|
Ann Baumgartner
Ann G. Baumgartner Carl (August 27, 1918 – March 20, 2008) was an American aviator who became the first American woman to fly a United States Army Air Forces jet aircraft when she flew the Bell YP-59A jet fighter at Wright Field as a test pilot during World War II. She was assigned to Wright Field as an assistant operations officer in the fighter test section as member of the Women Airforce Service Pilots program. Early life Ann G. Baumgartner was born in the United States Army Hospital in Augusta, Georgia, on August 27, 1918. Her father was stationed in France, so her mother moved the family to New Jersey to live with her grandparents. After her father returned to the United States, her family relocated to Plainfield, New Jersey. Her father was an engineer and patent attorney. Her inspiration to fly came from a visit by Amelia Earhart to her grade school. She went to Newark Airport with her father to watch the mail planes come in at night. Baumgartner graduated from Walnut H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine United States Minor Outlying Islands, Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in Compact of Free Association, free association with three Oceania, Pacific Island Sovereign state, sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Palau, Republic of Palau. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders Canada–United States border, with Canada to its north and Mexico–United States border, with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Airlines
Eastern Air Lines, also colloquially known as Eastern, was a major United States airline from 1926 to 1991. Before its dissolution, it was headquartered at Miami International Airport in an unincorporated area of Miami-Dade County, Florida. Eastern was one of the "Big Four" domestic airlines created by the Spoils Conferences of 1930, and was headed by World War I flying ace Eddie Rickenbacker in its early years. It had a near monopoly in air travel between New York and Florida from the 1930s until the 1950s and dominated this market for decades afterward. During airline deregulation in the late 1970s and early 1980s, labor disputes and high debt loads strained the company under the leadership of former astronaut Frank Borman. Frank Lorenzo acquired Eastern in 1985 and moved many of its assets to his other airlines, including Continental Airlines and Texas Air. After continued labor disputes and a crippling strike in 1989, Eastern ran out of money and was liquidated in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
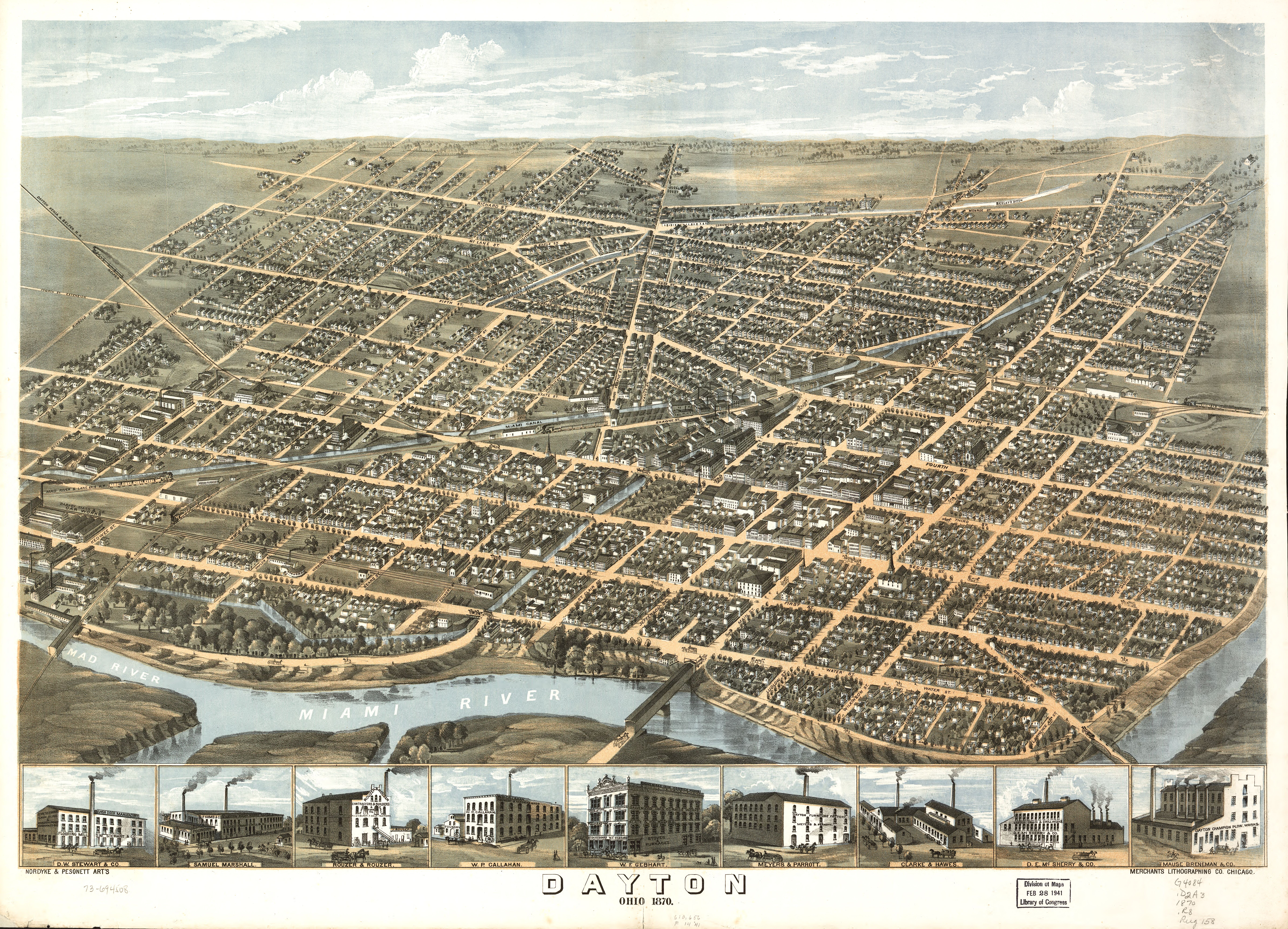
Dayton, Ohio
Dayton () is the sixth-largest city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Montgomery County. A small part of the city extends into Greene County. The 2020 U.S. census estimate put the city population at 137,644, while Greater Dayton was estimated to be at 814,049 residents. The Combined Statistical Area (CSA) was 1,086,512. This makes Dayton the fourth-largest metropolitan area in Ohio and 73rd in the United States. Dayton is within Ohio's Miami Valley region, north of the Greater Cincinnati area. Ohio's borders are within of roughly 60 percent of the country's population and manufacturing infrastructure, making the Dayton area a logistical centroid for manufacturers, suppliers, and shippers. Dayton also hosts significant research and development in fields like industrial, aeronautical, and astronautical engineering that have led to many technological innovations. Much of this innovation is due in part to Wright-Patterson Air Force Base and its place in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stinson L-5
The Stinson L-5 Sentinel is a World War II-era liaison aircraft used by the United States Army Air Forces, U.S. Army Ground Forces, U.S. Marine Corps and the British Royal Air Force. It was produced by the Stinson Division of the Vultee Aircraft Company (Consolidated-Vultee from mid-1943). Along with the Stinson L-1 Vigilant, the L-5 was the only other American liaison aircraft that was exclusively built for military use and had no civilian counterpart. Design and development The origins of the L-5 can be traced to the prewar civilian Stinson HW-75. This 75 horsepower civilian high-wing design was built by the Stinson Aircraft Company at Wayne, Michigan and first flew in 1939. It was marketed as the Model 105 and was first introduced to the public at the New York World's Fair. The three-place HW-75 featured two side-by-side seats and a third "jumpseat" in back on which a small passenger could sit facing sideways. Stylish, economical, spin resistant and easy to fly, the plane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cessna UC-78
The Cessna AT-17 Bobcat or Cessna Crane is a twin-engine advanced trainer aircraft designed and made in the United States, and used during World War II to bridge the gap between single-engine trainers and larger multi-engine combat aircraft. The commercial version was the Model T-50, from which the military versions were developed. Design and development In 1939, three years after Clyde Cessna Clyde Vernon Cessna (; December 5, 1879 – November 20, 1954) was an American aircraft designer, aviator, and early aviation entrepreneur. He is best known as the principal founder of the Cessna Aircraft Corporation, which he started in 1927 in ... retired, the Cessna T-50 made its first flight, becoming the company's first twin-engine airplane, and its first Landing gear, retractable undercarriage airplane. The prototype T-50 first flew on 26 March 1939,Wixley, 1984, p.13 and was issued Approved Type Certificate 722 on 24 March 1940.Juptner, 1994, pp.85-88 The AT-8, AT-17, C-78, UC- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
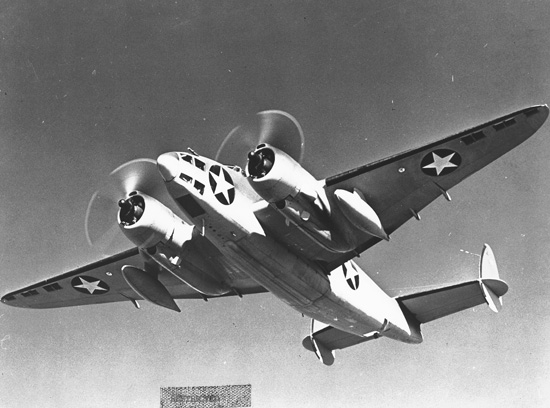
Lockheed B-34
The Lockheed Ventura is a twin-engine medium bomber and patrol bomber of World War II. The Ventura first entered combat in Europe as a bomber with the RAF in late 1942. Designated PV-1 by the United States Navy (US Navy), it entered combat in 1943 in the Pacific. The bomber was also used by the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF), which designated it the Lockheed B-34 (''Lexington'') and B-37 as a trainer. British Commonwealth forces also used it in several guises, including antishipping and antisubmarine search and attack. The Ventura was developed from the Lockheed Model 18 Lodestar transport, as a replacement for the Lockheed Hudson bombers then in service with the Royal Air Force. Used in daylight attacks against occupied Europe, they proved to have weaknesses and were removed from bomber duty and some used for patrols by Coastal Command. After USAAF monopolization of land-based bombers was removed, the US Navy ordered a revised design which entered service as the PV-2 H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curtiss A-25
The Curtiss SB2C Helldiver is a dive bomber developed by Curtiss-Wright during World War II. As a carrier-based bomber with the United States Navy (USN), in Pacific theaters, it supplemented and replaced the Douglas SBD Dauntless. A few survivors are extant. Initially poor handling characteristics and late modifications caused lengthy delays to production and deployment, to the extent that it was investigated by the Truman Committee, which turned in a scathing report. This contributed to the decline of Curtiss as a company. Neither pilots nor aircraft carrier skippers seemed to like it.Ethell 1995, p. 221. Nevertheless, the type was faster than the Dauntless, and by the end of the Pacific War, the Helldiver had become the main dive bomber and attack aircraft on USN carriers.Ethell 1995, p. 221. By the time a land-based variant, known as the A-25 Shrike, became available in late 1943, the Western Allied air forces had abandoned dedicated dive-bombers. A majority of A-25s deli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas A-24
The Douglas SBD Dauntless is a World War II American naval scout plane and dive bomber that was manufactured by Douglas Aircraft from 1940 through 1944. The SBD ("Scout Bomber Douglas") was the United States Navy's main carrier-based scout/dive bomber from mid-1940 through mid-1944. The SBD was also flown by the United States Marine Corps, both from land air bases and aircraft carriers. The SBD is best remembered as the bomber that delivered the fatal blows to the Japanese carriers at the Battle of Midway in June 1942.Parker, Dana T. ''Building Victory: Aircraft Manufacturing in the Los Angeles Area in World War II,'' pp. 25–34, Cypress, CA, 2013. . The type earned its nickname "Slow But Deadly" (from its SBD initials) during this period. During its combat service, the SBD proved to be an excellent naval scout plane and dive bomber. It possessed long range, good handling characteristics, maneuverability, potent bomb load, great diving characteristics from the perforated dive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and South Carolina to the south, and Tennessee to the west. In the 2020 census, the state had a population of 10,439,388. Raleigh is the state's capital and Charlotte is its largest city. The Charlotte metropolitan area, with a population of 2,595,027 in 2020, is the most-populous metropolitan area in North Carolina, the 21st-most populous in the United States, and the largest banking center in the nation after New York City. The Raleigh-Durham-Cary combined statistical area is the second-largest metropolitan area in the state and 32nd-most populous in the United States, with a population of 2,043,867 in 2020, and is home to the largest research park in the United States, Research Triangle Park. The earliest evidence of human occu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camp Davis
Marine Corps Outlying Field (MCOLF) Camp Davis is a military use airport northeast of the central business district of Holly Ridge, in Onslow County, North Carolina, United States. It is used as a training facility by the United States Marines of Camp Lejeune and Marine Corps Air Station New River. History In December 1940, Camp Davis was built by the United States Army as an anti-aircraft artillery training facility. Camp Davis was attached to the First Army, Fourth Corps Area and held a complement of about 20,000 officers and soldiers. It was an expansive facility consisting of more than 3,000 buildings on with access provided by newly built railroad spurs leading into the camp. Between 1942 and 1943, two paved runways were built for Camp Davis Army Air Field (AAF). Part of the runway for the airfield was built through one of the old Civil War fort's walls. Camp Davis AAF's Runway 5/23 was wider and was intended for use by transports, while Runway 19/01 was narrower a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by Measles morbillivirus, measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, Rhinitis, runny nose, and conjunctivitis, inflamed eyes. Small white spots known as Koplik's spots may form inside the mouth two or three days after the start of symptoms. A red, flat rash which usually starts on the face and then spreads to the rest of the body typically begins three to five days after the start of symptoms. Common complications include diarrhea (in 8% of cases), Otitis media, middle ear infection (7%), and pneumonia (6%). These occur in part due to measles-induced immunosuppression. Less commonly seizures, blindness, or encephalitis, inflammation of the brain may occur. Other names include ''morbilli'', ''rubeola'', ''red measles'', and ''English measles''. Both rubella, also known as ''German measl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houston, Texas
Houston (; ) is the most populous city in Texas, the most populous city in the Southern United States, the fourth-most populous city in the United States, and the sixth-most populous city in North America, with a population of 2,304,580 in 2020. Located in Southeast Texas near Galveston Bay and the Gulf of Mexico, it is the seat and largest city of Harris County and the principal city of the Greater Houston metropolitan area, which is the fifth-most populous metropolitan statistical area in the United States and the second-most populous in Texas after Dallas–Fort Worth. Houston is the southeast anchor of the greater megaregion known as the Texas Triangle. Comprising a land area of , Houston is the ninth-most expansive city in the United States (including consolidated city-counties). It is the largest city in the United States by total area whose government is not consolidated with a county, parish, or borough. Though primarily in Harris County, small portions o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)



