|
Anti-Jewish Legislation In Prewar Nazi Germany
Anti-Jewish legislation in pre-war Nazi Germany comprised several laws that segregated the Jews from German society and restricted Jewish people's political, legal and civil rights. Major legislative initiatives included a series of restrictive laws passed in 1933, the Nuremberg Laws of 1935, and a final wave of legislation preceding Germany's entry into World War II. 1933 Anti-Jewish Legislation Enabling Act The Enabling Act of 1933 established the power of the Nazi-led government to pass law by decree, bypassing the approval of parliament. It was passed on March 23, 1933, and effectively nullified the Weimar Constitution. Law for the Restoration of the Professional Civil Service In April 1933, the Law for the Restoration of the Professional Civil Service, or 'Civil Service Law', as it was more commonly known when passed, established the ability of the Nazi-led government to legally remove undesirables from the civil service profession, including doctors, teach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Socialist Program
The National Socialist Program, also known as the Nazi Party Program, the 25-point Program or the 25-point Plan (), was the party program of the National Socialist German Workers' Party (NSDAP, and referred to in English as the Nazi Party). Adolf Hitler announced the party's program on 24 February 1920 before approximately 2,000 people in the Munich Festival of the Hofbräuhaus; within the program was written "The leaders of the Party swear to go straight forward, if necessary to sacrifice their lives in securing fulfilment of the foregoing points" and declared the program unalterable. The National Socialist Program originated at a DAP congress in Vienna, then was taken to Munich by the civil engineer and theorist Rudolf Jung, who having explicitly supported Hitler had been expelled from Czechoslovakia because of his political agitation. The historian Karl Dietrich Bracher summarizes the program by saying that its components were "hardly new" and that "German, Austrian and Bohe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontkämpferprivileg
The ''Frontkämpferprivileg'' (''front-line fighter's privilege'') was an exemption granted by the government of Nazi Germany between 1933 and 1935 to German Jews who had fought for Germany during the First World War but faced dismissal from official posts under anti-Jewish legislation in prewar Nazi Germany. The "Law for the Restoration of the Professional Civil Service" of 7 April 1933 aimed to force all "non-Aryans" to retire from the legal profession and civil service, and other anti-Jewish laws passed in 1933 sought to drive Jews out of other areas of public life. These moves prompted a protest from Captain Leo Löwenstein, the president of the Reich Association of Jewish Frontline Soldiers, who wrote to the Nazi leader Adolf Hitler to complain. He pointed out that of Germany's half-million Jewish population, 96,000 had served in the war and 12,000 had perished. He wrote: It also met with the disapproval of Reich President Paul von Hindenburg Paul Ludwig Hans Anton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aryanization (Nazism)
Aryanization () was the Nazi term for the seizure of property from Jews and its transfer to non-Jews, and the forced expulsion of Jews from economic life in Nazi Germany, Axis-aligned states, and their occupied territories. It entailed the transfer of Jewish property into "Aryan" or non-Jewish hands. "Aryanization" is, according to Kreutzmüller and Zaltin in ''Dispossession: Plundering German Jewry, 1933-1953'', "a Nazi slogan that was used to camouflage theft and its political consequences." The process started in 1933 in Nazi Germany with transfers of Jewish property and ended with the Holocaust. Two phases have generally been identified: a first phase in which the theft from Jewish victims was concealed under a veneer of legality, and a second phase, in which property was more openly confiscated. In both cases, Aryanization corresponded to Nazi policy and was defined, supported, and enforced by Germany's legal and financial bureaucracy. Michael Bazyler wrote that the Hol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichsmark
The (; sign: ℛ︁ℳ︁; abbreviation: RM) was the currency of Germany from 1924 until the fall of Nazi Germany in 1945, and in the American, British and French occupied zones of Germany, until 20 June 1948. The Reichsmark was then replaced by the Deutsche Mark, to become the currency of West Germany and then all of Germany after the 1990 reunification. The Reichsmark was used in the Soviet occupation zone of Germany until 23 June 1948, where it was replaced by the East German mark. The Reichsmark was subdivided into 100 (Rpf or ℛ︁₰). The Mark is an ancient Germanic weight measure, traditionally a half pound, later used for several coins; (''realm'' in English) comes from the official name for the German state from 1871 to 1945, . History The Reichsmark was introduced in 1924 as a permanent replacement for the '' Papiermark''. This was necessary due to the 1920s German inflation which had reached its peak in 1923. The exchange rate between the old ''Papiermark'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kristallnacht
( ) or the Night of Broken Glass, also called the November pogrom(s) (, ), was a pogrom against Jews carried out by the Nazi Party's (SA) and (SS) paramilitary forces along with some participation from the Hitler Youth and German civilians throughout Nazi Germany on 9–10 November 1938. The German authorities looked on without intervening.German Mobs' Vengeance on Jews", ''The Daily Telegraph'', 11 November 1938, cited in The euphemistic name comes from the shards of broken glass that littered the streets after the windows of Jewish-owned stores, buildings, and synagogues were smashed. The pretext for the attacks was the assassination, on 9 November 1938, of the German diplomat Ernst vom Rath by Herschel Grynszpan, a 17-year-old German-born Polish Jew living in Paris. Jewish homes, hospitals and schools were ransacked as attackers demolished buildings with sledgehammers. Rioters destroyed over 1,400 synagogues and prayer rooms throughout Germany, Austria, and the Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bundesarchiv Bild 146-1970-083-42, Magdeburg, Zerstörtes Jüdisches Geschäft
The German Federal Archives or Bundesarchiv (BArch) (, lit. "Federal Archive") are the national archives of Germany. They were established at the current location in Koblenz in 1952. They are subordinated to the Federal Commissioner for Culture and the Media (Claudia Roth since 2021) under the German Chancellery, and before 1998, to the Federal Ministry of the Interior (Germany), Federal Ministry of the Interior. On 6 December 2008, the Archives donated 100,000 photos to the public, by making them accessible via Wikimedia Commons. History The federal archive for institutions and authorities in Germany, the first precursor to the present-day Federal Archives, was established in Potsdam, Brandenburg in 1919, a later date than in other European countries. This national archive documented German government dating from the founding of the North German Confederation in 1867. It also included material from the older German Confederation and the Imperial Chamber Court. The oldest docum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1936 Winter Olympics
The 1936 Winter Olympics, officially known as the IV Olympic Winter Games () and commonly known as Garmisch-Partenkirchen 1936, were a winter multi-sport event held from 6 to 16 February 1936 in the market town of Garmisch-Partenkirchen, Nazi Germany, Germany. Later that year, the country also hosted the 1936 Summer Olympics, which were held in Berlin. It was the last year in which the Summer and Winter Games both took place in the same country (the cancelled 1940 Olympics would have been held in Japan, with Tokyo hosting the 1940 Summer Olympics, Summer Games and Sapporo hosting the 1940 Winter Olympics, Winter Games). The 1936 Winter Games were organized on behalf of the National Socialist League of the Reich for Physical Exercise, German League of the Reich for Physical Exercise (DRL) by Karl Ritter von Halt, who had been named president of the committee for the organization of the Fourth Winter Olympics in Garmisch-Partenkirchen by ''Reichssportführer'' Hans von Tschammer und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1936 Summer Olympics
The 1936 Summer Olympics (), officially the Games of the XI Olympiad () and officially branded as Berlin 1936, were an international multi-sport event held from 1 to 16 August 1936 in Berlin, then capital of Nazi Germany. Berlin won the bid to host the Games over Barcelona on the 29th IOC Session on 26 April 1931. The 1936 Games marked the second and most recent time the International Olympic Committee gathered to vote in a city bidding to host those Games. Later rule modifications forbade cities hosting the bid vote from being awarded the games. To outdo the 1932 Summer Olympics, 1932 Los Angeles Games, Adolf Hitler had Olympiastadion (Berlin), a new 100,000-seat track and field stadium built, as well as six gymnasiums and other smaller arenas. The Games were the first to be Fernsehsender Paul Nipkow, televised, with radio broadcasts reaching 41 countries.Rader, Benjamin G. "American Sports: From the Age of Folk Games to the Age of Televised Sports", 5th ed. Filmmaker Leni Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
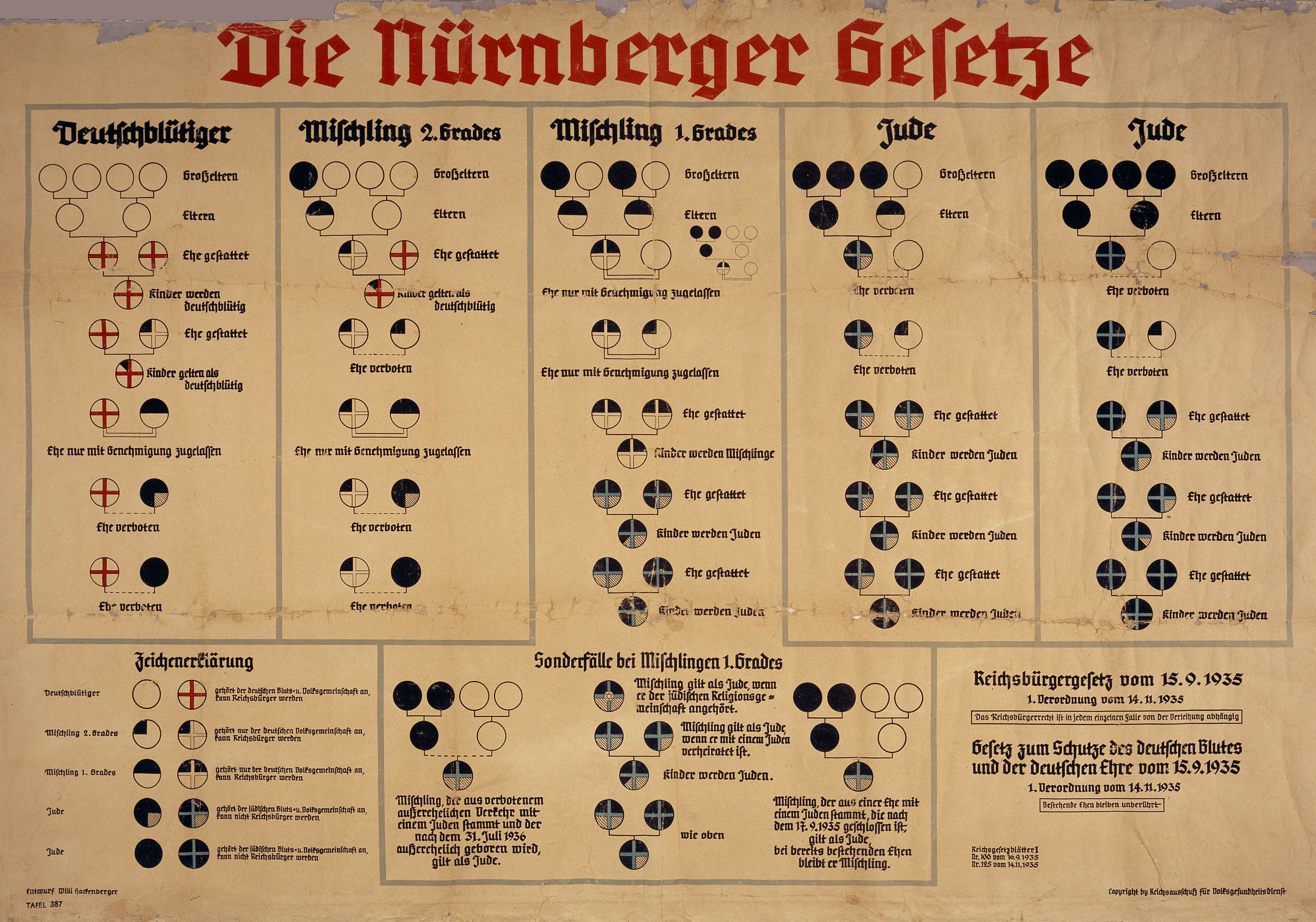
Mischling
(; ; ) was a pejorative legal term which was used in Nazi Germany to denote persons of mixed " Aryan" and "non-Aryan", such as Jewish, ancestry as they were classified by the Nuremberg racial laws of 1935. In German, the word has the general denotation of ' hybrid', ' mongrel', or ' half-breed'. Outside its use in official Nazi terminology, the term ('mixed children') was later used to refer to war babies born to non-white soldiers and German mothers in the aftermath of World War II. Nazi definitions of Mischling Nazis relied on one's ancestors' religious backgrounds to determine whether someone was of "German or related blood" ("Aryan") or a "Jew" ("non-Aryan"). Thus, the Nuremberg Laws in 1935 defined a "full Jew" (''Istjude'' or ''Volljude'' in Nazi terminology) as a person – regardless of religious affiliation or self-identification – who had at least three grandparents who had been enrolled with a Jewish congregation or were married to a Jewish spouse. A perso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-miscegenation Laws
Anti-miscegenation laws are laws that enforce racial segregation at the level of marriage and intimate relationships by criminalizing interracial marriage sometimes, also criminalizing sex between members of different races. In the United States, interracial marriage, cohabitation and sex have been termed " miscegenation" since the term was coined in 1863. Contemporary usage of the term is infrequent, except in reference to historical laws which banned the practice. Anti-miscegenation laws were first introduced in North America by the governments of several of the Thirteen Colonies from the late seventeenth century onward, and subsequently, they were introduced by the governments of many U.S. states and U.S. territories and they remained in force in many US states until 1967. After the Second World War, an increasing number of states repealed their anti-miscegenation laws. In 1967, in the landmark case '' Loving v. Virginia'', the remaining anti-miscegenation laws were ruled u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |