|
Anglo America (centered Orthographic Projection)
Anglo-America most often refers to a region in the Americas in which International English, English is the main language and culture of the United Kingdom, British culture and the British Empire have had significant historical, ethnic, linguistic, and cultural impact."Anglo-America", vol. 1, Micropædia, ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', 15th ed., Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., 1990. . This includes the United States, most of Canada, and some Caribbean countries. Anglo-America is distinct from Latin America, a region of the Americas where Romance languages (e.g., Spanish America, Spanish, Portuguese America, Portuguese, and French America, French) are prevalent. The adjective is commonly used, for instance, in the phrase "Anglo-American law", a concept roughly coterminous with Common Law. Geographic region While Canada is one of the two principal Anglo-American countries, the province of Quebec and the region of Inuit Nunangat both have non-English speaking majorities, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
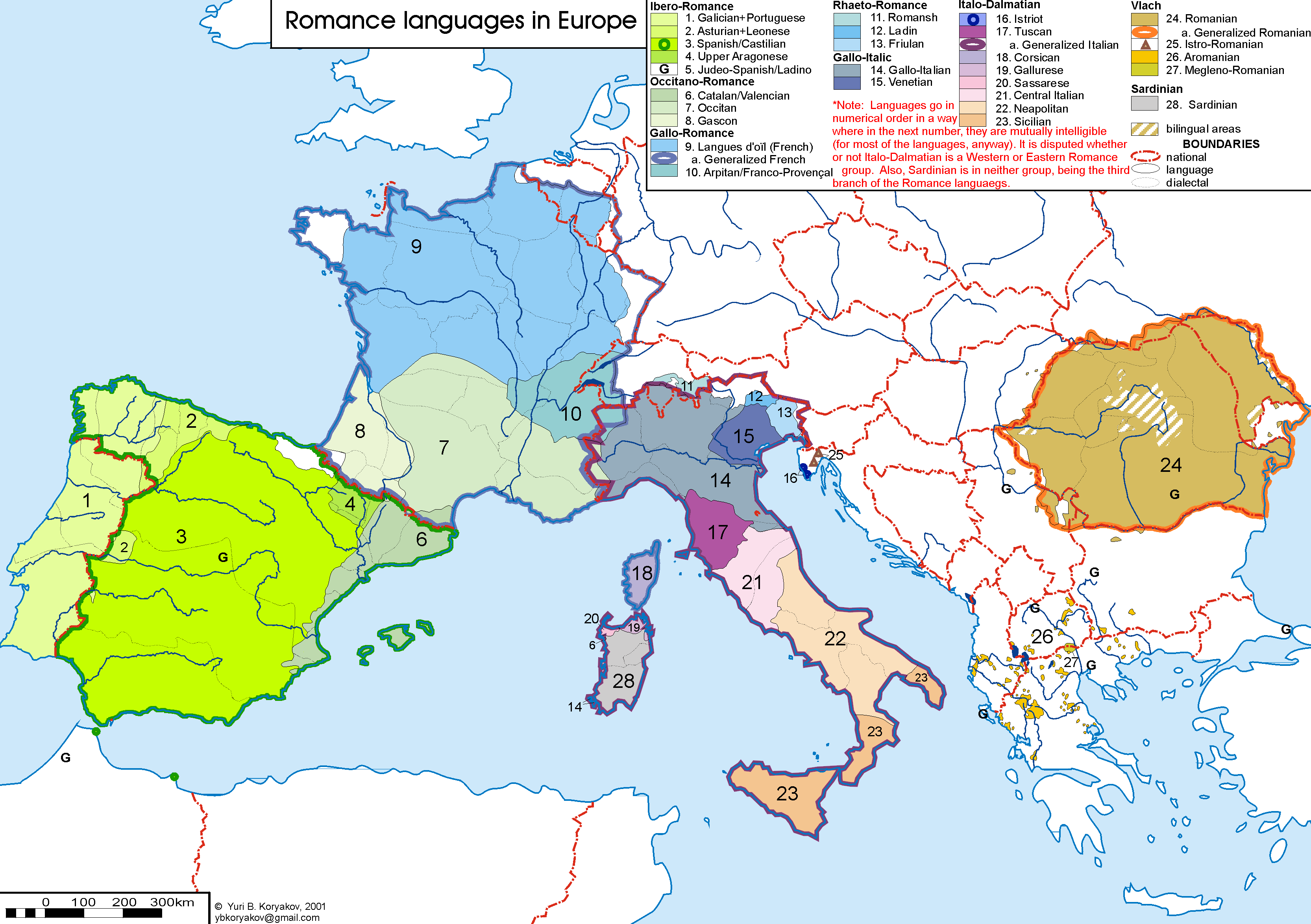
Romance Languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. The five list of languages by number of native speakers, most widely spoken Romance languages by number of native speakers are: * Spanish language, Spanish (489 million): official language in Spain, Mexico, Equatorial Guinea, the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, SADR, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico and most of Central America, Central and South America * French language, French (310 million): official in 26 countries * Portuguese language, Portuguese (240 million): official in Portugal, Brazil, Portuguese-speaking African countries, Portuguese-speaking Africa, Timor-Leste and Macau * Italian language, Italian (67 million): official in Italy, Vatican City, San Marino, Switzerland; mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cayman Islands
The Cayman Islands () is a self-governing British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory, and the largest by population. The territory comprises the three islands of Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac and Little Cayman, which are located south of Cuba and north-east of Honduras, between Jamaica and Mexico's Yucatán Peninsula. The capital city is George Town, Cayman Islands, George Town on Grand Cayman, which is the most populous of the three islands. The Cayman Islands is considered to be part of the geographic Western Caribbean zone as well as the Greater Antilles. The territory is a major offshore financial centre for international businesses and High-net-worth individual, the rich mainly due to the state charging no tax on income earned or stored. With a GDP per capita of US$97,750 in 2023, the Cayman Islands has the highest standard of living in the Caribbean, and one of the highest in the world. Immigrants from over 140 countries and territories reside in the Cayman I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Virgin Islands
The British Virgin Islands (BVI), officially the Virgin Islands, are a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean, to the east of Puerto Rico and the United States Virgin Islands, US Virgin Islands and north-west of Anguilla. The islands are geographically part of the Virgin Islands, Virgin Islands archipelago and are located in the Leeward Islands of the Lesser Antilles and part of the West Indies. The British Virgin Islands consist of the main islands of Tortola, Virgin Gorda, Anegada and Jost Van Dyke, along with more than 50 other smaller islands and cays. About 16 of the islands are inhabited. The capital, Road Town, is on Tortola, the largest island, which is about long and wide. The islands had a population of 28,054 at the 2010 Census, of whom 23,491 lived on Tortola; current estimates put the population at 35,802 (July 2018). The economy of the territory is overwhelmingly dominated by tourism and financial services. In terms of financi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bermuda
Bermuda is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean. The closest land outside the territory is in the American state of North Carolina, about to the west-northwest. Bermuda is an archipelago consisting of List of islands of Bermuda, 181 islands, although the most significant islands are connected by bridges and appear to form one landmass. It has a land area of . Bermuda has a tropical climate, with warm winters and hot summers. Its climate also exhibits Oceanic climate, oceanic features similar to other coastal areas in the Northern Hemisphere with warm, moist air from the ocean ensuring relatively high humidity and stabilising temperatures. Bermuda is prone to severe weather from Westerlies#Interaction with tropical cyclones, recurving tropical cyclones; however, it receives some protection from a coral reef and its position north of the Main Development Region, which limits the direction and severity of approach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anguilla
Anguilla is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is one of the most northerly of the Leeward Islands in the Lesser Antilles, lying east of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands and directly north of Saint Martin (island), Saint Martin. The territory consists of the main island of Anguilla, approximately long by wide at its widest point, together with a number of much smaller islands and cays with no permanent population. The territory's capital is The Valley, Anguilla, The Valley. The total land area of the territory is , with a population of approximately (). Etymology The native Arawak name for the island was ''Malliouhana''. In reference to the island's shape, the Italian ', meaning "eel" (in turn, from the Latin diminutive of ''anguis'', "snake") was used as its name. Anguillan tradition holds that Christopher Columbus named the island. History Anguilla was first settled by Indigenous Amerindian peoples who migrated from S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of The Netherlands
The Kingdom of the Netherlands (, ;, , ), commonly known simply as the Netherlands, is a sovereign state consisting of a collection of constituent territories united under the monarch of the Netherlands, who functions as head of state. The realm is not a federation; it is a unitary monarchy with its largest subdivision, the eponymous Netherlands, predominantly located in Northwestern Europe and with several smaller island territories located in the Caribbean. The four subdivisions of the Kingdom— Aruba, Curaçao, the Netherlands, and Sint Maarten—are constituent countries ( in Dutch; singular: ) and participate on a basis of equality as partners in the Kingdom. In practice, however, most of the Kingdom's affairs are administered by the Netherlands—which comprises roughly 98% of the Kingdom's land area and population—on behalf of the entire Kingdom. Consequently, Aruba, Curaçao, and Sint Maarten are dependent on the Netherlands for matters like foreign policy and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Body (Netherlands)
In the Netherlands, the term public body (a literal translation from the Dutch language, Dutch term ) is the general denomination for administrative divisions within the Dutch state, such as the central government, a province, a municipality or a water board (Netherlands), water board. These types of political entities are defined by the Constitution of the Netherlands. In addition, Article 134 of the constitution provides for the definition of other public bodies by law. Such bodies can be professionally oriented, like the ''Dutch Order of Advocates'' (), or be constituted to perform functions in a specific region. This means that the term public body is sometimes used to indicate a special or irregular type of public body (without a specifically defined name), which can also be an administrative division or a certain other type of governmental organisation. Caribbean Netherlands After the dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles on October 10, 2010, the three islands of Bonaire, S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saba (island)
Saba is a Caribbean island and the smallest Caribbean Netherlands, special municipality (officially "Public body (Netherlands), public body") of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands. It consists largely of the dormant volcano Mount Scenery, which at is the highest point of the entire Kingdom of the Netherlands. The island lies in the northern Leeward Islands portion of the West Indies, southeast of the Virgin Islands. Together with Bonaire and Sint Eustatius it forms the Caribbean Netherlands, BES islands, also known as the Caribbean Netherlands. Saba has a land area of . The population was 2,158 in January 2025, with a population density of . It is the smallest territory by permanent population in the Americas. Its towns and major settlements are The Bottom (the capital), Windwardside, Zion's Hill, and St. Johns, Saba, St. Johns. Etymology Theories about the origin of Saba's name include ''List of indigenous names of Eastern Caribbean islands#Leeward Islands, siba'' (t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sint Maarten
Sint Maarten () is a Countries of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands located in the Caribbean region of North America. With a population of 58,477 as of June 2023 on an area of , it encompasses the southern 44% of the divided island of Saint Martin (island), Saint Martin, while the northern 56% of the island constitutes the French overseas collectivity of Collectivity of Saint Martin, Saint Martin. Sint Maarten's Capital city, capital is Philipsburg, Sint Maarten, Philipsburg. Collectively, Sint Maarten and the other List of islands of the Netherlands, Dutch islands in the Caribbean are often called the Dutch Caribbean. Before 10 October 2010, Sint Maarten was known as the Island Territory of Sint Maarten (), and was one of six (from 1986 five) Island territories of the Netherlands Antilles, island territories () that constituted the Netherlands Antilles. Sint Maarten has the status of an EU overseas country; it is not part of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sint Eustatius
Sint Eustatius, known locally as Statia, is an island in the Caribbean. It is a Caribbean Netherlands, special municipality (officially "Public body (Netherlands), public body") of the Netherlands. The island is in the northern Leeward Islands, southeast of the Virgin Islands. Sint Eustatius is immediately to the northwest of Saint Kitts and southeast of Saba (island), Saba. The regional capital is Oranjestad, Sint Eustatius, Oranjestad. The island has an area of . Travelers to the island by air arrive through F. D. Roosevelt Airport. Formerly part of the Netherlands Antilles, Sint Eustatius Dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles, became a public body of the Netherlands in 2010. It is part of the Dutch Caribbean, which consists of Aruba, Bonaire, Curaçao, Saba (island), Saba, Sint Eustatius, and Sint Maarten. Together with Bonaire and Saba, it forms the BES Islands, also referred to as the Caribbean Netherlands. Etymology The island's name, Sint Eustatius, is Dutch for Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Law
Common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law primarily developed through judicial decisions rather than statutes. Although common law may incorporate certain statutes, it is largely based on precedent—judicial rulings made in previous similar cases. The presiding judge determines which precedents to apply in deciding each new case. Common law is deeply rooted in Precedent, ''stare decisis'' ("to stand by things decided"), where courts follow precedents established by previous decisions. When a similar case has been resolved, courts typically align their reasoning with the precedent set in that decision. However, in a "case of first impression" with no precedent or clear legislative guidance, judges are empowered to resolve the issue and establish new precedent. The common law, so named because it was common to all the king's courts across England, originated in the practices of the courts of the English kings in the centuries fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |