809, also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Europe at the beginning of the 19th century. It lasted from 18 May 1804 to 11 April 1814 and again briefly from 20 March 1815 to 7 July 1815. Although France had already established a colonial empire overseas since the early 17th century, the French state had remained a kingdom under the Bourbons and a republic after the French Revolution. Historians refer to Napoleon's regime as the ''First Empire'' to distinguish it from the restorationist '' Second Empire'' (1852–1870) ruled by his nephew Napoleon III. The First French Empire is considered by some to be a " Republican empire." On 18 May 1804, Napoleon was granted the title Emperor of the French (', ) by the French and was crowned on 2 December 1804, signifying the end of the French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_(14801629433).jpg)