|
Anopheles (Kerteszia)
The subgenus ''Kerteszia'' are Neotropical anopheline mosquitoes originally described in 1905 by Frederick V. Theobald as genus ''Kertészia'' with ''Kertészia boliviensis'' as the type species.Theobald, F. V. 1905. A catalogue of the Culicidae in the Hungarian National Museum with descriptions of new genera and species. ''Ann. Mus. Nat. Hungarici'', 3: 61-119; 66; http://www.mosquitocatalog.org/files/pdfs/131700-25.PDF, accessed 29 Feb 2016.Thomas J. Zavortink. 1973. Mosquito Studies (Diptera, Culicidae) XXIX. A Review of the Subgenus ''Kerteszia'' of ''Anopheles''. ''Contrib. Amer. Ent. Inst.'', 9(3): 1-54; http://www.mosquitocatalog.org/files/pdfs/144600-7.pdf. Bionomics Subgenus ''Kerteszia'' immatures develop primarily in the water in bromeliads, and less often in bamboo.W. H. W. Komp. 1937. The Species of the Subgenus ''Kerteszia'' of ''Anopheles'' (Diptera, Culicidae). ''Annals of the Entomological Society of America'', XXX: 492-529; http://www.mosquitocatalog.org/files/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Vincent Theobald
Frederick Vincent Theobald FES (15 May 1868 – 6 March 1930) was an English entomologist and "distinguished authority on mosquitoes". During his career, he was responsible for the economic zoology section of the Natural History Museum, London, vice-principal of the South-Eastern Agricultural College at Wye, Kent, Professor of Agricultural Zoology at London University, and advisory entomologist to the Board of Agriculture for the South-Eastern district of England. He wrote a five volume monograph and sixty scientific papers on mosquitoes. He was recognised for his work in entomology, tropical medicine, and sanitation; awards for his work include the Imperial Ottoman Order of Osmanieh, the Mary Kingsley Medal, and the Victoria Medal of Honour, as well as honorary fellowships of learned societies. Life and career Frederick Vincent Theobald was born on 15 May 1868 in Tooting (then in Surrey), the son of solicitor John P. Theobald and Anne Theobald (née Mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Reed Biosystematics Unit
The Walter Reed Biosystematics Unit ("WRBU") is a US Army organization that conducts laboratory and field research on the systematics of medically important arthropods in support of epidemiological investigations and disease prevention and control strategies of importance to the military.Pollie L.M. Rueda and Rick Wilkerson (2007)“Know The Vector, Know The Threat” accessed Feb. 7, 2016.Walter Reed Biosystematics Unit accessed 17 Oct 2017. Research is carried out worldwide, within geographic or restrictions of the material available and military requirements. Research efforts focus on the development of accurate and reliable means of identifying [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
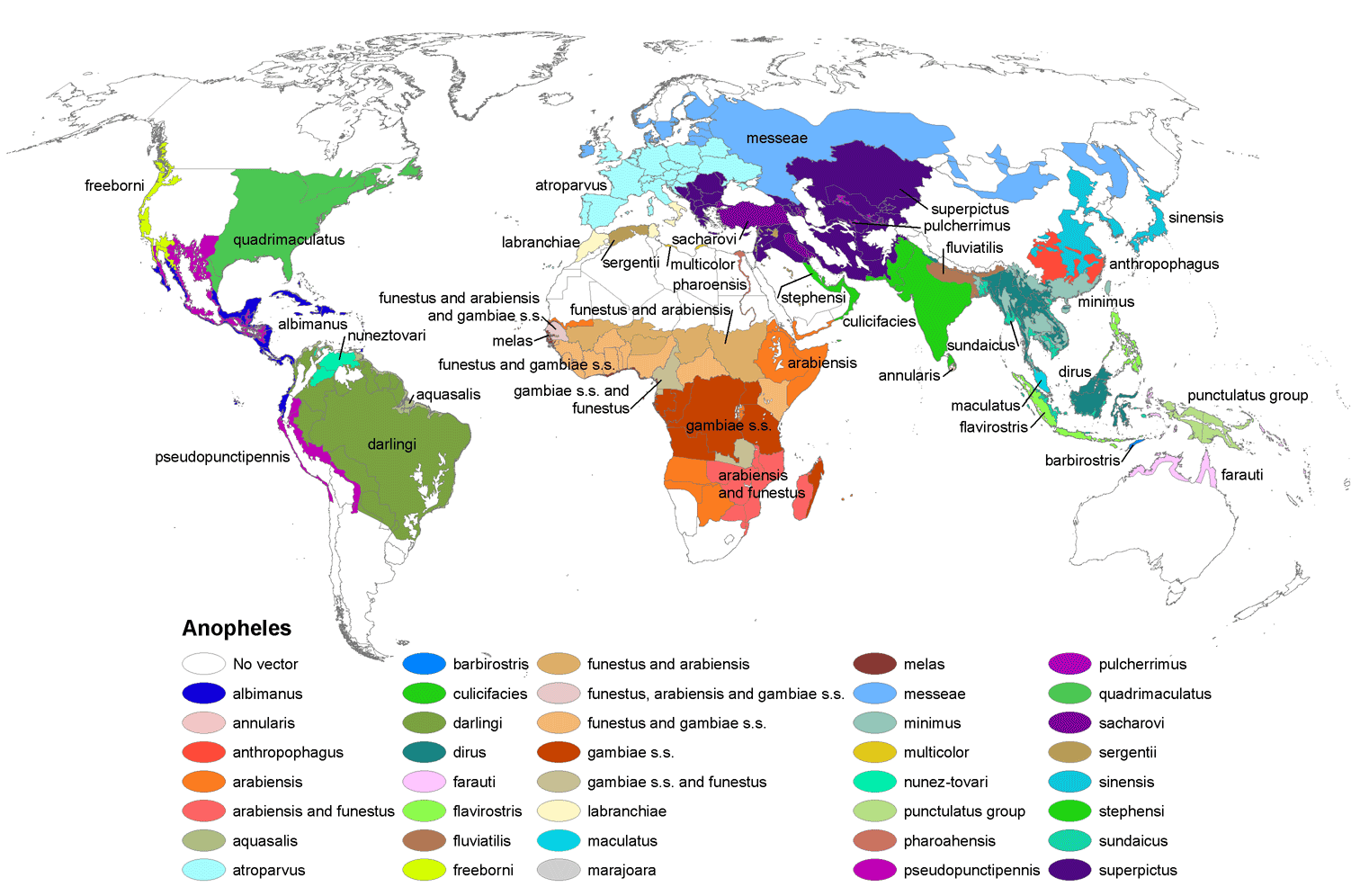
Anopheles Anoplus
''Anopheles'' () is a genus of mosquito first described by the German entomologist J. W. Meigen in 1818, and are known as nail mosquitoes and marsh mosquitoes. Many such mosquitoes are vectors of the parasite ''Plasmodium'', a genus of protozoans that cause malaria in birds, reptiles, and mammals, including humans. The ''Anopheles gambiae'' mosquito is the best-known species of marsh mosquito that transmits the ''Plasmodium falciparum'', which is a malarial parasite deadly to human beings; no other mosquito genus is a vector of human malaria. The genus ''Anopheles'' diverged from other mosquitoes approximately ( mya), and, like other mosquitoes, the eggs, larvae, and pupae are aquatic. The ''Anopheles'' larva has no respiratory siphon through which to breathe, so it breathes and feeds with its body horizontal to the surface of the water. The adult mosquito hatches from the surface and feeds on the nectar of flowers; the female mosquito also feeds on blood, which animal diet a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anopheles Cruzii
''Anopheles cruzii'' is the species of mosquito that mainly located in southern coast of Brazil, is main vector of malaria, ''Plasmodium vivax''. It has been going through microevolution Microevolution is the change in allele frequencies that occurs over time within a population. This change is due to four different processes: mutation, selection ( natural and artificial), gene flow and genetic drift. This change happens over ..., which appears in its wing-shape and is correlated with urbanization. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q13853984 Insects described in 1908 cruzii ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anopheles Boliviensis
''Anopheles'' () is a genus of mosquito first described by the German entomologist J. W. Meigen in 1818, and are known as nail mosquitoes and marsh mosquitoes. Many such mosquitoes are vectors of the parasite ''Plasmodium'', a genus of protozoans that cause malaria in birds, reptiles, and mammals, including humans. The ''Anopheles gambiae'' mosquito is the best-known species of marsh mosquito that transmits the ''Plasmodium falciparum'', which is a malarial parasite deadly to human beings; no other mosquito genus is a vector of human malaria. The genus ''Anopheles'' diverged from other mosquitoes approximately ( mya), and, like other mosquitoes, the eggs, larvae, and pupae are aquatic. The ''Anopheles'' larva has no respiratory siphon through which to breathe, so it breathes and feeds with its body horizontal to the surface of the water. The adult mosquito hatches from the surface and feeds on the nectar of flowers; the female mosquito also feeds on blood, which animal diet a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonym (taxonomy)
In taxonomy, the scientific classification of living organisms, a synonym is an alternative scientific name for the accepted scientific name of a taxon. The Botanical nomenclature, botanical and Zoological nomenclature, zoological codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In nomenclature, botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a Binomial nomenclature, scientific name that applies to a taxon that now goes by a different scientific name. For example, Carl Linnaeus, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, ''Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different Binomial nomenclature, binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |