|
Aniseikonia
Aniseikonia is an ocular condition where there is a significant difference in the perceived size of images. It can occur as an overall difference between the two eyes, or as a difference in a particular meridian. If the ocular image size in both eyes are equal, the condition is known as ''iseikonia''. Symptoms and signs Up to 7% difference in image size is well tolerated. If magnification difference becomes excessive the effect can cause diplopia, suppression, disorientation, eyestrain, headache, and dizziness and balance disorders. Asthenopic symptoms alone may occur even if image size difference is less than 7%. Causes Retinal image size is determined by many factors. The size and position of the object being viewed affects the characteristics of the light entering the system. Corrective lenses affect these characteristics and are used commonly to correct refractive error. The optics of the eye including its refractive power and axial length also play a major role in retinal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anisometropia
Anisometropia is a condition in which a person's eyes have substantially differing refractive power. Generally, a difference in power of one diopter (1D) is the threshold for diagnosis of the condition. Patients may have up to 3 diopters of anisometropia before the condition becomes clinically significant due to headache, eye strain, double vision or photophobia. In certain types of anisometropia, the visual cortex of the brain cannot process images from both eyes simultaneously (binocular summation), but will instead suppress the central vision of one of the eyes. If this occurs too often during the first 10 years of life, while the visual cortex is developing, it can result in amblyopia, a condition where, even when correcting the refractive error properly, the person's vision in the affected eye may still not be fully correctable to 20/20. The name of the condition comes from its four Greek components: ''an-'' "not", ''iso-'' "same", ''metr-'' "measure", ''ops'' "eye". Antim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimetropia
Anisometropia is a condition in which a person's eyes have substantially differing refractive power. Generally, a difference in power of one diopter (1D) is the threshold for diagnosis of the condition. Patients may have up to 3 diopters of anisometropia before the condition becomes clinically significant due to headache, eye strain, double vision or photophobia. In certain types of anisometropia, the visual cortex of the brain cannot process images from both eyes simultaneously (binocular summation), but will instead suppress the central vision of one of the eyes. If this occurs too often during the first 10 years of life, while the visual cortex is developing, it can result in amblyopia, a condition where, even when correcting the refractive error properly, the person's vision in the affected eye may still not be fully correctable to 20/20. The name of the condition comes from its four Greek components: ''an-'' "not", ''iso-'' "same", ''metr-'' "measure", ''ops'' "eye". Antime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anisometropia
Anisometropia is a condition in which a person's eyes have substantially differing refractive power. Generally, a difference in power of one diopter (1D) is the threshold for diagnosis of the condition. Patients may have up to 3 diopters of anisometropia before the condition becomes clinically significant due to headache, eye strain, double vision or photophobia. In certain types of anisometropia, the visual cortex of the brain cannot process images from both eyes simultaneously (binocular summation), but will instead suppress the central vision of one of the eyes. If this occurs too often during the first 10 years of life, while the visual cortex is developing, it can result in amblyopia, a condition where, even when correcting the refractive error properly, the person's vision in the affected eye may still not be fully correctable to 20/20. The name of the condition comes from its four Greek components: ''an-'' "not", ''iso-'' "same", ''metr-'' "measure", ''ops'' "eye". Antim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epiretinal Membrane
Epiretinal membrane or macular pucker is a disease of the eye in response to changes in the vitreous humor or more rarely, diabetes. Sometimes, as a result of immune system response to protect the retina, cells converge in the macular area as the vitreous ages and pulls away in posterior vitreous detachment (PVD). PVD can create minor damage to the retina, stimulating exudate, inflammation, and leucocyte response. These cells can form a transparent layer gradually and, like all scar tissue, tighten to create tension on the retina which may bulge and pucker, or even cause swelling or macular edema. Often this results in distortions of vision that are clearly visible as bowing and blurring when looking at lines on chart paper (or an Amsler grid) within the macular area, or central 1.0 degree of visual arc. Usually it occurs in one eye first, and may cause binocular diplopia or double vision if the image from one eye is too different from the image of the other eye. The dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suppression (eye)
Suppression of an eye is a subconscious adaptation by a person's brain to eliminate the symptoms of disorders of binocular vision such as strabismus, convergence insufficiency and aniseikonia. The brain can eliminate double vision by ignoring all or part of the image of one of the eyes. The area of a person's visual field that is suppressed is called the suppression scotoma (with a scotoma meaning, more generally, an area of partial alteration in the visual field). Suppression can lead to amblyopia. Effect Nobel-prize winner David H. Hubel described suppression in simple terms as follows: :"Suppression is familiar to anyone who has trained himself to look through a monocular microscope, sight a gun, or do any other strictly one-eye task, with the other eye open. The scene simply disappears for the suppressed eye."David H. Hubel: ''Eye, Brain, and Vision'', Chapter 9 "Deprivation and development"section "Strabismus" Published online by Harvard Medical School (downloaded 30 Septembe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Error
Refractive error is a problem with focus (optics), focusing light accurately on the retina due to the shape of the eye and/or cornea. The most common types of refractive error are myopia, near-sightedness, hyperopia, far-sightedness, astigmatism, and presbyopia. Near-sightedness results in far away objects being blurred vision, blurry, far-sightedness and presbyopia result in close objects being blurry, and astigmatism causes objects to appear stretched out or blurry. Other symptoms may include double vision, headaches, and eye strain. Near-sightedness is due to the length of the eyeball being too long; far-sightedness the eyeball too short; astigmatism the cornea being the wrong shape, while presbyopia results from aging of the lens of the eye such that it cannot change shape sufficiently. Some refractive errors occur more often among those whose parents are affected. Diagnosis is by eye examination. Refractive errors are corrected with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or surgery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intraocular Lens
An intraocular lens (IOL) is a lens (optics), lens implanted in the human eye, eye usually as part of a treatment for cataracts or for correcting other vision problems such as myopia, near-sightedness (myopia) and farsightedness, far-sightedness (hyperopia); a form of refractive surgery. If the natural lens is left in the eye, the IOL is known as Phakic intraocular lens, ''phakic'', otherwise it is a ''pseudophakic'' lens (or false lens). Both kinds of IOLs are designed to provide the same light-focusing function as the natural crystalline lens. This can be an alternative to LASIK, but LASIK is not an alternative to an IOL for treatment of cataracts. IOLs usually consist of a small plastic lens with plastic side struts, called haptics, to hold the lens in place in the capsular bag inside the eye. IOLs were originally made of a rigid material (Poly(methyl methacrylate), PMMA), although this has largely been superseded by the use of flexible materials, such as silicone. Most IOLs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
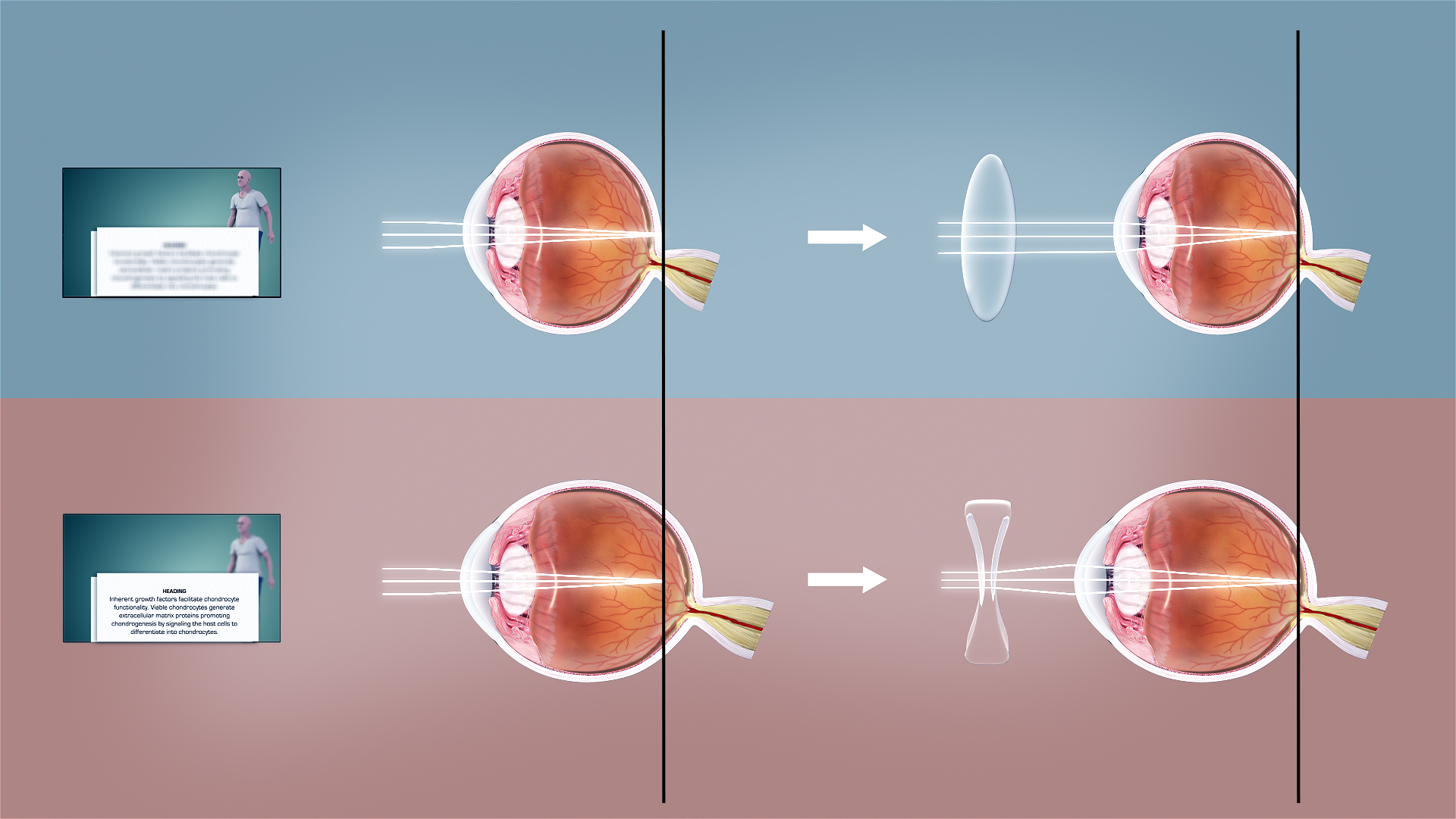
Corrective Lens
A corrective lens is a transmissive optical device that is worn on the eye to improve visual perception. The most common use is to treat refractive errors: myopia, hypermetropia, astigmatism, and presbyopia. Glasses or "spectacles" are worn on the face a short distance in front of the eye. Contact lenses are worn directly on the surface of the eye. Intraocular lenses are surgically implanted most commonly after cataract removal but can be used for purely refractive purposes. Prescription of corrective lenses Corrective lenses are typically prescribed by an ophthalmologist or an optometrist. The prescription consists of all the specifications necessary to make the lens. Prescriptions typically include the power specifications of each lens (for each eye). Strengths are generally prescribed in quarter- diopter steps (0.25 D), because most people cannot generally distinguish between smaller increments (e.g., eighth-diopter steps / 0.125 D). The use of improper corr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center Thickness
Center or centre may refer to: Mathematics *Center (geometry), the middle of an object * Center (algebra), used in various contexts ** Center (group theory) ** Center (ring theory) * Graph center, the set of all vertices of minimum eccentricity * Central tendency, measures of the central tendency (center) in a set of data Places United States * Centre, Alabama * Center, Colorado * Center, Georgia * Center, Indiana * Center, Warrick County, Indiana * Center, Kentucky * Center, Missouri * Center, Nebraska * Center, North Dakota * Centre County, Pennsylvania * Center, Portland, Oregon * Center, Texas * Center, Washington * Center, Outagamie County, Wisconsin * Center, Rock County, Wisconsin **Center (community), Wisconsin *Center Township (other) *Centre Township (other) *Centre Avenue (other) *Center Hill (other) Other countries * Centre region, Hainaut, Belgium * Centre Region, Burkina Faso * Centre Region (Cameroon) * Centre-Val de Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertex Distance
Vertex distance is the distance between the back surface of a corrective lens, i.e. glasses (spectacles) or contact lenses, and the front of the cornea. Increasing or decreasing the vertex distance changes the optical properties of the system, by moving the focal point forward or backward, effectively changing the power of the lens relative to the eye. Since most refractions (the measurement that determines the power of a corrective lens) are performed at a vertex distance of 12–14 mm, the power of the correction may need to be modified from the initial prescription so that light reaches the patient's eye with the same effective power that it did through the phoropter or trial frame. Vertex distance is important when converting between contact lens and glasses prescriptions and becomes significant if the glasses prescription is beyond ±4.00 diopters (often abbreviated D). The formula for vertex correction is F_c = \left(F^ - x\right)^, where F is the power corrected for v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
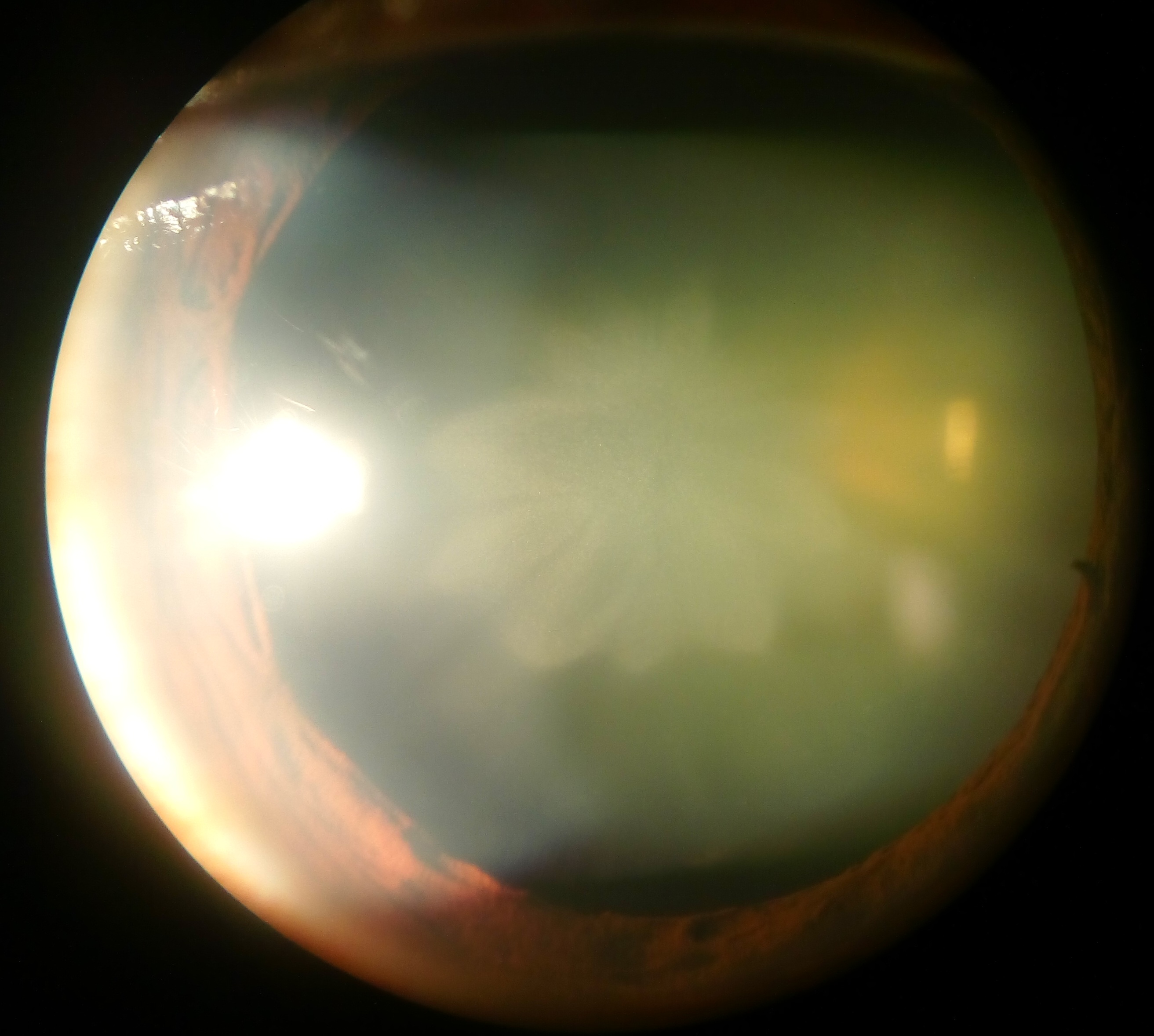
Cataract
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens (anatomy), lens of the eye that leads to a visual impairment, decrease in vision of the eye. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colours, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble with bright lights, and Nyctalopia, difficulty seeing at night. This may result in trouble driving, reading, or recognizing faces. Poor vision caused by cataracts may also result in an increased risk of Falling (accident), falling and Depression (mood), depression. Cataracts cause 51% of all cases of blindness and 33% of visual impairment worldwide. Cataracts are most commonly due to senescence, aging but may also occur due to Trauma (medicine), trauma or radiation exposure, be congenital cataract, present from birth, or occur following eye surgery for other problems. Risk factors include diabetes mellitus, diabetes, longstanding use of corticosteroid medication, smoking tobacco, prolonged exposu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |