|
Androcalva Stowardii
''Androcalva stowardii'' is a species of flowering plant in the family Malvaceae and is endemic to inland parts of the south-west of Western Australia. It is a prostrate to low-lying shrub with elliptic to egg-shaped leaves, the edges smoothly serrated, and clusters of three to nine or more white to cream-coloured flowers. Description ''Androcalva stowardii'' is a prostrate to low-lying shrub that typically grows to high and wide, its new growth covered with scaly, yellowish hairs. Its leaves are elliptic to egg-shaped, sometimes with the narrower end towards the base, long and wide on a petiole long with narrowly triangular stipules long at the base. The edges of the leaves are smoothly serrated and both surfaces are covered with white, star-shaped hairs, more densely so on the lower surface. The flowers are arranged in groups of three to nine or more, on a peduncle long, each flower on a pedicel long, with narrowly triangular bracts long at the base. The flowers are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotype (biology)
A holotype (Latin: ''holotypus'') is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany and mycology, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, generally pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same genetic individual. A holotype is not necessarily "typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spencer Le Marchant Moore
Spencer Le Marchant Moore (1 November 1850 – 14 March 1931) was an English botanist. Biography Moore was born in Hampstead. He worked at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, from about 1870 to 1879, wrote a number of botanical papers, and then worked in an unofficial capacity at the Natural History Museum from 1896 until his death. He was involved in an expedition to remote parts of Western Australia Western Australia (WA) is the westernmost state of Australia. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Aust ... from December 1894 to October 1895, travelling from Goldfields–Esperance to places like Siberia Soak—near Waverley—and Goongarrie. Moore is commemorated in the plant genus '' Spenceria''. References External links * 1850 births 1931 deaths Botanists active in Kew Gardens English botanists English explorers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Western Australia
The flora of Western Australia comprises 10,842 published native vascular plant species and a further 1,030 unpublished species. They occur within 1,543 genus, genera from 211 Family (biology), families; there are also 1,335 naturalised alien or invasive plant species more commonly known as weeds. There are an estimated 150,000 cryptogam species or nonvascular plants which include lichens, and fungi although only 1,786 species have been published, with 948 algae and 672 lichen the majority. History Indigenous Australians have a long history with the flora of Western Australia. They have for over 50,000 years obtained detailed information on most plants. The information includes its uses as sources for food, shelter, tools and medicine. As Indigenous Australians passed the knowledge along orally or by example, most of this information has been lost, along many of the names they gave the flora. It was not until Europeans started to explore Western Australia that systematic written de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Androcalva
''Androcalva'' is a genus of 33 species of flowering plants in the family Malvaceae and is endemic to continental Australia. Description Plants in the genus ''Androcalva'' are shrubs or trees and have stems, leaves and flowers covered with star-like hairs. The leaves are Leaf#Divisions of the blade, simple, often with irregularly-toothed or lobed edges, and with ligules at the base but that are sometimes deciduous. The flowers are Plant reproductive morphology#Bisexual, bisexual, arranged in Cyme (botany), cymes opposite leaf axils, with 5 sepals, 5 petals, 5 stamens, and 5 staminodes sometimes with 3 lobes. The fruit is a bristly Capsule (botany), capsule with five Ovary (botany)#Parts of the ovary, valves, and is covered with star-shaped hairs. Taxonomy The genus ''Androcalva'' was first formally described in 2011 by Carolyn F. Wilkins, Carolyn Wilkins and Barbara Ann Whitlock, Barbara Whitlock in ''Australian Systematic Botany'' and comprises species formerly included in '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malvales Of Australia
The Malvales are an order of flowering plants. As circumscribed by APG II-system, the order includes about 6000 species within nine families. The order is placed in the eurosids II, which are part of the eudicots. The plants are mostly shrubs and trees; most of its families have a cosmopolitan distribution in the tropics and subtropics, with limited expansion into temperate regions. An interesting distribution occurs in Madagascar, where three endemic families of Malvales (Sphaerosepalaceae, Sarcolaenaceae and Diegodendraceae) occur. Many species of Malvaceae, '' sensu lato'' (in the broad sense), are valued for their wood, with that of '' Ochroma'' (balsa) being known for its lightness, and that of ''Tilia'' (lime, linden, or basswood) as a popular wood for carving. Fruit of the cacao tree (''Theobroma cacao'') are used as an ingredient for chocolate. Kola nuts (genus ''Cola'') are notable for their high caffeine content and were commonly used in the past in preparation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of Biodiversity, Conservation And Attractions (Western Australia)
The Department of Biodiversity, Conservation and Attractions (DBCA) is the Government of Western Australia, Western Australian government department responsible for managing lands and waters described in the ''Conservation and Land Management Act 1984'', the ''Rottnest Island Authority Act 1987'', the ''Swan and Canning Rivers Management Act 2006'', the ''Botanic Gardens and Parks Authority Act 1998'', and the ''Zoological Parks Authority Act 2001'', and implementing the state's conservation and environment legislation and regulations. The Department reports to the Minister for Environment and the Minister for Tourism. DBCA was formed on 1 July 2017 by the merger of the Department of Parks and Wildlife (DPaW), the Botanic Gardens and Parks Authority, the Zoological Parks Authority and the Rottnest Island Authority. The former DPaW became the Parks and Wildlife Service. Status Parks and Wildlife Service The Formerly Department of Parks and Wildlife. the Parks and Wildlife Servi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yalgoo Bioregion
Yalgoo is an interim Australian bioregion located in Western Australia. It has an area of . The bioregion, together with the Avon Wheatbelt and Geraldton Sandplains bioregions, is part of the larger Southwest Australia savanna ecoregion as classified by the World Wildlife Fund. Geography The Yalgoo bioregion extends southeastwards from the southern end of Shark Bay on Australia's west coast nearly to Lake Barlee in the interior of Western Australia. The western portion, known as the Edel subregion, includes the Edel Land peninsula and Dirk Hartog, Bernier, and Dorre islands, which enclose Shark Bay on the west. It also includes the coastal plain south of Shark Bay nearly to Kalbarri, where it transitions to the Geraldton Sandplains bioregion. The Edel subregion rests on the Carnarvon and Perth sedimentary basins. The Zuytdorp Cliffs line the coast from the northern end of Edel Land to the mouth of the Murchison River. Soils are generally white sands along the coast, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
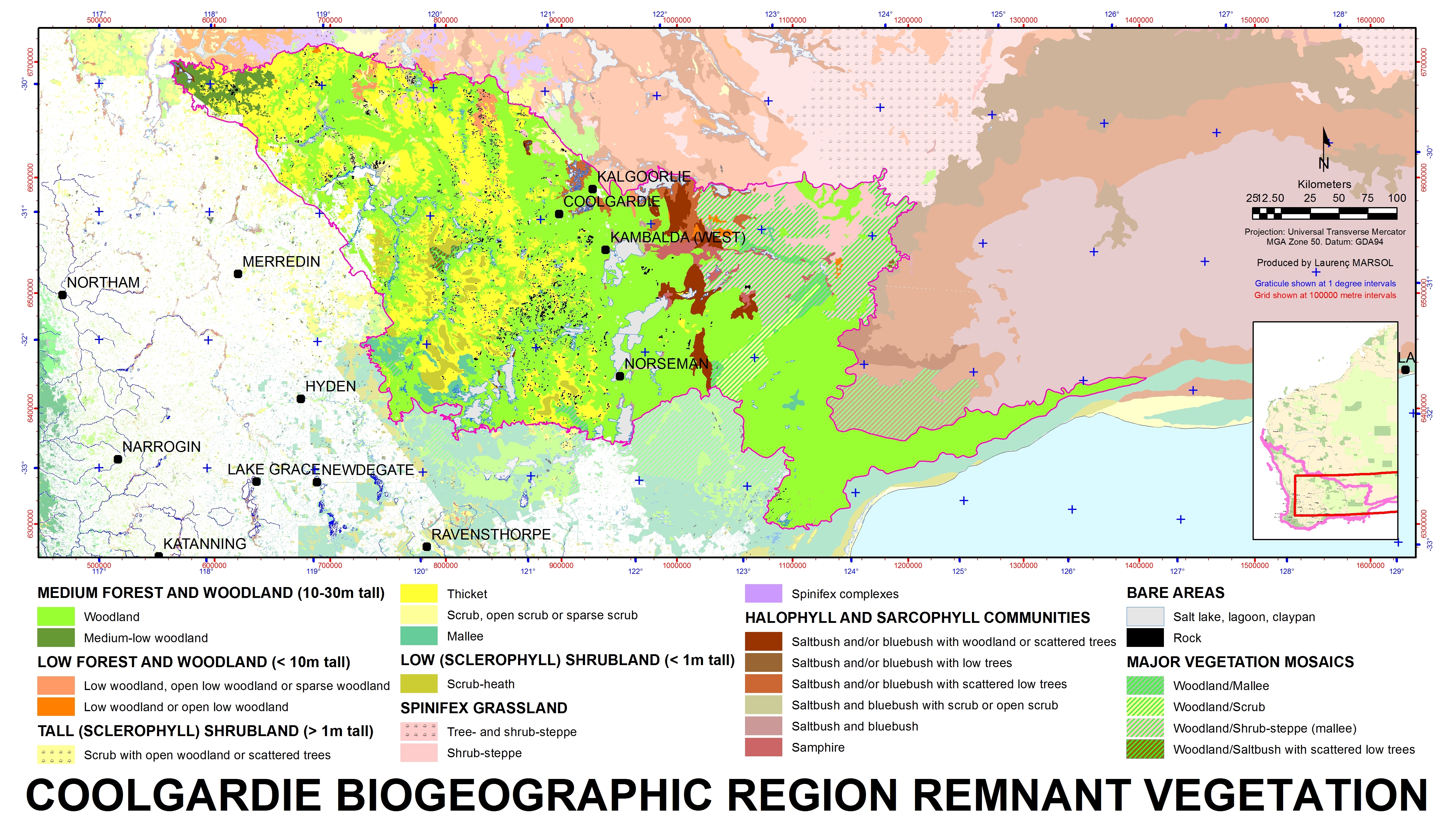
Coolgardie Bioregion
Coolgardie is an Australian bioregion consisting of an area of low hills and plains of infertile sandy soil in Western Australia. It has an area of . It includes much of the Great Western Woodlands. Location and description This is a transition zone between the Mediterranean climate of Australia's south-west coast and the country's dry interior. The poor soil makes it unsuitable for agriculture but Coolgardie has been a gold and nickel mining area. It is bounded on the north by the arid Murchison bioregion, characterised by open Mulga woodlands and steppe. The low shrublands of the arid Nullarbor Plain lie to the east. The Mallee bioregion adjoins Coolgardie on the south. The Avon Wheatbelt bioregion is to the west. The Coolgardie bioregion, together with the coastal Hampton bioregion to the southeast, constitute the Coolgardie woodlands ecoregion defined by the World Wildlife Fund. Flora and fauna The low hills are home to woodland of endemic species of eucalyptus while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avon Wheatbelt
The Avon Wheatbelt is a bioregion in Western Australia. It has an area of . It is considered part of the larger Southwest Australia savanna ecoregion. Geography The Avon Wheatbelt bioregion is mostly a gently undulating landscape with low relief. It lies on the Yilgarn craton, an ancient block of crystalline rock, which was uplifted in the Tertiary and dissected by rivers. The craton is overlain by laterite deposits, which in places have decomposed into yellow sandplains, particularly on low hills. Steep-sided erosional gullies, known as breakaways, are common. Beecham, Brett (2001). "Avon Wheatbelt 2 (AW2 - Re-juvenated Drainage subregion)" in ''A Biodiversity Audit of Western Australia’s 53 Biogeographical Subregions in 2002''. Department of Conservation and Land Management, Government of Western Australia, November 2001. Accessed 15 May 2022/ref> In the south and west (the Katanning subregion), streams are mostly perennial, and feed rivers which drain westwards to empt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type (biology)
In biology, a type is a particular specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally associated. In other words, a type is an example that serves to anchor or centralizes the defining features of that particular taxon. In older usage (pre-1900 in botany), a type was a taxon rather than a specimen. A taxon is a scientifically named grouping of organisms with other like organisms, a set that includes some organisms and excludes others, based on a detailed published description (for example a species description) and on the provision of type material, which is usually available to scientists for examination in a major museum research collection, or similar institution. Type specimen According to a precise set of rules laid down in the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) and the ''International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants'' (ICN), the scientific name of every taxon is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binomial Nomenclature
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name (often shortened to just "binomial"), a binomen, name, or a scientific name; more informally, it is also called a Latin name. In the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), the system is also called nomenclature, with an "n" before the "al" in "binominal", which is a typographic error, meaning "two-name naming system". The first part of the name – the '' generic name'' – identifies the genus to which the species belongs, whereas the second part – the specific name or specific epithet – distinguishes the species within the genus. For example, modern humans belong to the genus ''Homo'' and within this genus to the species ''Hom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Systematic Botany
''Australian Systematic Botany'' is an international peer-reviewed scientific journal published by CSIRO Publishing. It is devoted to publishing original research, and sometimes review articles, on topics related to systematic botany, such as biogeography, taxonomy and evolution. The journal is broad in scope, covering all plant, algal and fungal groups, including fossils. First published in 1978 as ''Brunonia'', the journal adopted its current name in 1988. The current editor-in-chief is Daniel Murphy ( Royal Botanic Gardens Melbourne). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in BIOSIS, CAB Abstracts, Current Contents (Agriculture, Biology & Environmental Sciences), Elsevier BIOBASE, Kew Index, Science Citation Index and Scopus. Impact factor According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2015 impact factor of 0.648. References External links * Australian Systematic Botanyat SCImago Journal Rank Australian Systematic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |