|
Andrew Berg
Andrew Berg (Anders Berg; October 16, 1869 — March 1, 1939) was an immigrant to the District of Alaska who was a prominent fisher, hunter, and trapper. He became the first licensed big game guide in Alaska. Early life and emigration Andrew Berg was born Anders Berg on October 16, 1869, in Nykarleby, Finland, then part of the Russian Empire. His father Johan and mother Lovisa owned a small farm. The family also hunted and fished. Because of extreme poverty, Andrew left Finland in 1887 at the age of 16. Along with two other boys from his town, Berg sailed to Hull in England, before travelling to Liverpool by train. He was one of 500 emigrants that were to sail to New York City aboard the ''St. Andreas''. Because of a cholera outbreak, the ship instead sailed to Quebec. The boys travelled to Chicago, then to Michigan City, Indiana, where they obtained work at a sawmill.Cassidy, pg. 2 After working at the mill for a short time, Berg travelled to his uncle Erik's home in San Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
District Of Alaska
The District of Alaska was the federal government’s designation for Alaska from May 17, 1884, to August 24, 1912, when it became the Territory of Alaska. Previously (1867–1884) it had been known as the Department of Alaska, a military designation. The designation as a district meant that Alaska became an incorporated but Territories of the United States#Formerly unorganized territories, unorganized territory with a civil government. The List of governors of Alaska#Governors of the District of Alaska, governor of the District of Alaska was appointed by the president of the United States. Prelude to District status At the time of the 1867 Alaska Purchase, legislators in Washington, D.C., were occupied with post–American Civil War, Civil War Reconstruction era, reconstruction issues, and had little time to dedicate to Alaska. As a Department (United States Army), department, Alaska was handled as a strategic military area, variously under the jurisdiction of the United Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sawmill
A sawmill (saw mill, saw-mill) or lumber mill is a facility where logging, logs are cut into lumber. Modern sawmills use a motorized saw to cut logs lengthwise to make long pieces, and crosswise to length depending on standard or custom sizes (dimensional lumber). The Portable sawmill, "portable" sawmill is simple to operate. The log lies flat on a steel bed, and the motorized saw cuts the log horizontally along the length of the bed, by the operator manually pushing the saw. The most basic kind of sawmill consists of a chainsaw and a customized jig ("Alaskan sawmill"), with similar horizontal operation. Before the invention of the sawmill, boards were made in various manual labour, manual ways, either wood splitting, rived (split) and plane (tool), planed, hewing, hewn, or more often hand sawn by two men with a whipsaw, one above and another in a saw pit below. The earliest known mechanical mill is the Hierapolis sawmill, a Roman water-powered stone mill at Hierapolis, Asia M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trophy Hunting
Trophy hunting is a form of hunting for field sports, sport in which parts of the hunted wild animals are kept and displayed as trophies. The animal being targeted, known as the "game (hunting), game", is typically a mature male specimen from a popular species of collectable interests, usually of large sizes, holding impressive horn (anatomy), horns, antlers, furs, or manes. Most trophies consist of only select parts of the animal, which are prepared for display by a taxidermy, taxidermist. The parts most commonly kept vary by species but often include the head, Hide (skin), hide, tusks, horns, or antlers. Trophies are often displayed in trophy rooms or game rooms, or in gun rooms along with the hunter's gun collection. Trophy hunting has strong supporters and opponents. The controversy focuses on the morality of hunting for pleasure rather than for practical use, as well as questions about the extent to which big-game hunting benefits Nature conservation, conservation efforts. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower 48
The contiguous United States, also known as the U.S. mainland, officially referred to as the conterminous United States, consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the District of Columbia of the United States in central North America. The term excludes the only two non-contiguous states and the last two to be admitted to the Union, which are Alaska and Hawaii, and all other offshore insular areas, such as the U.S. territories of American Samoa, Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. The colloquial term ''Lower48'' is also used, especially in relation to Alaska. The term The Mainland is used in Hawaii. The related but distinct term ''continental United States'' includes Alaska, which is also on North America, but separated from the 48 states by British Columbia in Canada, but excludes Hawaii and all the insular areas in the Caribbean and the Pacific. The greatest distance on a great-circle route entirely within the contiguous U.S. is 2, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moose
The moose (: 'moose'; used in North America) or elk (: 'elk' or 'elks'; used in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is the world's tallest, largest and heaviest extant species of deer and the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is also the tallest, and the second-largest, land animal in North America, falling short only to the American bison in body mass. Most adult male moose have broad, palmate ("open-hand shaped") antlers; other members of the deer family have pointed antlers with a dendritic ("twig-like") configuration. Moose inhabit the circumpolar boreal forests or temperate broadleaf and mixed forests of the Northern Hemisphere, thriving in cooler, temperate areas as well as subarctic climates. Hunting shaped the relationship between moose and humans, both in Eurasia and North America. Prior to the colonial era (around 1600–1700 CE), moose were one of many valuable sources of sustenance for certain tribal groups and First Nations. Hunting and habitat loss hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska (magazine)
''Alaska '' is a periodical devoted to news and discussion of issues and features of and from Alaska. Most of its readership consists of persons Outside (Alaska), outside of Alaska who are interested in the Alaskan way of life. History and profile ''Alaska'' magazine was founded in 1935 in Ketchikan, Alaska, by Emery Fridolf Tobin (1895-1977) and J. Ray Roady (1907-1997). Tobin established himself as an opponent of Alaska statehood, although this may have been contradictory, given his ties to the Democratic party and the fact that he and Roady served as State Representatives in 1959. ''Alaska'' magazine was originally titled the ''Alaska Sportsman Magazine'', a name it retained until 1969. Another major difference is that the editorial and sales offices have moved to Alaska's economic center, the city of Anchorage, Alaska, Anchorage. The magazine was sold to the partnership of fur trader Robert A. Henning and journalist R. N. DeArmond, Robert N. DeArmond in 1958. Henning helmed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outdoor Life
''Outdoor Life'' is an outdoors magazine about camping, fishing, hunting, and survival. For years, it was a sister magazine of '' Field & Stream''. Together with '' Sports Afield'', they are considered the Big Three of American outdoor publishing by ''Money'' magazine. ''Outdoor Life'' was launched in Denver, Colorado, in January 1898. Founder and editor-in-chief (1898–1929), J. A. McGuire, intended ''Outdoor Life'' to be a magazine for sportsmen, written by sportsmen, covering all aspects of the outdoor arena. History The first issue covered topics including a moose hunt in Alaska and advice about Native Americans. Some of the original sections were titled, "Photography", "Trap and Target", and "In the Game and Field". ''Outdoor Life'' was an innovative publication. In 1903, the first photograph was printed on the cover in black and white. A short time later, in 1906, the first color cover appeared on the magazine. ''Outdoor Lifes editorial coverage followed its a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caribou
The reindeer or caribou (''Rangifer tarandus'') is a species of deer with circumpolar distribution, native to Arctic, subarctic, tundra, boreal, and mountainous regions of Northern Europe, Siberia, and North America. It is the only representative of the genus ''Rangifer''. More recent studies suggest the splitting of reindeer and caribou into six distinct species over their range. Reindeer occur in both migratory and sedentary populations, and their herd sizes vary greatly in different regions. The tundra subspecies are adapted for extreme cold, and some are adapted for long-distance migration. Reindeer vary greatly in size and color from the smallest, the Svalbard reindeer (''R.'' (''t.'') ''platyrhynchus''), to the largest, Osborn's caribou (''R. t. osborni''). Although reindeer are quite numerous, some species and subspecies are in decline and considered vulnerable. They are unique among deer (Cervidae) in that females may have antlers, although the prevalence of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
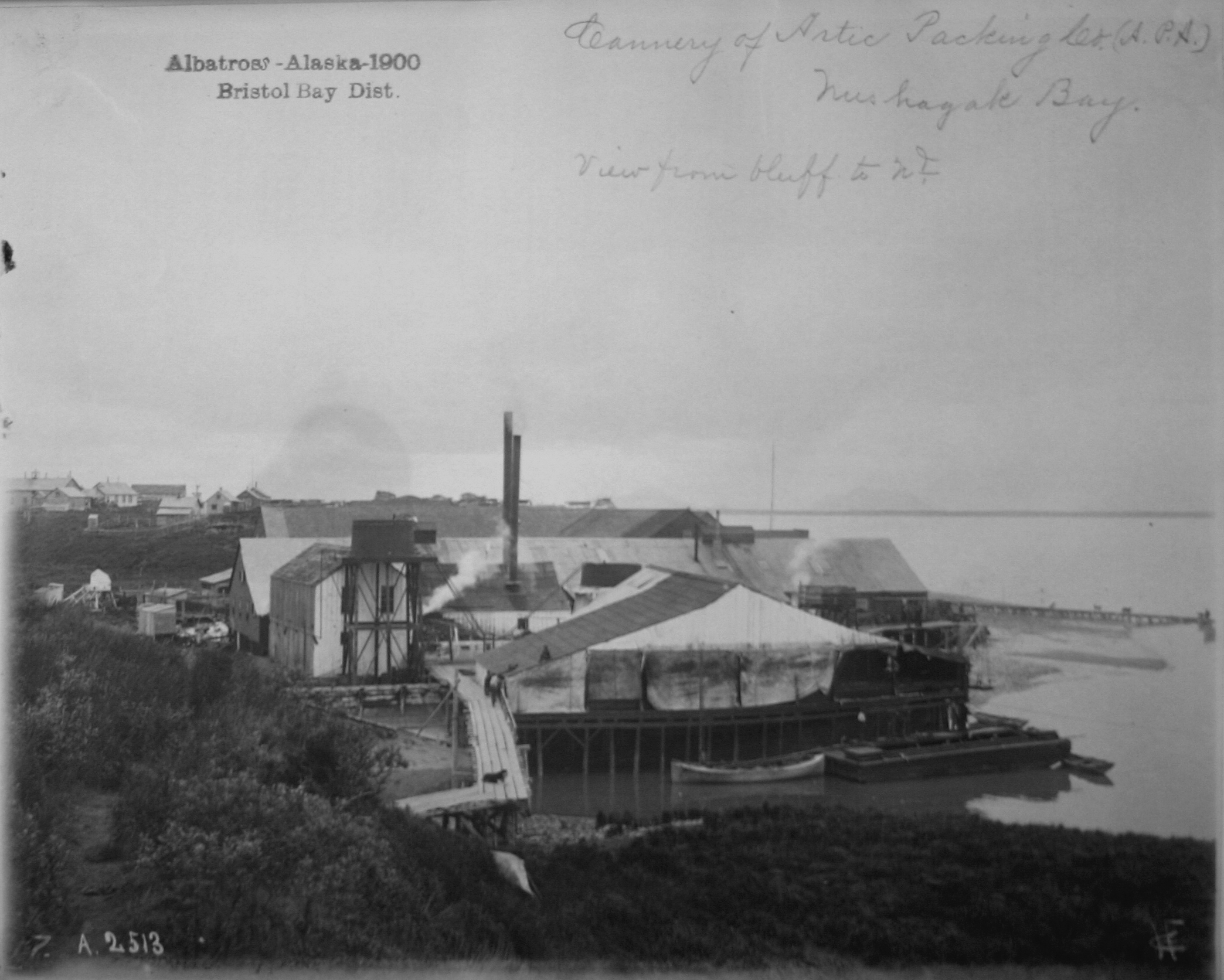
Alaska Packers' Association
The Alaska Packers' Association (APA) was a San Francisco-based manufacturer of Alaska canned salmon founded in 1891 and sold in 1982. As the largest salmon packer in Alaska, the member canneries of APA were active in local affairs, and had considerable political influence. The Alaska Packers' Association is best known for operating the "Star Fleet," the last fleet of commercial sailing vessels on the West Coast of North America, as late as 1927. Foundation The APA was formed in 1891 when the Alaska salmon industry was in its infancy but already produced more canned salmon than the market could bear. The association was initially formed to sell off the surplus pack and it proved so successful that it incorporated in 1892 as the Alaska Packing Association to better manage canned salmon production to meet demand. Of the original 31 member canneries across Alaska, 9 were idled that year. With minor changes, the association reincorporated as the Alaska Packers Association in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenai, Alaska
Kenai (, ; Dena'ina: ; , ''Kenay'') is a city in the Kenai Peninsula Borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. By road, it is 158 miles southwest of Anchorage. The population was 7,424 as of the 2020 census, up from 7,100 in 2010, the fifteenth-most populated city in the state. History The city of Kenai is named after the local Dena'ina word 'ken' or 'kena', which means 'flat, meadow, open area with few trees; base, low ridge', according to the Dena'ina Topical Dictionary by James Kari, Ph.D., published in 2007. This describes the area along the mouth and portion of the Kenai River near the City of Kenai. Archaeological evidence suggests that the area was first occupied by the Kachemak people from 1000 B.C., until they were displaced by the Dena'ina Athabaskan people around 1000 A.D. Before the arrival of the Russians, Kenai was a Dena'ina village called ''Shk'ituk't'', meaning "where we slide down." When Russian fur traders first arrived in 1741, about 1,000 Dena'ina l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannery
Canning is a method of food preservation in which food is processed and sealed in an airtight container ( jars like Mason jars, and steel and tin cans). Canning provides a shelf life that typically ranges from one to five years, although under specific circumstances, it can be much longer. A freeze-dried canned product, such as canned dried lentils, could last as long as 30 years in an edible state. In 1974, samples of canned food from the wreck of the '' Bertrand'', a steamboat that sank in the Missouri River in 1865, were tested by the National Food Processors Association. Although appearance, smell, and vitamin content had deteriorated, there was no trace of microbial growth and the 109-year-old food was determined to be still safe to eat. History and development French origins Shortly before the Napoleonic Wars, the French government offered a hefty cash award of 12,000 francs to any inventor who could devise a cheap and effective method of preserving large amounts o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmon
Salmon (; : salmon) are any of several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the genera ''Salmo'' and ''Oncorhynchus'' of the family (biology), family Salmonidae, native to tributary, tributaries of the North Atlantic (''Salmo'') and North Pacific (''Oncorhynchus'') basins. ''Salmon'' is a colloquial or common name used for fish in this group, but is not a scientific name. Other closely related fish in the same family include trout, Salvelinus, char, Thymallus, grayling, Freshwater whitefish, whitefish, lenok and Hucho, taimen, all coldwater fish of the subarctic and cooler temperate regions with some sporadic endorheic populations in Central Asia. Salmon are typically fish migration, anadromous: they hatch in the shallow gravel stream bed, beds of freshwater headstreams and spend their juvenile fish, juvenile years in rivers, lakes and freshwater wetlands, migrate to the ocean as adults and live like sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |