|
Anoplogaster Cornuta
''Anoplogaster cornuta'', the common fangtooth, is a species of deep sea fish found in temperate and tropical oceans worldwide. It is found at depths of from with the adults usually found from and the young usually found near the surface. This species grows to a total length of about . While a source of food for pelagic carnivorous fishes, this species is of no interest for human fisheries. Description The common fangtooth has a distinctive appearance and grows to a total length of about . Adults are dark brown to black, the head is very large, bony and finely sculptured but does not bear any spines. The eye is small and the gill rakers have bony bases and are tooth-like. The body is deepest just behind the head, tapering rapidly to the caudal peduncle. The mouth is well-armed with sharp fangs and the skin is granular. The dorsal fin has no spines and 17 to 20 soft rays while the anal fin has no spines and 7 to 9 soft rays. The lateral line takes the form of an open groove, br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achille Valenciennes
Achille Valenciennes (9 August 1794 – 13 April 1865) was a French zoologist. Valenciennes was born in Paris, and studied under Georges Cuvier. His study of parasitic worms in humans made an important contribution to the study of parasitology. He also carried out diverse systematic classifications, linking fossil and current species. He worked with Cuvier on the 22-volume "'' Histoire Naturelle des Poissons''" (Natural History of Fish) (1828–1848), carrying on alone after Cuvier died in 1832. In 1832, he succeeded Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville (1777–1850) as chair of ''Histoire naturelle des mollusques, des vers et des zoophytes'' at the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle. Early in his career, he was given the task of classifying animals described by Alexander von Humboldt (1769–1859) during his travels in the American tropics (1799 to 1803), and a lasting friendship was established between the two men. He is the binomial authority for many species of fish, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albacore
The albacore (''Thunnus alalunga''), known also as the longfin tuna, is a species of tuna of the order Perciformes. It is found in temperate and tropical waters across the globe in the epipelagic and mesopelagic zones. There are six distinct stocks known globally in the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian oceans, as well as the Mediterranean Sea. The albacore has an elongate, fusiform body with a conical snout, large eyes, and remarkably long pectoral fins. Its body is a deep blue dorsally and shades of silvery white ventrally. Individuals can reach up to in length. Albacore are pelagic predators that eat a wide variety of foods, including but not limited to fish, crustaceans, and cephalopods. They are unique among most tuna in that their primary food source is cephalopods, with fish making up a much smaller portion of their diet. Reproduction usually occurs from November to February and is oviparous. An adult female can release over two million eggs in a single cycle. Fry (juvenile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anoplogastridae
Fangtooths are beryciform fish of the family Anoplogastridae (sometimes spelled "Anoplogasteridae") that live in the deep sea. The name is from the Greek , meaning "unarmed", and (), meaning "stomach". With a circumglobal distribution in tropical and cold-temperate waters, the family contains only two very similar species in one genus, with no known close relatives. Species The currently recognized species in this genus are: * ''Anoplogaster brachycera'' Kotlyar, 1986 (shorthorn fangtooth) * ''Anoplogaster cornuta'' (Valenciennes, 1833) (common fangtooth) Description While named for their disproportionately large, fang-like teeth and unapproachable visage, fangtooths are actually quite small and harmless to humans: the larger of the two species, the common fangtooth, reaches a maximum length of just ; the shorthorn fangtooth is less than half this size though currently known only from juvenile specimens. ''Anoplogaster cornuta'' are in the smaller size range of fishes. They ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmopolitan Animals
Cosmopolitan may refer to: Food and drink * Cosmopolitan (cocktail), also known as a "Cosmo" History * Rootless cosmopolitan, a Soviet derogatory epithet during Joseph Stalin's anti-Semitic campaign of 1949–1953 Hotels and resorts * Cosmopolitan of Las Vegas, a luxury resort casino and hotel in Las Vegas, Nevada, which opened in December 2010 * Cosmopolitan Hotel in Hong Kong Internationalism * World citizen, one who eschews traditional geopolitical divisions derived from national citizenship * Cosmopolitanism, the idea that all of humanity belongs to a single moral community * Cosmopolitan localism, a way of linking local communities in global networks that bring production and consumption closer together Media * ''Cosmopolitan'' (magazine), a magazine for women, sometimes referred to as "''Cosmo''" * ''Cosmopolitan'' (film), a 2003 film starring Roshan Seth * Cosmopolitan Television, a satellite/cable television channel * Cosmopolitan Productions, a defunct United State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided into two layers, the superficial area adjacent to the epidermis called the papillary region and a deep thicker area known as the reticular dermis.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology'' (10th ed.). Saunders. Pages 1, 11–12. . The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis through a basement membrane. Structural components of the dermis are collagen, elastic fibers, and extrafibrillar matrix.Marks, James G; Miller, Jeffery (2006). ''Lookingbill and Marks' Principles of Dermatology'' (4th ed.). Elsevier Inc. Page 8–9. . It also contains mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and thermoreceptors that provide the sense of heat. In addition, hair follicles, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
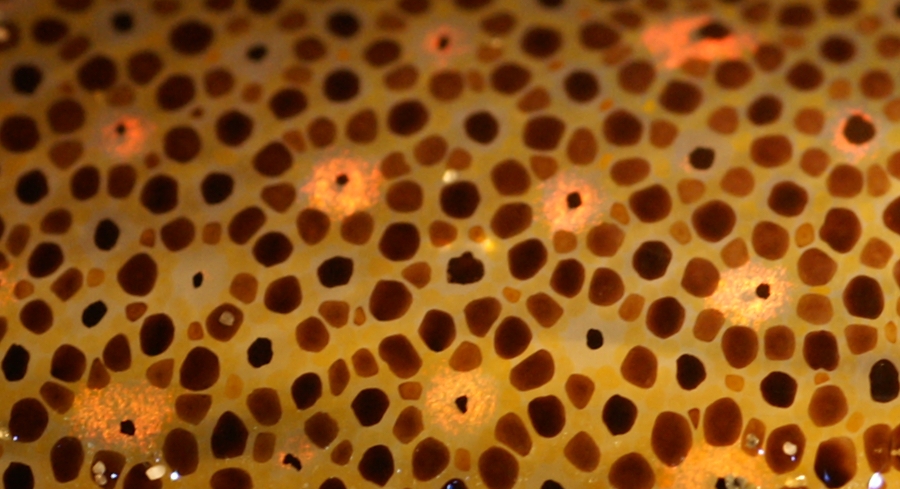
Chromatophore
Chromatophores are cells that produce color, of which many types are pigment-containing cells, or groups of cells, found in a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopods. Mammals and birds, in contrast, have a class of cells called melanocytes for coloration. Chromatophores are largely responsible for generating skin and eye colour in ectothermic animals and are generated in the neural crest during embryonic development. Mature chromatophores are grouped into subclasses based on their colour (more properly "hue") under white light: xanthophores (yellow), erythrophores (red), iridophores (reflective / iridescent), leucophores (white), melanophores (black/brown), and cyanophores (blue). While most chromatophores contain pigments that absorb specific wavelengths of light, the color of leucophores and iridophores is produced by their respective scattering and optical interference properties. Some species can rapidly change colour through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino acid tyrosine is followed by polymerization. The melanin pigments are produced in a specialized group of cells known as melanocytes. Functionally, eumelanin serves as protection against UV radiation. There are five basic types of melanin: eumelanin, pheomelanin, neuromelanin, allomelanin and pyomelanin. The most common type is eumelanin, of which there are two types— brown eumelanin and black eumelanin. Pheomelanin, which is produced when melanocytes are malfunctioning due to derivation of the gene to its recessive format is a cysteine-derivative that contains poly benzothiazine portions that are largely responsible for the of red yellow tint given to some skin or hair colors. Neuromelanin is found in the brain. Research has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioluminescence
Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by living organisms. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms including some bioluminescent bacteria, and terrestrial arthropods such as fireflies. In some animals, the light is bacteriogenic, produced by symbiotic bacteria such as those from the genus '' Vibrio''; in others, it is autogenic, produced by the animals themselves. In a general sense, the principal chemical reaction in bioluminescence involves a light-emitting molecule and an enzyme, generally called luciferin and luciferase, respectively. Because these are generic names, luciferins and luciferases are often distinguished by the species or group, e.g. firefly luciferin. In all characterized cases, the enzyme catalyzes the oxidation of the luciferin. In some species, the luciferase requires other cofactors, such as calcium or magnesium ions, and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otolith
An otolith ( grc-gre, ὠτο-, ' ear + , ', a stone), also called statoconium or otoconium or statolith, is a calcium carbonate structure in the saccule or utricle of the inner ear, specifically in the vestibular system of vertebrates. The saccule and utricle, in turn, together make the ''otolith organs''. These organs are what allows an organism, including humans, to perceive linear acceleration, both horizontally and vertically (gravity). They have been identified in both extinct and extant vertebrates. Counting the annual growth rings on the otoliths is a common technique in estimating the age of fish. Description Endolymphatic infillings such as otoliths are structures in the saccule and utricle of the inner ear, specifically in the vestibular labyrinth of all vertebrates (fish, amphibians, reptiles, mammals and birds). In vertebrates, the saccule and utricle together make the ''otolith organs''. Both statoconia and otoliths are used as gravity, balance, movement, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in water (or air) that are unable to propel themselves against a current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucial source of food to many small and large aquatic organisms, such as bivalves, fish and whales. Marine plankton include bacteria, archaea, algae, protozoa and drifting or floating animals that inhabit the saltwater of oceans and the brackish waters of estuaries. Freshwater plankton are similar to marine plankton, but are found in the freshwaters of lakes and rivers. Plankton are usually thought of as inhabiting water, but there are also airborne versions, the aeroplankton, that live part of their lives drifting in the atmosphere. These include plant spores, pollen and wind-scattered seeds, as well as microorganisms swept into the air from terrestrial dust storms and oceanic plankton swept into the air by sea spray. Though m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oviparity
Oviparous animals are animals that lay their eggs, with little or no other embryonic development within the mother. This is the reproductive method of most fish, amphibians, most reptiles, and all pterosaurs, dinosaurs (including birds), and monotremes. In traditional usage, most insects (one being '' Culex pipiens'', or the common house mosquito), molluscs, and arachnids are also described as oviparous. Modes of reproduction The traditional modes of reproduction include oviparity, taken to be the ancestral condition, traditionally where either unfertilised oocytes or fertilised eggs are spawned, and viviparity traditionally including any mechanism where young are born live, or where the development of the young is supported by either parent in or on any part of their body. However, the biologist Thierry Lodé recently divided the traditional category of oviparous reproduction into two modes that he named ovuliparity and (true) oviparity respectively. He distinguished ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marlin
Marlins are fish from the family Istiophoridae, which includes about 10 species. A marlin has an elongated body, a spear-like snout or bill, and a long, rigid dorsal fin which extends forward to form a crest. Its common name is thought to derive from its resemblance to a sailor's marlinspike. Marlins are among the fastest marine swimmers. However, greatly exaggerated speeds are often claimed in popular literature, based on unreliable or outdated reports. The larger species include the Atlantic blue marlin, ''Makaira nigricans'', which can reach in length and in weight and the black marlin, ''Istiompax indica'', which can reach in excess of in length and in weight. They are popular sporting fish in tropical areas. The Atlantic blue marlin and the white marlin are endangered owing to overfishing. Classification The marlins are Istiophoriform fish, most closely related to the swordfish, which is the sole member of Xiphiidae. The carangiformes is believed to be the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)