|
Anfa
Anfa (Berber language: ''Anfa'' or ''Anaffa'', ⴰⵏⴼⴰ; ; ; ) was the ancient toponym for Casablanca during the classical period. The city was founded by Berbers around the 10th century BC, with the Romans under Augustus later establishing the commercial port of "Anfus" in 15 BC. Anfa is now the name of a district in the oldest part of Casablanca, located in the Casablanca-Settat region of Morocco. The district covers an area of 37.5 square kilometres (14.5 square miles), and as of 2024 has 344.000 inhabitants. Roman Anfa The area which is today Casablanca was founded and settled by the Berbers by about the 10th century BC.''Casablanca'' - Jewish Virtual Library It was used as a port by the |
Casablanca
Casablanca (, ) is the largest city in Morocco and the country's economic and business centre. Located on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of the Chaouia (Morocco), Chaouia plain in the central-western part of Morocco, the city has a population of about 3.22 million in the urban area, and over 4.27 million in Greater Casablanca, making it the most populous city in the Maghreb region, and the List of largest cities in the Arab world, eighth-largest in the Arab world. Casablanca is Morocco's chief port, with the Port of Casablanca being one of the largest artificial ports in Africa, and the third-largest port in North Africa, after Tanger-Med ( east of Tangier) and Port Said. Casablanca also hosts the primary naval base for the Royal Moroccan Navy. Casablanca is a significant financial centre, ranking 54th globally in the September 2023 Global Financial Centres Index rankings, between Brussels and Rome. The Casablanca Stock Exchange is Africa's third-largest in terms of market c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sala Colonia
The Chellah or Shalla ( or ; ), is a medieval fortified Muslim necropolis and ancient archeological site in Rabat, Morocco, located on the south (left) side of the Bou Regreg estuary. The earliest evidence of the site's occupation suggests that the Phoenicians established a Emporium (antiquity), trading emporium here in the first millennium BC. This was later the site of Sala Colonia, an ancient Roman colonia, Roman colony in the Roman province, province of Mauretania Tingitana, before it was abandoned in Late antiquity, Late Antiquity. In the late 13th century the site began to be used as a dynastic necropolis for the Marinid Sultanate, Marinid dynasty. By the mid-14th century Marinid sultans had enclosed a part of the site with a new set of walls and built a religious complex inside it to accompany their mausoleums. In the 15th century the necropolis began to decline and it suffered damage over the centuries due to earthquakes and looting. Archeological excavations in the 20th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
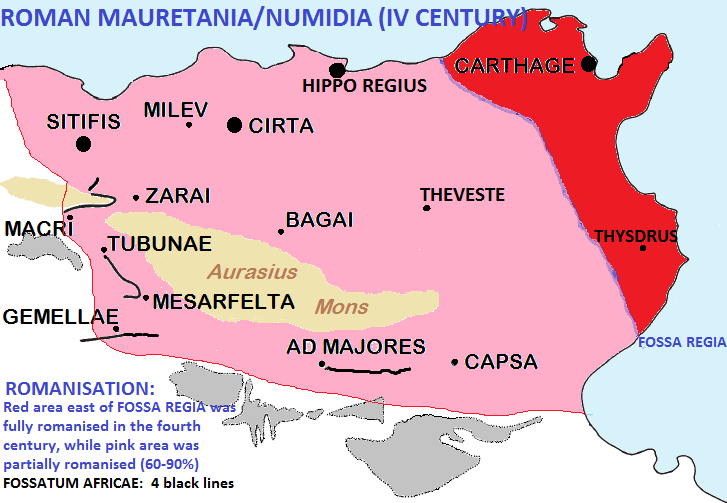
Mauretania Tingitana
Mauretania Tingitana (Latin for "Tangerine Mauretania") was a Roman province, coinciding roughly with the northern part of present-day Morocco. The territory stretched from the northern peninsula opposite Gibraltar, to Sala Colonia (or Chellah) and Volubilis to the south, and as far east as the Mulucha (or Malva) river. Its capital city was Tingis, which is the modern Tangier. Other major cities of the province were Iulia Valentia Banasa, Septem, Rusadir, Lixus and Tamuda. History After the death in 40 AD of Ptolemy of Mauretania, the last Ptolemaic ruler of the Kingdom of Mauretania, in about 44 AD Roman Emperor Claudius annexed the kingdom to the Roman Empire and partitioned it into two Roman provinces: Mauretania Tingitana and Mauretania Caesariensis. The Mulucha ( Moulouya River), located around 60 km west of modern Oran, Algeria, became the border separating them. The Roman occupation did not extend very far into the continent. In the far west, the south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madeira
Madeira ( ; ), officially the Autonomous Region of Madeira (), is an autonomous Regions of Portugal, autonomous region of Portugal. It is an archipelago situated in the North Atlantic Ocean, in the region of Macaronesia, just under north of the Canary Islands, Spain, west of the Morocco and southwest of mainland Portugal. Madeira sits on the African Plate, African Tectonic Plate, but is culturally, politically and ethnically associated with Europe, with its population predominantly descended from Portuguese settlers. Its population was 251,060 in 2021. The capital of Madeira is Funchal, on the main island's south coast. The archipelago includes the islands of Madeira Island, Madeira, Porto Santo Island, Porto Santo, and the Desertas Islands, Desertas, administered together with the separate archipelago of the Savage Islands. Roughly half of the population lives in Funchal. The region has political and administrative autonomy through the Autonomous Regions of Portugal#Const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berber People
Berbers, or the Berber peoples, also known as Amazigh or Imazighen, are a diverse grouping of distinct ethnic groups indigenous to North Africa who predate the arrival of Arabs in the Maghreb. Their main connections are identified by their usage of Berber languages, most of them mutually unintelligible, which are part of the Afroasiatic language family. They are indigenous to the Maghreb region of North Africa, where they live in scattered communities across parts of Morocco, Algeria, Libya, and to a lesser extent Tunisia, Mauritania, northern Mali and northern Niger. Smaller Berber communities are also found in Burkina Faso and Egypt's Siwa Oasis. Descended from Stone Age tribes of North Africa, accounts of the Imazighen were first mentioned in Ancient Egyptian writings. From about 2000 BC, Berber languages spread westward from the Nile Valley across the northern Sahara into the Maghreb. A series of Berber peoples such as the Mauri, Masaesyli, Massyli, Musulamii, Ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almoravid
The Almoravid dynasty () was a Berber Muslim dynasty centered in the territory of present-day Morocco. It established an empire that stretched over the western Maghreb and Al-Andalus, starting in the 1050s and lasting until its fall to the Almohads in 1147. The Almoravids emerged from a coalition of the Lamtuna, Gudala, and Massufa, nomadic Berber tribes living in what is now Mauritania and the Western Sahara, traversing the territory between the Draa, the Niger, and the Senegal rivers. During their expansion into the Maghreb, they founded the city of Marrakesh as a capital, . Shortly after this, the empire was divided into two branches: a northern one centered in the Maghreb, led by Yusuf ibn Tashfin and his descendants, and a southern one based in the Sahara, led by Abu Bakr ibn Umar and his descendants. The Almoravids expanded their control to al-Andalus (the Muslim territories in Iberia) and were crucial in temporarily halting the advance of the Christian kingdoms in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barghawata
The Barghawatas (or Barghwata, Berghouata) were a Berbers, Berber tribal confederation and religious movement that ruled a region of the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast in present-day Morocco between the 8th and 11th centuries. They belonged to the Masmuda confederacy. After allying with the Sufri Berber Revolt, rebellion against the Umayyad Caliphate, they established an independent state (AD744-1058) in the area of Tamasna, Tamesna on the Atlantic coast between Safi, Morocco, Safi and Salé under the leadership of Tarif al-Matghari. Etymology Some historians believe that the term ''Barghawata'' is a phonetic deformation of the term ''Barbati'', a nickname which Tarif carried. It is thought that he was born in the area of Barbate, near Cádiz in Spain. However, Jérôme Carcopino and other historians think the name is much older and the tribe is the same as that which the Ancient Rome, Romans called ''Baquates'', who up until the 7th century lived near Volubilis. History Few deta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tingis
Tingis (Latin; ''Tíngis'') or Tingi ( Ancient Berber:), was the ancient name of Tangier in Morocco and an important Carthaginian, Moor, and Roman port on the Atlantic Ocean. It was eventually granted the status of a Roman colony and made the capital of the province of Mauretania Tingitana and, after Diocletian's reforms, the diocese of Hispania. Legends The Greeks claimed that Tingis had been named for a daughter of the titan Atlas, who was supposed to support the vault of heaven nearby. They claimed that the Berber legends comported with the stories of Hercules's labors, which carried him to North Africa and the North Atlantic to retrieve the golden apples of the Hesperides. Having killed her husband Antaeus and again condemned her father to eternally supporting the firmament, Hercules slept with Tinja and fathered the Berber hero Syphax. Syphax supposedly founded the port of Tingis and named it his mother's honor after her death.. The gigantic skeleton and tomb of A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who were first reported in the written records as inhabitants of what is now Poland, during the period of the Roman Empire. Much later, in the fifth century, a group of Vandals led by kings established Vandal kingdoms first within the Iberian Peninsula, and then in the western Mediterranean islands, and North Africa. Archaeologists associate the early Vandals with the Przeworsk culture, which has led to some authors equating them to the Lugii, who were another group of Germanic peoples associated with that same archaeological culture and region. Expanding into Dacia during the Marcomannic Wars and to Pannonia during the Crisis of the Third Century, the Vandals were confined to Pannonia by the Goths around 330 AD, where they received permission to settle from Constantine the Great. Around 400, raids by the Huns from the east forced many Germanic tribes to migrate west into the territory of the Roman Empire and, fearing that they might be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volubilis
Volubilis (; ; ) is a partly excavated Berber-Roman city in Morocco, situated near the city of Meknes, that may have been the capital of the Kingdom of Mauretania, at least from the time of King Juba II. Before Volubilis, the capital of the kingdom may have been at Gilda. Built in a fertile agricultural area, it developed from the 3rd century BC onward as a Berber, then proto-Ancient Carthage, Carthaginian, settlement before being the capital of the kingdom of Mauretania. It grew rapidly under Roman rule from the 1st century AD onward and expanded to cover about with a circuit of walls. The city gained a number of major public buildings in the 2nd century, including a basilica, Roman temple, temple and triumphal arch. Its prosperity, which was derived principally from olive growing, prompted the construction of many fine town-houses with large Roman mosaic, mosaic floors. The city fell to local tribes around 285 and was never retaken by Rome because of its remoteness and inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman 'Coloniae' In Berber Africa
Roman colonies in North Africa are the cities—populated by Roman citizens—created in North Africa by the Roman Empire, mainly in the period between the reigns of Augustus and Trajan. Characteristics Since the second half of the first century BC and as a result of increasing communities of Roman citizens living in the North African centers, Rome started to create colonies in North Africa. The main reason was to control the area with Roman citizens, who had been legionaries in many cases. The second reason was to give land and urban properties to the Roman military troops who had fought for the Roman Empire and so decrease the demographic problem in the Italian peninsula. The third reason was to facilitate the Romanization of the area and so the integration of the local Berbers -through marriage and other relationships in the Roman Empire's social and cultural world. It is indicative that two of the main characteristics of the Roman world, Latin language and Christianity, were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limes (Roman Empire)
(Latin; , : ) is a term used primarily for the Germanic border defence or delimiting system of ancient Rome marking the borders of the Roman Empire. The term has been extended in modern times to refer to the Roman military frontiers and fortifications, frontier defences in other parts of the empire, such as in the east and in Africa. Overview The Roman frontier stretched for more than from the Atlantic coast of northern Roman Britain, Britain, through Europe to the Black Sea, and from there to the Red Sea and across North Africa to the Atlantic coast. The positions of the borders changed especially during the main periods of Roman expansion and contraction, and first became more stable during the early Roman Empire, Empire period under Augustus, but the borders continued to change with time in different provinces. The borders had different constituents depending on local needs; often they consisted of natural boundaries (e.g. rivers) with roads behind for easier movement o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |