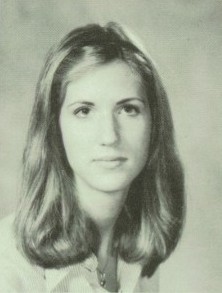|
Ann Coulter
Ann Hart Coulter (; born December 8, 1961) is an American conservative media pundit, author, syndicated columnist, and lawyer. She became known as a media pundit in the late 1990s, appearing in print and on cable news as an outspoken critic of the Clinton administration. Her first book concerned the impeachment of Bill Clinton and sprang from her experience writing legal briefs for Paula Jones's attorneys, as well as columns she wrote about the cases. Coulter's syndicated column for Universal Press Syndicate appears in newspapers and is featured on conservative websites. Coulter has also written 13 books. Early life Ann Hart Coulter was born on December 8, 1961, in New York City, to John Vincent Coulter (1926–2008), an FBI agent from a working class Catholic Irish American and German American familySmolenyak, Megan. in Albany, New York, and Nell Husbands Coulter (née Martin; 1928–2009), a homemaker who was born in Paducah, Kentucky. Coulter's mother's ancestry has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive with a respective county. The city is the geographical and demographic center of both the Northeast megalopolis and the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the United States by both population and urban area. New York is a global center of finance and commerce, culture, technology, entertainment and media, academics, and scientific output, the arts and fashion, and, as home to the headquarters of the United Nations, international diplomacy. With an estimated population in 2024 of 8,478,072 distributed over , the city is the most densely populated major city in the United States. New York City has more than double the population of Los Angeles, the nation's second-most populous city. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.Gerald O'Collins, O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical rites#Churches, ''sui iuris'' (autonomous) churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and Eparchy, eparchies List of Catholic dioceses (structured view), around the world, each overseen by one or more Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishops. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the Papal supremacy, chief pastor of the church. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
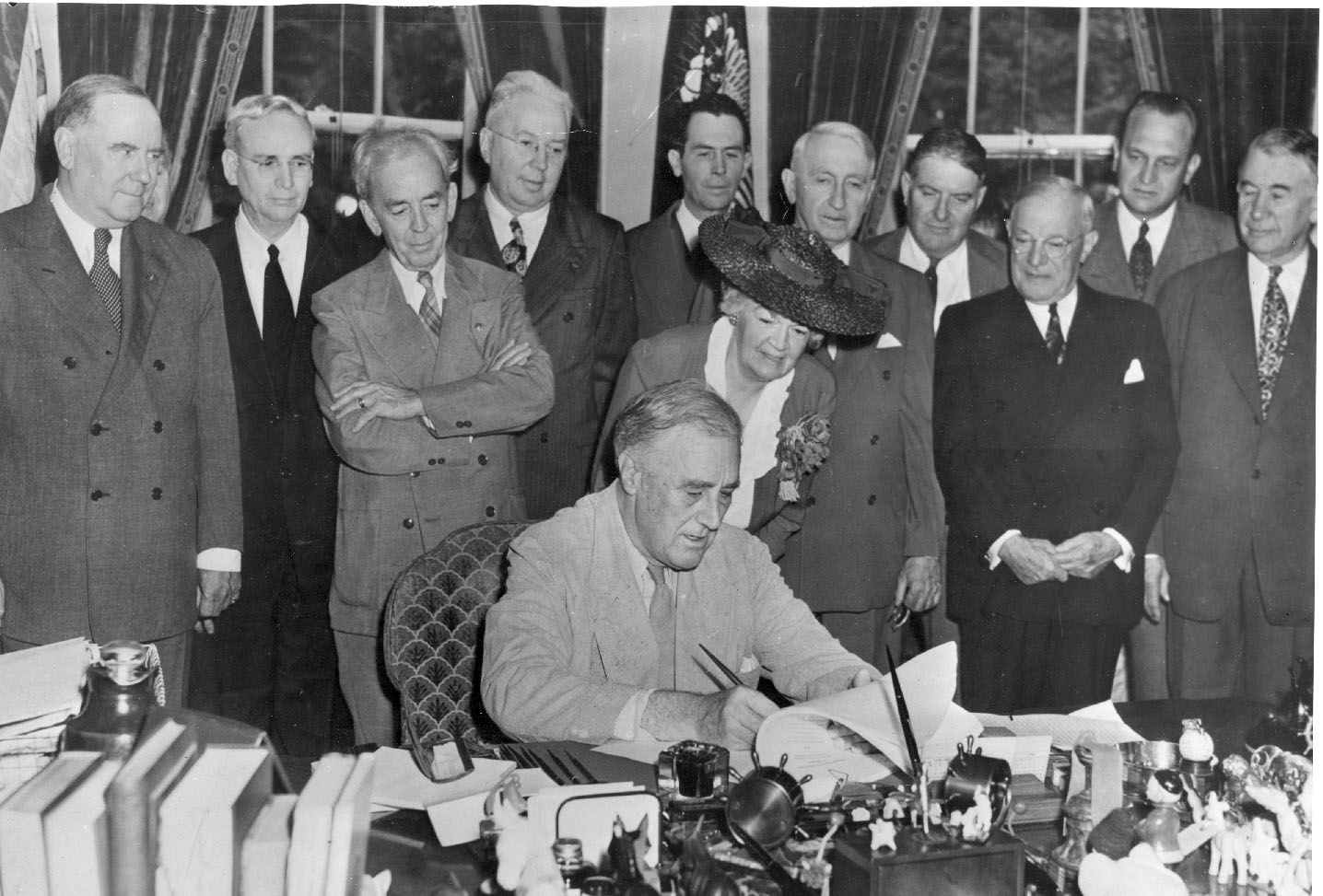
GI Bill
The G.I. Bill, formally the Servicemen's Readjustment Act of 1944, was a law that provided a range of benefits for some of the returning World War II veterans (commonly referred to as G.I.s). The original G.I. Bill expired in 1956, but the term "G.I. Bill" is still used to refer to programs created to assist American military veterans. It was largely designed and passed through Congress in 1944 in a bipartisan effort led by the American Legion, which wanted to reward practically all wartime veterans. John H. Stelle, a former Democratic governor of Illinois, served as the Chairman of the Legion's Executive Committee, which drafted and mobilized public opinion to get the G.I. Bill to President Roosevelt's desk on June 22, 1944. Stelle was rewarded for his efforts by the Legion which unanimously elected him its National Commander in 1945. He is commonly referred to as the "Father of the G.I. Bill." Since the First World War the Legion had been in the forefront of lobbying C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagman (rail)
On the railroads, a flagman is an employee of the railroad who is assigned to protect contractors or anyone performing work on a railroad right of way. A flagman is also assigned to protect a train that has stopped on a section of track. When a train approaches a location a flagman is posted, the train crew will have to get permission from the flagman to pass the area. Before the advent of automated level crossing gates, and still where automatic gates are not installed, flagmen were also assigned to protect the crossings. The flagman would stop road traffic from crossing the tracks as trains used the crossing. Additional information Rules pertaining to a flagman may vary depending on different railroad's operating rules. For instance on CSX Transportation a train approaching the work area is to call the flagman for permission through the work area. If workers are in the clear the flagman will advise crew to proceed and advise the crew that workers are not fouling the track. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Famine
The Great Famine, also known as the Great Hunger ( ), the Famine and the Irish Potato Famine, was a period of mass starvation and disease in Ireland lasting from 1845 to 1852 that constituted a historical social crisis and had a major impact on Irish society and history as a whole. The most severely affected areas were in the western and southern parts of Ireland—where the Irish language was dominant—hence the period was contemporaneously known in Irish as , which literally translates to "the bad life" and loosely translates to "the hard times". The worst year of the famine was 1847, which became known as "Black '47".Éamon Ó Cuív – the impact and legacy of the Great Irish Famine The population of Ireland on the eve of the famine was about 8.5 million; by 1901, it was just 4.4 million. During the Great Hunger, roughly 1 million people died and more than 1 million more Irish diaspora, fled the country, causing the country's population to fall by 20–25% between 184 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Hooker
Thomas Hooker (July 5, 1586 – July 7, 1647) was a prominent English colonial leader and Congregational church, Congregational minister, who founded the Connecticut Colony after dissenting with Puritan leaders in Massachusetts. He was known as an outstanding speaker and an advocate of universal Christian suffrage. Called today "the Father of Connecticut", Thomas Hooker was a towering figure in the early development of colonial New England. He was one of the great preachers of his time, an erudite writer on Christian subjects, the first minister of Cambridge, Massachusetts, and one of the first settlers and founders of both the city of Hartford and the state of Connecticut. He has been cited by many as the inspiration for the "Fundamental Orders of Connecticut", which some have described as the world's first written democratic constitution establishing a representative government. Life Early life Thomas Hooker was likely born in Leicestershire at "Marfield" (Marefield or p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Griffin (ship)
''Griffin'' was the name of a 17th-century ship known to have sailed between England and English settlements along Massachusetts Bay in British America. Several historical and genealogical references show ''Griffin'' making such journeys in 1633 and 1634. The 1633 journey left from Downs, England, and landed at Plymouth in Plymouth Colony on September 3. This 1633 journey carried religious dissidents, including Thomas Hooker, Samuel Stone, John Cotton, and others totaling 200 people. The ship ''Griffin'' weighed in at 300 tons and she saw the birth of at least one child, Seaborn Cotton, during the 1633 voyage. In 1634 ''Griffin'' carried Anne Hutchinson to the Massachusetts colony. Hutchinson's oldest son had preceded her the previous year, also on ''Griffin''. There are at least several other ships known to have used ''Griffin'' or similar names in preceding or following centuries. Most if not all such non-17th-century references probably refer to another vessel carrying t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British America
British America collectively refers to various British colonization of the Americas, colonies of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and its predecessors states in the Americas prior to the conclusion of the American Revolutionary War in 1783. The British monarchy of the Kingdom of England and Kingdom of Scotland—later named the Kingdom of Great Britain, of the British Isles and Western Europe—governed many colonies in the Americas beginning in 1585. From 1607, numerous permanent English settlements were made, ultimately reaching from Hudson Bay, to the Mississippi River and the Caribbean Sea. Much of these territories were occupied by Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous peoples, whose populations declined due to Epidemic, epidemics, wars, and massacres. In the Atlantic slave trade, England and other European empires shipped Africans to the Americas for labor in their colonies. Slavery became essential to colonial production, as on Barbados, Jamaica, and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plymouth Colony
Plymouth Colony (sometimes spelled Plimouth) was the first permanent English colony in New England from 1620 and the third permanent English colony in America, after Newfoundland and the Jamestown Colony. It was settled by the passengers on the '' Mayflower'' at a location that had previously been surveyed and named by Captain John Smith. The settlement served as the capital of the colony and developed as the town of Plymouth, Massachusetts. At its height, Plymouth Colony occupied most of what is now the southeastern portion of Massachusetts. Many of the people and events surrounding Plymouth Colony have become part of American folklore, including the American tradition of Thanksgiving and the monument of Plymouth Rock. Plymouth Colony was founded by a group of Protestant Separatists initially known as the Brownist Emigration, who came to be known as the Pilgrims. The colony established a treaty with Wampanoag chief Massasoit which helped to ensure its success; in this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Settler
A settler or a colonist is a person who establishes or joins a permanent presence that is separate to existing communities. The entity that a settler establishes is a Human settlement, settlement. A settler is called a pioneer if they are among the first settling at a place that is new to the settler community. The process of settling land can be, and has often been, controversial: while human migration is a normal phenomenon by itself, it has not been uncommon throughout human history for settlers to have arrived in already-inhabited lands Settler colonialism, without the intention of living alongside the native population. In these cases, the conflict that arises between the settlers and the natives (or Indigenous peoples) may result in the dispossession of the latter within the contested territory, usually violently. While settlers can act independently, they may receive support from the government of their country or colonial empire or from a non-governmental organization as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puritan
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to rid the Church of England of what they considered to be Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should become more Protestant. Puritanism played a significant role in English and early American history, especially in the Protectorate in Great Britain, and the earlier settlement of New England. Puritans were dissatisfied with the limited extent of the English Reformation and with the Church of England's religious toleration of certain practices associated with the Catholic Church. They formed and identified with various religious groups advocating greater purity of worship and doctrine, as well as personal and corporate piety. Puritans adopted a covenant theology, and in that sense they were Calvinists (as were many of their earlier opponents). In church polity, Puritans were divided between supporters of episcopal, presbyterian, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paducah, Kentucky
Paducah ( ) is a List of cities in Kentucky, home rule-class city in the Upland South, and the county seat of McCracken County, Kentucky, United States. The most populous city in the Jackson Purchase region, it is located in the Southeastern United States at the confluence of the Tennessee River, Tennessee and the Ohio River, Ohio rivers, halfway between St. Louis, St. Louis, Missouri, to the northwest and Nashville, Tennessee, to the southeast. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 27,137, up from 25,024 in 2010. Twenty blocks of the city's downtown have been designated as a historic district and listed on the National Register of Historic Places. Paducah is the principal city of the Paducah micropolitan area, Paducah metropolitan area, which includes McCracken, Ballard County, Kentucky, Ballard, Carlisle County, Kentucky, Carlisle and Livingston County, Kentucky, Livingston list of counties in Kentucky, counties in Kentucky and Massac County, Illin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |