|
Anna Eufrozyna Chodkiewicz
The House of Chodkiewicz (; ) was one of the most influential Szlachta, noble families of Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Lithuanian-Ruthenians, Ruthenian descent within the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in the 16th and 17th century.Chester S. L. Dunning, Caryl Emerson, Aleksandr Sergeevich Pushkin, ''The Uncensored Boris Godunov'', Univ of Wisconsin Press, 2007, SBN 0299207641Google Print, p. 498/ref> History Chodko Jurewicz, chamberlain to Grand Duke Vytenis, was probably the ancestor of the whole clan and gave it the name ''Chodkiewicz'', meaning "son of Chodzko". Surnames were not used in that time, but apparently later in history, the name ''Chodzko'' became a surname after Christianization of Chodzko Juriewicz, father of Iwan (later Jan) Chodkiewicz. They bore the Coat of arms of Chodkiewicz, Chodkiewicz coat of arms. In 1572, Jan Hieronimowicz Chodkiewicz converted from Calvinism to Roman Catholicism with his two sons, which made them the first polonization, Polonized gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calvinism
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed Christian, Presbyterian, Congregational, and Waldensians traditions, as well as parts of the Methodist, Anglican (known as "Episcopal" in some regions) and Baptist traditions. Reformed theology emphasizes the authority of the Bible and the sovereignty of God, as well as covenant theology, a framework for understanding the Bible based on God's covenants with people. Reformed churches emphasize simplicity in worship. Several forms of ecclesiastical polity are exercised by Reformed churches, including presbyterian, congregational, and some episcopal. Articulated by John Calvin, the Reformed faith holds to a spiritual (pneumatic) presence of Christ in the Lord's Supper. Emerging in the 16th century, the Reformed tradition developed over several genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Count
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York: Barnes & Noble, 1992. p. 73. . Especially in earlier medieval periods the term often implied not only a certain status, but also that the ''count'' had specific responsibilities or offices. The etymologically related English term " county" denoted the territories associated with some countships, but not all. The title of ''count'' is typically not used in England or English-speaking countries, and the term ''earl'' is used instead. A female holder of the title is still referred to as a ''countess'', however. Origin of the term The word ''count'' came into English from the French ', itself from Latin '—in its accusative form ''comitem''. It meant "companion" or "attendant", and as a title it indicated that someone was delegated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
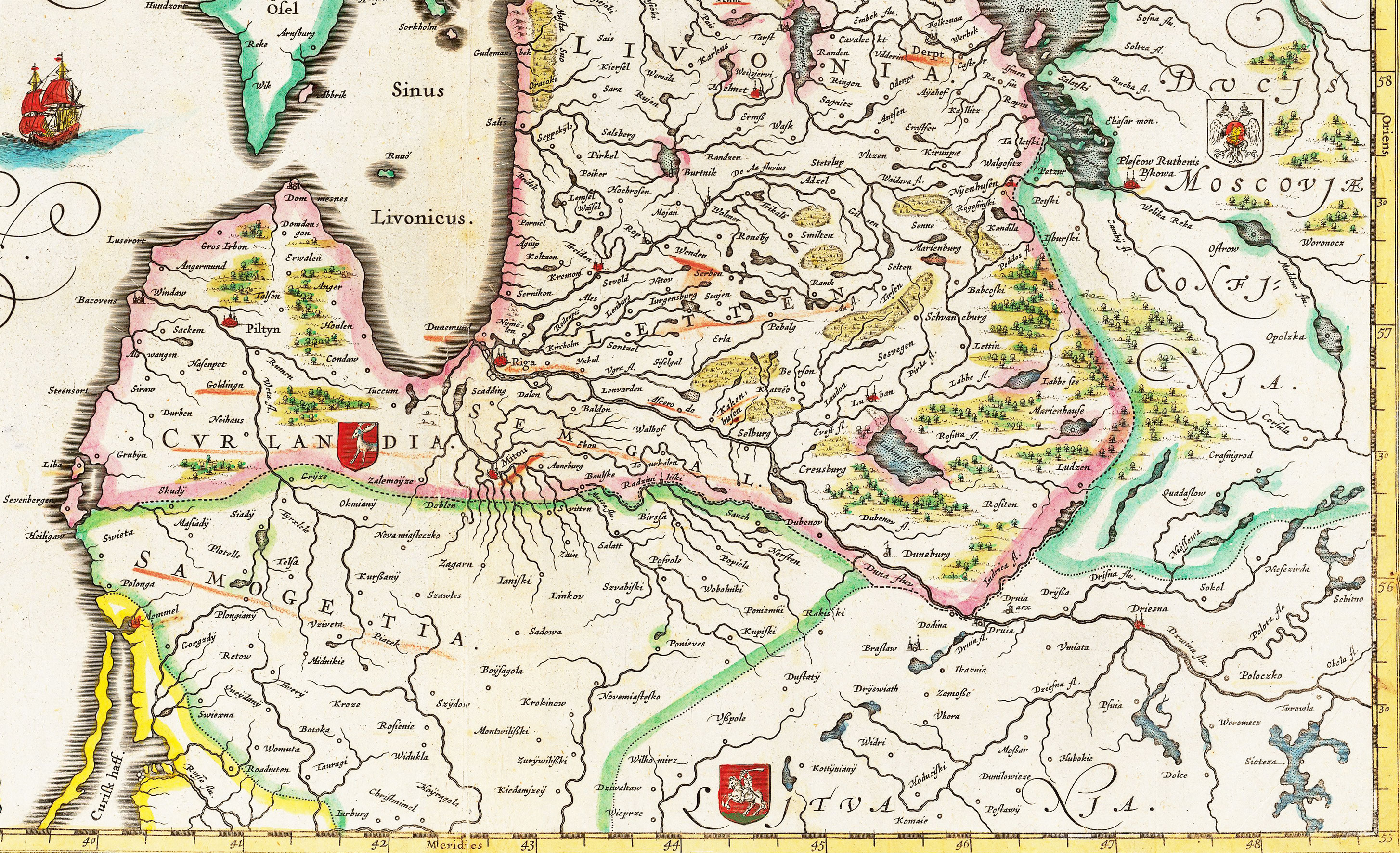
Elder Of Samogitia
The Duchy of Samogitia (, , ) was an administrative unit of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania from 1422 (and from 1569, a member country of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth). Between 1422 and 1441 it was known as the Eldership of Samogitia. Since the 1540s the Grand Duke of Lithuania also held the title of Duke of Samogitia, although the actual ruler of the province, responsible to the Grand Duke, was known as the General Elder () of Samogitia who was self-elected by the Samogitian nobility. The Duchy was located in the western part of the present Republic of Lithuania. Historically, in the west it had access to the Baltic Sea; in the north, it bordered the Duchy of Courland and Ducal Prussia in the south. During the Middle Ages and until the last partition in 1795, Samogitia had clearly defined borders as the Duchy of Samogitia. Afterwards the area encompassed the Samogitian Diocese. Today Samogitia is one of several ethnographic regions and is not defined administrativel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podczaszy
Deputy cup-bearer (, ) was since the 13th century a court office in Poland and later in Lithuania. Deputy cup-bearer was the deputy of the cup-bearer, but at the time was more important than his superior. Since the 14th–16th century an honorable court title and a district office in Crown of Poland and Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and later Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. * ''podczaszy wielki koronny'' – Great Royal Deputy Cup-bearer of the Crown * ''podczaszy wielki litewski'' – Great Royal Deputy Cup-bearer of Lithuania * ''podczaszy koronny'' – Royal Deputy Cup-bearer of the Crown * ''podczaszy litewski'' – Royal Deputy Cup-bearer of Lithuania * ''podczaszy ziemski'' – District Royal Deputy Cup-bearer See also *Offices in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth An office is a space where the employees of an organization perform administrative work in order to support and realize the various goals of the organization. The word "office" may also denote a position wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hieronim Chodkiewicz
Hieronim Chodkiewicz (; ca. 1515–1561) was a noble from the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, who was Elder of Samogitia from 1545 until his death. He was son of Aleksander and brother of Hrehory and Yurii Chodkiewiczs. Due to the political success of Chodkiewicz and his brothers, the Chodkiewicz family became the second wealthiest family in the Grand Duchy after the Radziwiłłs according to a military census of 1567 – a significant increase from the 1528 census when their father Alexander was 11th on the list. Chodkiewicz distanced himself from his Eastern Orthodox roots—he possibly converted to Catholicism around 1530 and to Lutheranism around 1550. Religion Traditional historiography usually states that Chodkiewicz was born around 1500. However, Lithuanian historian Genutė Kirkienė has noted that in such a case Chodkiewicz would have begun his political career in his mid-forties, when most nobles started in late twenties or early thirties. Kirkienė suggested that his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yurii Chodkiewicz
Knyaz Yurii Chodkiewicz (; c. 1515–1569) was a Lithuanian- Ruthenian noble, Bielsk starost in 1556, Puńsk starost in 1568, Great Master of the Pantry of Lithuania in 1554, Grand Krajczy of Lithuania in 1555, and Trakai castellan in 1566. He married Eugenia Hornostajowna before 1555 in Trakai. They had two children, Konstanty, born in Trakai in 1553, and Zofia, born in Zhytomir the following year. Eugenia died in 1557. In 1558, he married Princess Sophia Olelkovich-Slutska. She gave birth to Hieronim in 1560 in Vilnius, Halszka 1564 in Trakai, and Jerzy in 1570 in Žemaitkiemis. Ancestry See also * House of Chodkiewicz *Lithuanian nobility *Grand Duchy of Lithuania The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a sovereign state in northeastern Europe that existed from the 13th century, succeeding the Kingdom of Lithuania, to the late 18th century, when the territory was suppressed during the 1795 Partitions of Poland, ... {{DEFAULTSORT:Chodkiewicz, Yurii 151 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Marshal Of Lithuania
Grand may refer to: People with the name * Grand (surname) * Grand L. Bush (born 1955), American actor Places * Grand, Oklahoma, USA * Grand, Vosges, village and commune in France with Gallo-Roman amphitheatre * Grand County (other), several places * Grand Geyser, Upper Geyser Basin of Yellowstone, USA * Le Grand, California, USA; census-designated place * Mount Grand, Brockville, New Zealand Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Grand'' (Erin McKeown album), 2003 * "Grand" (Kane Brown song), 2022 * ''Grand'' (Matt and Kim album), 2009 * ''Grand'' (magazine), a lifestyle magazine related to related to grandparents * ''Grand'' (TV series), American sitcom, 1990 * Grand Production, Serbian record label company Other uses * Great Recycling and Northern Development Canal, also known as GRAND Canal * Grand (slang), one thousand units of currency * Giant Radio Array for Neutrino Detection, also known as GRAND See also * * * Grand Hotel (other) * Grand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nowogródek Voivodeship (1507–1795)
Nowogródek Voivodeship (; ; ; ) was a voivodeship of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania from 1507 to 1795, with the capital in the town of Nowogródek (now Novogrudok, Belarus). Since 1569 it was located in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, as part of Lithuania. History The Voivodeship was composed of three counties, Novogrudok, Vawkavysk, Slonim, as well as the Duchy of Slutsk. It had two senators, two deputies for the Sejm, and two deputies for the Lithuanian Tribunal. Its capital was the town of Nyazvizh with the Radziwiłł family's castle and treasury.Nowogrodek Voivodeship, description by Zygmunt Gloger. Geografia historyczna ziem dawnej Polski. Novogrudok Voivodeship ceased to exist along with the Pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voivode
Voivode ( ), also spelled voivod, voievod or voevod and also known as vaivode ( ), voivoda, vojvoda, vaivada or wojewoda, is a title denoting a military leader or warlord in Central, Southeastern and Eastern Europe in use since the Early Middle Ages. It primarily referred to the medieval rulers of the Romanian-inhabited states and of governors and military commanders of Poles, Hungarian, Lithuanian, Balkan, Russian people and other Slavic-speaking populations. In the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, ''voivode'' was interchangeably used with '' palatine''. In the Tsardom of Russia, a voivode was a military governor. Among the Danube principalities, ''voivode'' was considered a princely title. Etymology The term ''voivode'' comes from two roots. , means "war, fight," while , means "leading", thus in Old Slavic together meaning "war leader" or "warlord". The Latin translation is for the principal commander of a military force, serving as a deputy for the monarch. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Chodkiewicz
Ivan Chodkiewicz (; 1420 – 1484) was a Ruthenian nobility, Ruthenian noble from the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. He was a son of Chodko Jurewicz and ancestor of the Chodkiewicz family. Ivan married Jawnuta (Agnieszka) Belska, first cousin of Casimir IV Jagiellon. The marriage into the royal line helped him to obtain positions of starosta of Lutsk (1473) and voivode of Kiev (1480). During a Tatars, Tatar invasion in 1482, Ivan and his family were taken hostage. Ivan died in captivity while his wife, daughter Agrafena, and son Aleksander Chodkiewicz were ransomed and continued the family line. Biography Early life Traditionally, historiography states that Ivan Chodkiewicz first appears in written sources in 1453 as a member of a Lithuanian delegation sent to the Sejm of the Kingdom of Poland in Parczew. However, this note is based on an unreliable account by Albert Wijuk Kojałowicz. According to Lithuanian historian Genutė Kirkienė, the first reliable mention of Ivan was on 6 Jun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Count
Imperial Count (, ) was a title in the Holy Roman Empire. During the medieval era, it was used exclusively to designate the holder of an imperial county, that is, a fief held directly ( immediately) from the emperor, rather than from a prince who was a vassal of the emperor or of another sovereign, such as a duke or prince-elector. These imperial counts sat on one of the four "benches" of ''Counts'', whereat each exercised a fractional vote in the Imperial Diet until 1806. Imperial counts rank above counts elevated by lesser sovereigns. In the post–Middle Ages era, anyone granted the title of ''Count'' by the emperor in his specific capacity as ruler of the Holy Roman Empire (rather than, e.g. as ruler of Austria, Bohemia, Hungary, the Spanish Netherlands, etc.) became, ''ipso facto'', an "Imperial Count" (''Reichsgraf''), whether he reigned over an immediate county or not. Origins In the Merovingian and Franconian Empire, a ''Graf'' ("Count") was an official who exerci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |