|
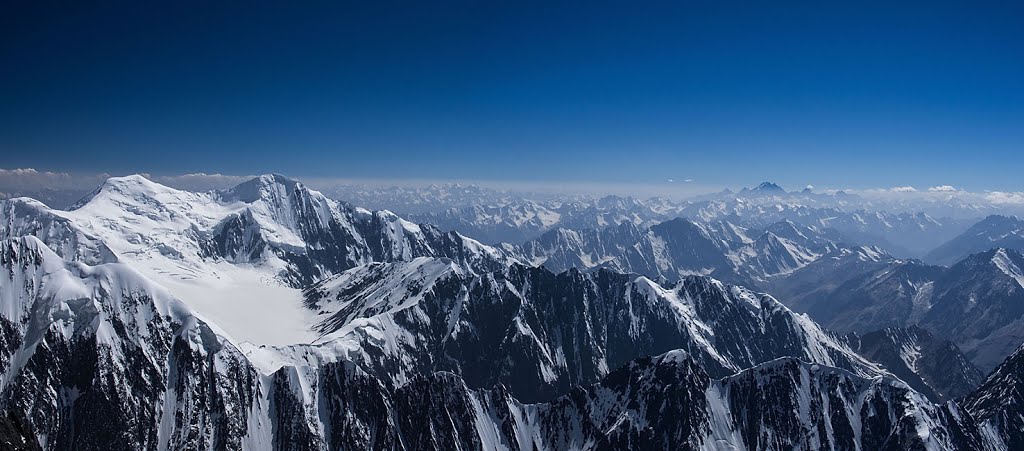
Anjuman Pass
The Anjuman Pass ( ''Kotal-e Anjoman'') (also written Anjoman Pass) (4,430 m) is a mountain pass in the Hindu Kush in Afghanistan. It connects the Panjshir Valley and beyond in the south-west with Badakhshan province and beyond to the north-east, which is the most north-easterly province of Afghanistan. The Anjuman Pass is located on Panjshir Province's border with Badakhshan and Takhar province Takhar (Dari/Pashto: ) is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan, located in the northeast of the country next to Tajikistan. It is surrounded by Badakhshan in the east, Panjshir in the south, and Baghlan and Kunduz in the west. The .... The climate in this area is usually cold with snow. The roads are narrow and slippery. References External links Lonely Planet Travel Guide (2007): ''Afghanistan''p. 166 Mountain passes of Afghanistan Landforms of Panjshir Province Landforms of Badakhshan Province {{Badakhshan-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Pass
A mountain pass is a navigable route through a mountain range or over a ridge. Since mountain ranges can present formidable barriers to travel, passes have played a key role in trade, war, and both Human migration, human and animal migration throughout history. At lower elevations it may be called a hill pass. A mountain pass is typically formed between two volcanic peaks or created by erosion from water or wind. Overview Mountain passes make use of a gap (landform), gap, saddle (landform), saddle, col or notch (landform), notch. A topographic saddle is analogous to the mathematical concept of a saddle surface, with a saddle point marking the minimum high point between two valleys and the lowest point along a ridge. On a topographic map, passes can be identified by contour lines with an hourglass shape, which indicates a low spot between two higher points. In the high mountains, a difference of between the summit and the mountain is defined as a mountain pass. Passes are o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in Central Asia, Central and South Asia to the west of the Himalayas. It stretches from central and eastern Afghanistan into northwestern Pakistan and far southeastern Tajikistan. The range forms the western section of the ''Hindu Kush Himalayan Region'' (''HKH''); to the north, near its northeastern end, the Hindu Kush buttresses the Pamir Mountains near the point where the borders of China, Pakistan and Afghanistan meet, after which it runs southwest through Pakistan and into Afghanistan near their border. The eastern end of the Hindu Kush in the north merges with the Karakoram Range. Towards its southern end, it connects with the White Mountains, Afghanistan, White Mountains near the Kabul River. It divides the valley of the Amu Darya (the ancient ''Oxus'') to the north from the Indus River valley to the south. The range has numerous high snow-capped peaks, with the highest point being Tirich Mir or Terichmir at in the Chitral District ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
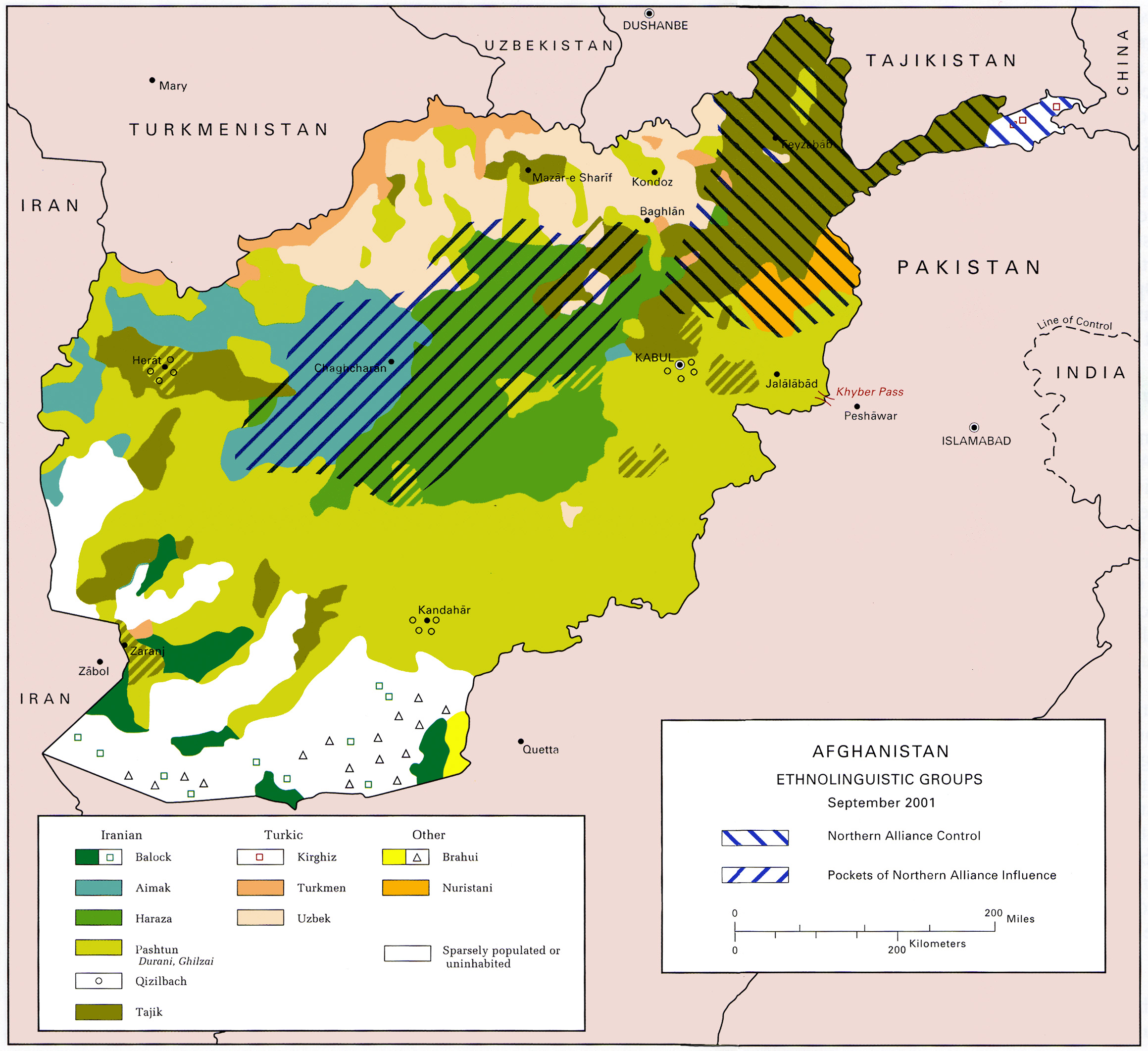
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran border, west, Turkmenistan to the Afghanistan–Turkmenistan border, northwest, Uzbekistan to the Afghanistan–Uzbekistan border, north, Tajikistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, northeast, and China to the Afghanistan–China border, northeast and east. Occupying of land, the country is predominantly mountainous with plains Afghan Turkestan, in the north and Sistan Basin, the southwest, which are separated by the Hindu Kush mountain range. Kabul is the country's capital and largest city. Demographics of Afghanistan, Afghanistan's population is estimated to be between 36 and 50 million. Ancient history of Afghanistan, Human habitation in Afghanistan dates to the Middle Paleolithic era. Popularly referred to as the graveyard of empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Badakhshan Province
Badakhshan Province (Dari: بدخشان) is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, located in the northeastern part of the country. It is bordered by Tajikistan's Gorno-Badakhshan in the north and the Pakistani regions of Lower and Upper Chitral and Gilgit-Baltistan in the southeast. The province also has Afghanistan's only border with China spanning 91 kilometers (57 miles) in the eastern side of the province via its Wakhan District. It is part of a broader historical Badakhshan region, parts of which now also lie in Tajikistan and China. The province contains 22 districts, over 1,200 villages and approximately 1,055,000 people. Fayzabad serves as the provincial capital. Resistance activity has been reported in the province since the 2021 Taliban takeover of Afghanistan. Etymology During the Sassanids' reign it was called "bidix", and in Parthian times "bthšy". In Sassanid manuscripts found in Ka'ba-ye Zartosht it was called "Bałasakan". In Chinese sources fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panjshir Province
Panjshir (Dari: , literally "Five Lions," pronounced /pand͡ʒʃeːɾ/, also spelled as Panjsher) is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan, located in the northeastern part of the country containing the Panjshir Valley. The province is divided into seven districts and contains 512 villages. The main inhabitants of the province are Tajiks Shamali, who speak Persian language. As of 2021, the population of Panjshir province was about 334,940. Its current governor is Mohammad Agha Hakim. Panjshir became an independent province from neighboring Parwan Province in 2004. It is bordered by Baghlan and Takhar in the north, Badakhshan and Nuristan in the east, Laghman and Kapisa in the south, and Parwan in the west. History The territory fell to Babur in the early 16th century. It was later conquered by Ahmad Shah Durrani, and officially became part of the Durrani Empire. The rule of the Durranis was followed by that of the Barakzai dynasty. During th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Takhar Province
Takhar (Dari/Pashto: ) is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan, located in the northeast of the country next to Tajikistan. It is surrounded by Badakhshan in the east, Panjshir in the south, and Baghlan and Kunduz in the west. The city of Taloqan serves as its capital. The province contains 17 districts, over 1,000 villages, and approximately 1,113,173 people, which is multi-ethnic and mostly a rural society. History Early history 7th to 16th centuries 16th to 20th centuries Between the early 16th century and the mid-18th century, the territory was ruled by the Khanate of Bukhara. It was given to Ahmad Shah Durrani by Murad Beg of Bukhara after a treaty of friendship was reached in or about 1750, and became part of the Durrani Empire. It was ruled by the Durranis followed by the Barakzai dynasty and was untouched by the British during the three Anglo-Afghan wars that were fought in the 19th and early 20th centuries. 1964–2001 It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Passes Of Afghanistan
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and climate, mountains t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Panjshir Province
A landform is a land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. They may be natural or may be anthropogenic (caused or influenced by human activity). Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great oceanic basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, structure stratification, rock exposure, and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, cliffs, hills, mounds, peninsulas, ridges, rivers, valleys, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |