|
Anorectics
An anorectic is a drug that reduces appetite, resulting in lower food consumption, leading to weight loss. These substances work by affecting the central nervous system or certain neurotransmitters to create a feeling of fullness or reduce the desire to eat. The understanding of anorexiant effects is crucial in the development of interventions for weight management, eating disorders, and related health concerns. The anorexiant effect can be induced through diverse mechanisms, ranging from hormonal regulation to neural signaling. Ghrelin, leptin, and peptide YY are among the hormones involved in appetite control. Additionally, neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine in the central nervous system contribute significantly to the regulation of food intake. By contrast, an appetite stimulant is referred to as orexigenic. The term is (from the Greek and ), and such drugs are also known as anorexigenic, anorexiant, or appetite suppressant. History Used on a short-term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fenfluramine
Fenfluramine, sold under the brand name Fintepla, is a serotonergic medication used for the treatment of seizures associated with Dravet syndrome and Lennox–Gastaut syndrome. It was formerly used as an appetite suppressant in the treatment of obesity, but was discontinued for this use due to cardiovascular toxicity before being repurposed for new indications. Fenfluramine was used for weight loss both alone under the brand name Pondimin and in combination with phentermine commonly known as fen-phen. Side effects of fenfluramine in people treated for seizures include decreased appetite, somnolence, sedation, lethargy, diarrhea, constipation, abnormal echocardiogram, fatigue, malaise, asthenia, ataxia, balance disorder, gait disturbance, increased blood pressure, drooling, excessive salivation, fever, upper respiratory tract infection, vomiting, appetite loss, weight loss, falls, and status epilepticus. Fenfluramine acts as a serotonin and norepinephrin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminorex
Aminorex, sold under the brand names Menocil and Apiquel among others, is a weight loss (anorectic) stimulant drug. It was withdrawn from the market after it was found to cause pulmonary hypertension (PPH). In the United States, aminorex is a Schedule I controlled substance. Aminorex, in the 2-amino-5-aryloxazoline group, was developed by McNeil Laboratories in 1962. It is closely related to 4-methylaminorex (4-MAR). Aminorex has been shown to have locomotor-stimulant effects, lying midway between dextroamphetamine and methamphetamine. Aminorex effects have been attributed to the release of catecholamines. It can be produced as a metabolite of the deworming medication levamisole, which is sometimes used as a cutting agent of illicitly produced cocaine. Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics Aminorex is a serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (SNDRA). Its values for induction of monoamine release are 26.4nM for norepinephrine, 49.4nM for dopamine, and 193nM fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from Alpha and beta carbon, alpha-methylphenethylamine, methylphenethylamine) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity; it is also used to treat binge eating disorder in the form of its inactive prodrug lisdexamfetamine. Amphetamine was discovered as a chemical in 1887 by Lazăr Edeleanu, and then as a drug in the late 1920s. It exists as two enantiomers: levoamphetamine and dextroamphetamine. ''Amphetamine'' properly refers to a specific chemical, the Racemic mixture, racemic free base, which is equal parts of the two enantiomers in their pure amine forms. The term is frequently used informally to refer to any combination of the enantiomers, or to either of them alone. Historically, it has been used to treat nasal congestion and depression. Amphetamine is also used as an Performance-enhancing substance, athletic performance enhancer and Nootropic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methamphetamine
Methamphetamine (contracted from ) is a potent central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is mainly used as a recreational drug use, recreational or Performance-enhancing substance, performance-enhancing drug and less commonly as a second-line treatment for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). It has also been researched as a potential treatment for traumatic brain injury. Methamphetamine was discovered in 1893 and exists as two enantiomers: levo-methamphetamine and dextro-methamphetamine. ''Methamphetamine'' properly refers to a specific chemical substance, the racemic mixture, racemic free base, which is an equal mixture of levomethamphetamine and dextromethamphetamine in their pure amine forms, but the hydrochloride salt, commonly called crystal meth, is widely used. Methamphetamine is rarely prescribed over concerns involving its potential for recreational use as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant, among other concerns, as well as the availability of safer subst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from Alpha and beta carbon, alpha-methylphenethylamine, methylphenethylamine) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity; it is also used to treat binge eating disorder in the form of its inactive prodrug lisdexamfetamine. Amphetamine was discovered as a chemical in 1887 by Lazăr Edeleanu, and then as a drug in the late 1920s. It exists as two enantiomers: levoamphetamine and dextroamphetamine. ''Amphetamine'' properly refers to a specific chemical, the Racemic mixture, racemic free base, which is equal parts of the two enantiomers in their pure amine forms. The term is frequently used informally to refer to any combination of the enantiomers, or to either of them alone. Historically, it has been used to treat nasal congestion and depression. Amphetamine is also used as an Performance-enhancing substance, athletic performance enhancer and Nootropic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenethylamine
Phenethylamine (PEA) is an organic compound, natural monoamine alkaloid, and trace amine, which acts as a central nervous system stimulant in humans. In the brain, phenethylamine regulates monoamine neurotransmission by binding to trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) and inhibiting vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) in monoamine neurons. To a lesser extent, it also acts as a neurotransmitter in the human central nervous system. In mammals, phenethylamine is produced from the amino acid L-phenylalanine by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase via enzymatic decarboxylation. In addition to its presence in mammals, phenethylamine is found in many other organisms and foods, such as chocolate, especially after microbial fermentation. Phenethylamine is sold as a dietary supplement for purported mood and weight loss-related therapeutic benefits; however, in orally ingested phenethylamine, a significant amount is metabolized in the small intestine by mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
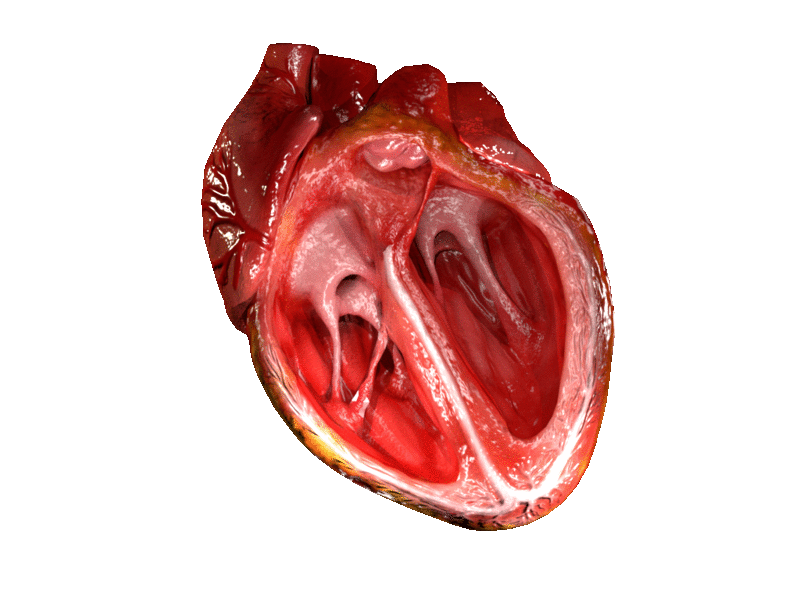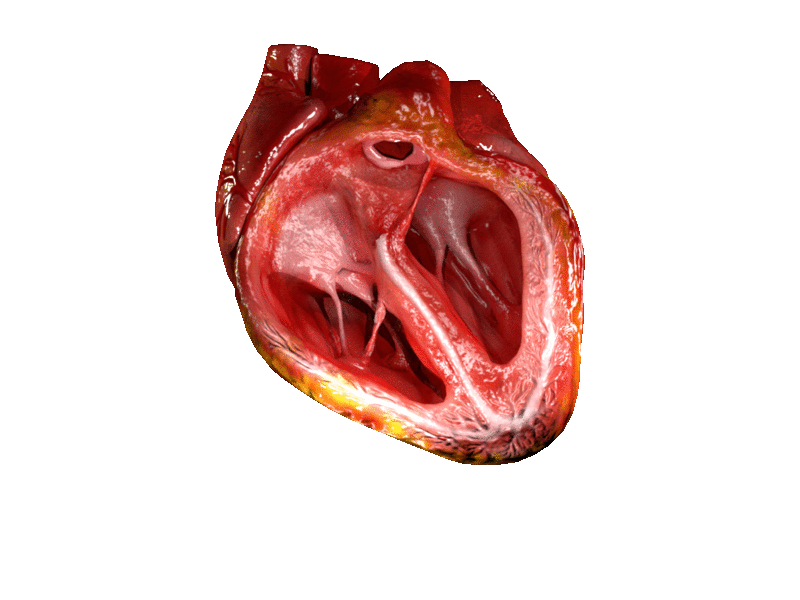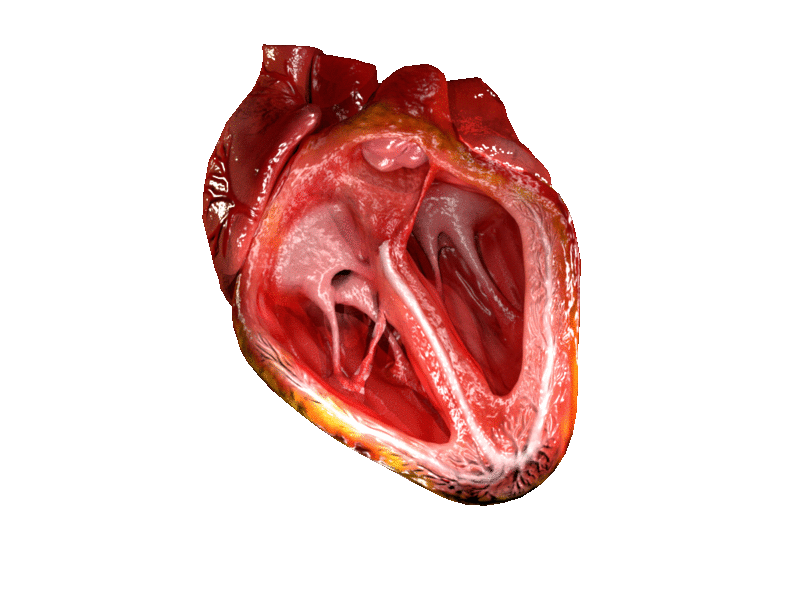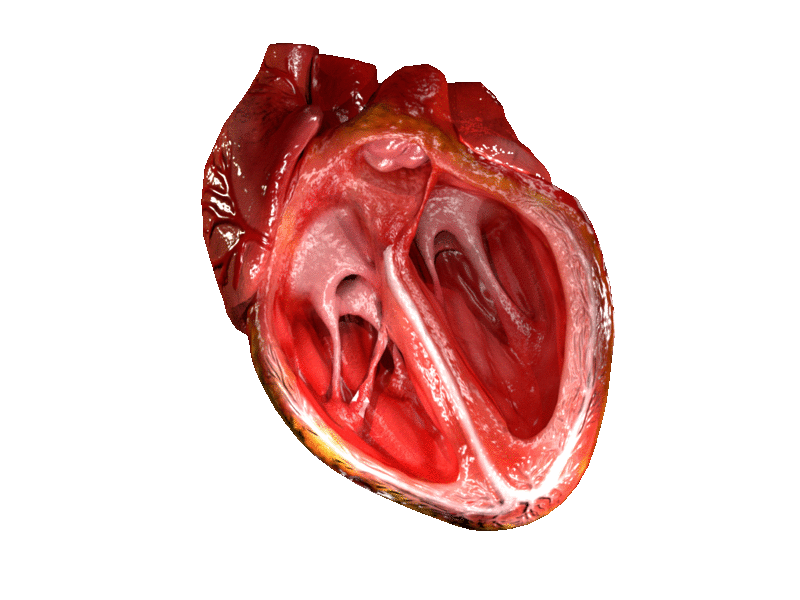
Heart Valve
A heart valve is a biological one-way valve that allows blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart. A mammalian heart usually has four valves. Together, the valves determine the direction of blood flow through the heart. Heart valves are opened or closed by a difference in blood pressure on each side. The mammalian heart has two atrioventricular valves separating the upper atria from the lower ventricles: the mitral valve in the left heart, and the tricuspid valve in the right heart. The two semilunar valves are at the entrance of the arteries leaving the heart. These are the aortic valve at the aorta, and the pulmonary valve at the pulmonary artery. The heart also has a coronary sinus valve and an inferior vena cava valve, not discussed here. Structure The heart valves and the chambers are lined with endocardium. Heart valves separate the atria from the ventricles, or the ventricles from a blood vessel. Heart valves are situated around the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension (PH or PHTN) is a condition of increased blood pressure in the pulmonary artery, arteries of the lungs. Symptoms include dypsnea, shortness of breath, Syncope (medicine), fainting, tiredness, chest pain, pedal edema, swelling of the legs, and a fast heartbeat. The condition may make it difficult to exercise. Onset is typically gradual. According to the definition at the 6th World Symposium of Pulmonary Hypertension in 2018, a patient is deemed to have pulmonary hypertension if the pulmonary mean arterial pressure is greater than 20mmHg at rest, revised down from a purely arbitrary 25mmHg, and pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) greater than 3 Wood units. The cause is often unknown. Risk factors include a family history, prior pulmonary embolism (blood clots in the lungs), HIV/AIDS, sickle cell disease, cocaine use, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, sleep apnea, living at high altitudes, and problems with the mitral valve. The underlying mechanism typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms itself. It is, however, a major risk factor for stroke, coronary artery disease, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, peripheral arterial disease, vision loss, chronic kidney disease, and dementia. Hypertension is a major cause of premature death worldwide. High blood pressure is classified as essential hypertension, primary (essential) hypertension or secondary hypertension. About 90–95% of cases are primary, defined as high blood pressure due to non-specific lifestyle and Genetics, genetic factors. Lifestyle factors that increase the risk include excess salt in the diet, overweight, excess body weight, smoking, physical inactivity and Alcohol (drug), alcohol use. The remaining 5–10% of cases are categorized as secondary hypertension, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachycardia
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal (such as with exercise) or abnormal (such as with electrical problems within the heart). Complications Tachycardia can lead to fainting. When the rate of blood flow becomes too rapid, or fast blood flow passes on damaged endothelium, it increases the friction within vessels resulting in turbulence and other disturbances. According to the Virchow's triad, this is one of the three conditions (along with hypercoagulability and endothelial injury/dysfunction) that can lead to thrombosis (i.e., blood clots within vessels). Causes Some causes of tachycardia include: * Adrenergic storm * Anaemia * Anxiety * Atrial fibrillation * Atrial flutter * Atrial tachycardia * Atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia * AV nodal reentrant tachy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substance Dependence
Substance dependence, also known as drug dependence, is a biopsychological situation whereby an individual's functionality is dependent on the necessitated re-consumption of a psychoactive substance because of an adaptive state that has developed within the individual from psychoactive substance consumption that results in the experience of withdrawal and that necessitates the re-consumption of the drug. A ''drug addiction'', a distinct concept from substance dependence, is defined as compulsive, out-of-control drug use, despite negative consequences. An ''addictive drug'' is a drug which is both rewarding and reinforcing. ΔFosB, a gene transcription factor, is now known to be a critical component and common factor in the development of virtually all forms of behavioral and drug addictions, but not dependence. The International Classification of Diseases classifies substance dependence as a mental and behavioural disorder. In the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Armed Forces
The United States Armed Forces are the Military, military forces of the United States. U.S. United States Code, federal law names six armed forces: the United States Army, Army, United States Marine Corps, Marine Corps, United States Navy, Navy, United States Air Force, Air Force, United States Space Force, Space Force, and the United States Coast Guard, Coast Guard. Since 1949, all of the armed forces, except the Coast Guard, have been permanently part of the United States Department of Defense. They form six of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Each of the different military services is assigned a role and domain. The Army conducts land operations. The Navy and Marine Corps conduct maritime operations, the Marine Corps specializing in amphibious and maritime littoral operations primarily for supporting the Navy. The Air Force conducts air operations. The Space Force conducts space operations. The Coast Guard is unique in that it specializes in maritime opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |