|
Android Science
Android science is an interdisciplinary framework for studying human interaction and cognition based on the premise that a very humanlike robot (that is, an android) can elicit human-directed social responses in human beings. The android's ability to elicit human-directed social responses enables researchers to employ an android in experiments with human participants as an apparatus that can be controlled more precisely than a human actor. While mechanical-looking robots may be able to elicit social responses to some extent, a robot that looks and acts like a human being is in a better position to stand in for a human actor in social, psychological, cognitive, or neuroscientific experiments. This gives experiments with androids a level of ecological validity with respect to human interaction found lacking in experiments with mechanical-looking robots. An experimental setting for human-android interaction also provides a testing ground for models concerning how cognitive or neural p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Robot
A robot is a machine—especially one programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the control may be embedded within. Robots may be constructed to evoke human form, but most robots are task-performing machines, designed with an emphasis on stark functionality, rather than expressive aesthetics. Robots can be autonomous or semi-autonomous and range from humanoids such as Honda's ''Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility'' ( ASIMO) and TOSY's ''TOSY Ping Pong Playing Robot'' ( TOPIO) to industrial robots, medical operating robots, patient assist robots, dog therapy robots, collectively programmed ''swarm'' robots, UAV drones such as General Atomics MQ-1 Predator, and even microscopic nano robots. By mimicking a lifelike appearance or automating movements, a robot may convey a sense of intelligence or thought of its own. Autonomous things are expected to proliferat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
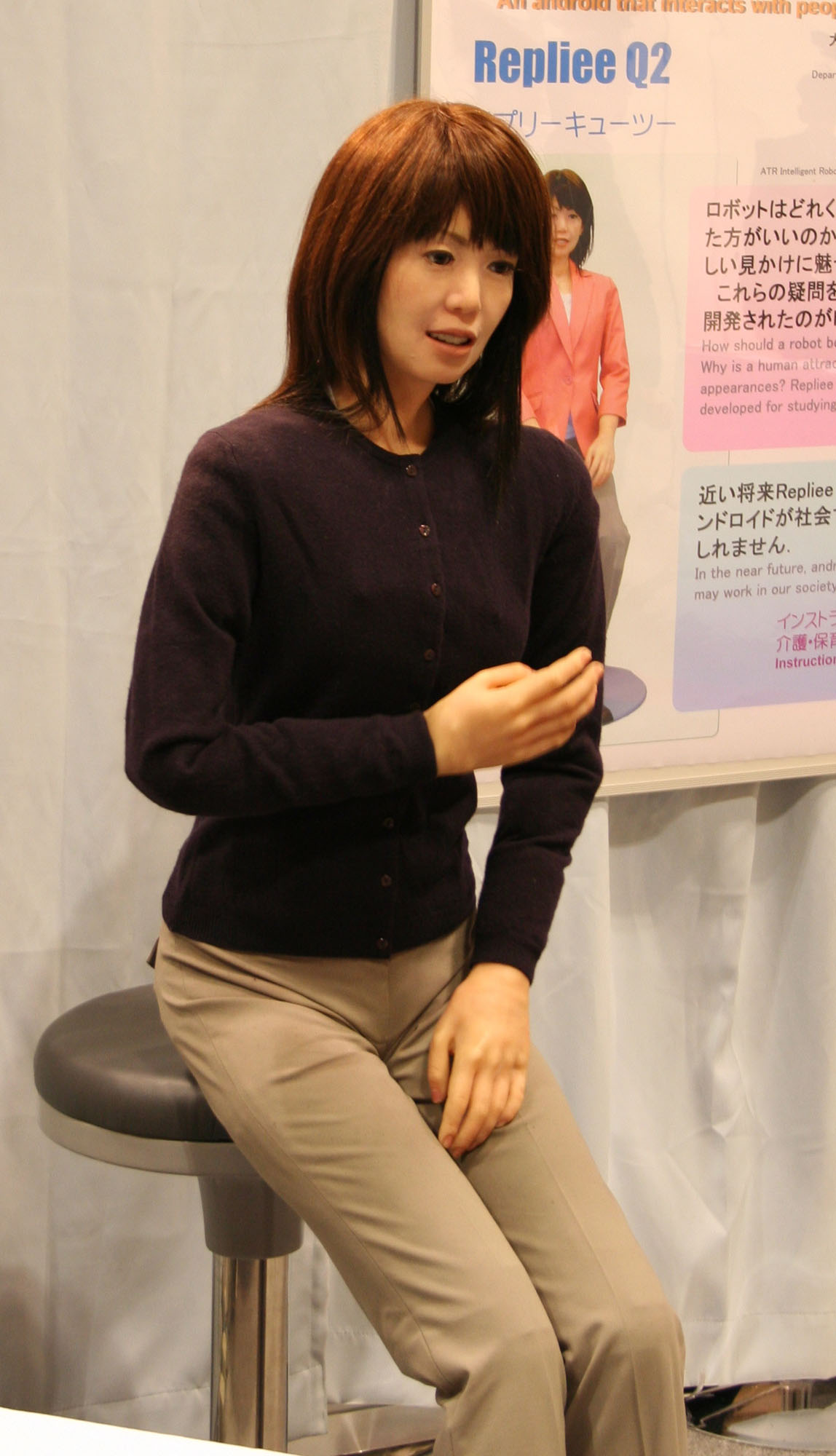
Android (robot)
An android is a humanoid robot or other artificial being often made from a flesh-like material. Historically, androids were completely within the domain of science fiction and frequently seen in film and television, but advances in robot technology now allow the design of functional and realistic humanoid robots. Terminology The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' traces the earliest use (as "Androides") to Ephraim Chambers' 1728 ''Cyclopaedia,'' in reference to an automaton that St. Albertus Magnus allegedly created. By the late 1700s, "androides", elaborate mechanical devices resembling humans performing human activities, were displayed in exhibit halls. The term "android" appears in US patents as early as 1863 in reference to miniature human-like toy automatons. The term ''android'' was used in a more modern sense by the French author Auguste Villiers de l'Isle-Adam in his work '' Tomorrow's Eve'' (1886). This story features an artificial humanlike robot named Hadaly. As said ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Clifford Nass
Clifford Ivar Nass (April 3, 1958 – November 2, 2013) was a professor of communication at Stanford University, co-creator of ''The Media Equation'' theory, and a renowned authority on human-computer interaction (HCI). He was also known for his work on individual differences associated with media multitasking. Nass was the Thomas M. Storke Professor at Stanford and held courtesy appointments in Computer Science, Education, Law, and Sociology. He was also affiliated with the programs in Symbolic Systems and Science, Technology, and Society. Nass was the director of thCommunication between Humans and Interactive Media(CHIMe) Lab, co-director of Kozmetsky Global Collaboratory (KGC) and its Real-time Venture Design Laboratory (ReVeL), and a co-founder of TeachAids. Early life and education Nass was born in Jersey City, New Jersey and raised in Teaneck, the son of Florence and Jules Nass. His parents formed New Jersey's first Mothers Against Drunk Driving chapter after Nas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
The Media Equation
The Media Equation is a general communication theory that claims people tend to assign human characteristics to computers and other media, and treat them as if they were real social actors. The effects of this phenomenon on people experiencing these media are often profound, leading them to behave and to respond to these experiences in unexpected ways, most of which they are completely unaware of.Reeves, B., & Nass, C. I. (1996). ''The media equation : how people treat computers, television, and new media like real people and places.'' Cambridge University Press. Originally based on the research of Clifford Nass anByron Reevesat Stanford University, the theory explains that people tend to respond to media as they would either to another person (by being polite, cooperative, attributing personality characteristics such as aggressiveness, humor, expertise, and gender) – or to places and phenomena in the physical world – depending on the cues they receive from the media. Nume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Anthropomorphism
Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human traits, emotions, or intentions to non-human entities. It is considered to be an innate tendency of human psychology. Personification is the related attribution of human form and characteristics to abstract concepts such as nations, emotions, and natural forces, such as seasons and weather. Both have ancient roots as storytelling and artistic devices, and most cultures have traditional fables with anthropomorphized animals as characters. People have also routinely attributed human emotions and behavioral traits to wild as well as domesticated animals. Etymology Anthropomorphism and anthropomorphization derive from the verb form ''anthropomorphize'', itself derived from the Greek ''ánthrōpos'' (, "human") and ''morphē'' (, "form"). It is first attested in 1753, originally in reference to the heresy of applying a human form to the Christian God.''Oxford English Dictionary'', 1st ed. "anthropomorphism, ''n.''" Oxford University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Masahiro Mori (roboticist)
is a Japanese roboticist noted for his pioneering work in the fields of robotics and automation, his research achievements in humans' emotional responses to non-human entities, as well as for his views on religion. The ASIMO robot was designed by one of Masahiro's students. In 1970, Mori published "Bukimi No Tani" (不気味の谷 ''The Uncanny Valley'') in ''Energy''. The article forwarded the hypothesis that as robots become more humanlike, they appear more familiar until a point is reached at which subtle imperfections of appearance make them look eerie. The observation led Mori to the belief that robot builders should not attempt to make their creations overly lifelike in appearance and motion. In 1974, Mori published ''The Buddha in the Robot: a Robot Engineer's Thoughts on Science and Religion'' in which he discussed the metaphysical implications of robotics. In the book, he wrote "I believe robots have the buddha-nature within them--that is, the potential for attainin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Uncanny Valley
In aesthetics, the uncanny valley ( ja, 不気味の谷 ''bukimi no tani'') is a hypothesized relation between an object's degree of resemblance to a human being and the emotional response to the object. The concept suggests that humanoid objects that imperfectly resemble actual human beings provoke uncanny or strangely familiar feelings of uneasiness and revulsion in observers. "Valley" denotes a dip in the human observer's affinity for the replica, a relation that otherwise increases with the replica's human likeness. Examples can be found in robotics, 3D computer animations and lifelike dolls. With the increasing prevalence of virtual reality, augmented reality, and photorealistic computer animation, the "valley" has been cited in reaction to the verisimilitude of the creation as it approaches indistinguishability from reality. The uncanny valley hypothesis predicts that an entity appearing almost human will risk eliciting cold, eerie feelings in viewers. Etymology Robot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
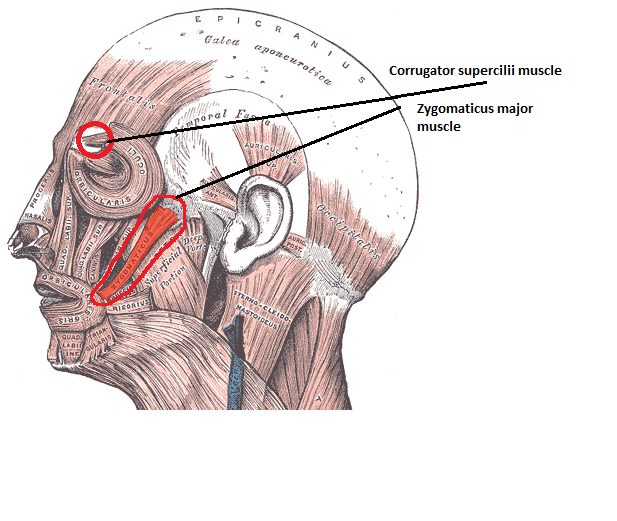 |
Affective Computing
Affective computing is the study and development of systems and devices that can recognize, interpret, process, and simulate human affects. It is an interdisciplinary field spanning computer science, psychology, and cognitive science. While some core ideas in the field may be traced as far back as to early philosophical inquiries into emotion, the more modern branch of computer science originated with Rosalind Picard's 1995 paper on affective computing and her book ''Affective Computing'' published by MIT Press. One of the motivations for the research is the ability to give machines emotional intelligence, including to simulate empathy. The machine should interpret the emotional state of humans and adapt its behavior to them, giving an appropriate response to those emotions. Areas Detecting and recognizing emotional information Detecting emotional information usually begins with passive sensors that capture data about the user's physical state or behavior without interp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Robot
A robot is a machine—especially one programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the control may be embedded within. Robots may be constructed to evoke human form, but most robots are task-performing machines, designed with an emphasis on stark functionality, rather than expressive aesthetics. Robots can be autonomous or semi-autonomous and range from humanoids such as Honda's ''Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility'' ( ASIMO) and TOSY's ''TOSY Ping Pong Playing Robot'' ( TOPIO) to industrial robots, medical operating robots, patient assist robots, dog therapy robots, collectively programmed ''swarm'' robots, UAV drones such as General Atomics MQ-1 Predator, and even microscopic nano robots. By mimicking a lifelike appearance or automating movements, a robot may convey a sense of intelligence or thought of its own. Autonomous things are expected to proliferat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Uncanny Valley
In aesthetics, the uncanny valley ( ja, 不気味の谷 ''bukimi no tani'') is a hypothesized relation between an object's degree of resemblance to a human being and the emotional response to the object. The concept suggests that humanoid objects that imperfectly resemble actual human beings provoke uncanny or strangely familiar feelings of uneasiness and revulsion in observers. "Valley" denotes a dip in the human observer's affinity for the replica, a relation that otherwise increases with the replica's human likeness. Examples can be found in robotics, 3D computer animations and lifelike dolls. With the increasing prevalence of virtual reality, augmented reality, and photorealistic computer animation, the "valley" has been cited in reaction to the verisimilitude of the creation as it approaches indistinguishability from reality. The uncanny valley hypothesis predicts that an entity appearing almost human will risk eliciting cold, eerie feelings in viewers. Etymology Robot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |