|
Andrea Moro
Andrea Carlo Moro (born July 24, 1962) is an Italian linguist, neuroscientist and novelist. He is currently full professor of general linguistics at the Institute for Advanced Study IUSS Pavia, Italy, founder and former director of NeTS and of the Department of Cognitive Behavioural and Social Sciences. He was professor of at the University of Bologna and at the Università Vita-Salute San Raffaele. He is member of the Academia Europaea and the Pontifical Academy of Fine Arts and Letters of the Virtuosi al Pantheon. His main fields of research are syntax and neurolinguistics. He has pursued at least two distinct lines of research: the theory of syntax and the neurological correlates of syntax with the brain. For the first field, see the critical comments in Graffi (2000), Hale - Keyser (2003), Kayne (2011), Richards (2010) and Chomsky (2013) among others. As for a critical evaluation of the second field see in particular the first chapter of Kandel et al. (2013); see also Kaan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguistics is concerned with both the cognitive and social aspects of language. It is considered a scientific field as well as an academic discipline; it has been classified as a social science, natural science, cognitive science,Thagard, PaulCognitive Science, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2008 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). or part of the humanities. Traditional areas of linguistic analysis correspond to phenomena found in human linguistic systems, such as syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences); semantics (meaning); morphology (structure of words); phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages); phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language); and pragmatics (how soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntax
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning ( semantics). There are numerous approaches to syntax that differ in their central assumptions and goals. Etymology The word ''syntax'' comes from Ancient Greek roots: "coordination", which consists of ''syn'', "together", and ''táxis'', "ordering". Topics The field of syntax contains a number of various topics that a syntactic theory is often designed to handle. The relation between the topics is treated differently in different theories, and some of them may not be considered to be distinct but instead to be derived from one another (i.e. word order can be seen as the result of movement rules derived from grammatical relations) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PROSE Awards
The PROSE Awards (Professional and Scholarly Excellence) are presented by the Association of American Publishers’ (AAP) Professional and Scholarly Publishing (PSP) Division. Presented since 1976, the awards annually recognize distinguished professional and scholarly books, reference works, journals, and electronic content. The awards are judged by peer publishers, academics, librarians, and medical professionals. Publishers and authors are honored at a luncheon ceremony at the PSP Annual Conference in Washington, DC. In recent years, the PROSE Awards luncheon has featured a live webcast of the event, original short films and several multimedia presentations highlighting winners. Awards by the numbers: * Five “best of” awards chosen from 53 book, reference, journal and e-product categories; * Forty-five book subject categories for traditional print, electronic publications and print/electronic packages; and * Six awards for electronic products, including electronic platfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negation
In logic, negation, also called the logical complement, is an operation that takes a proposition P to another proposition "not P", written \neg P, \mathord P or \overline. It is interpreted intuitively as being true when P is false, and false when P is true. Negation is thus a unary logical connective. It may be applied as an operation on notions, propositions, truth values, or semantic values more generally. In classical logic, negation is normally identified with the truth function that takes ''truth'' to ''falsity'' (and vice versa). In intuitionistic logic, according to the Brouwer–Heyting–Kolmogorov interpretation, the negation of a proposition P is the proposition whose proofs are the refutations of P. Definition ''Classical negation'' is an operation on one logical value, typically the value of a proposition, that produces a value of ''true'' when its operand is false, and a value of ''false'' when its operand is true. Thus if statement is true, then \ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recursion
Recursion (adjective: ''recursive'') occurs when a thing is defined in terms of itself or of its type. Recursion is used in a variety of disciplines ranging from linguistics to logic. The most common application of recursion is in mathematics and computer science, where a function being defined is applied within its own definition. While this apparently defines an infinite number of instances (function values), it is often done in such a way that no infinite loop or infinite chain of references ("crock recursion") can occur. Formal definitions In mathematics and computer science, a class of objects or methods exhibits recursive behavior when it can be defined by two properties: * A simple ''base case'' (or cases) — a terminating scenario that does not use recursion to produce an answer * A ''recursive step'' — a set of rules that reduces all successive cases toward the base case. For example, the following is a recursive definition of a person's ''ancestor''. One's anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Grammar
Universal grammar (UG), in modern linguistics, is the theory of the genetic component of the language faculty, usually credited to Noam Chomsky. The basic postulate of UG is that there are innate constraints on what the grammar of a possible human language could be. When linguistic stimuli are received in the course of language acquisition, children then adopt specific syntactic rules that conform to UG. The advocates of this theory emphasize and partially rely on the poverty of the stimulus (POS) argument and the existence of some universal properties of natural human languages. However, the latter has not been firmly established, as some linguists have argued languages are so diverse that such universality is rare. It is a matter of empirical investigation to determine precisely what properties are universal and what linguistic capacities are innate. Argument The theory of universal grammar proposes that if human beings are brought up under normal conditions (not those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Antisymmetry
Dynamic antisymmetry is a theory of syntactic movement presented in Andrea Moro's 2000 monograph ''Dynamic Antisymmetry'' based on the work presented in Richard S. Kayne's 1994 monograph ''The Antisymmetry of Syntax''. A premise: the antisymmetry of syntaxThe crux of Kayne's theory is that hierarchical structure in natural language maps universally onto a particular surface linearization, namely specifier-head-complement branching order. To understand what is meant by hierarchical structure, consider the sentence, ''The King of England likes apples''. We can replace this by, ''He likes apples''. Since the phrase ''the King of England'' can be replaced by a pronoun, we say that it constitutes a hierarchical unit (called a constituent). Further constituency tests reveal the phrase ''likes apples'' to be a constituent. Hierarchical units are built up according to the principles of phrase structure into a branching tree formation rather than into a linear order. Older theories of linea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antisymmetry
In linguistics, antisymmetry is a syntactic theory presented in Richard S. Kayne's 1994 monograph ''The Antisymmetry of Syntax''. It asserts that grammatical hierarchies in natural language follow a universal order, namely specifier-head-complement branching order. The theory is built on the foundation of X-bar theory. Kayne hypothesizes that all phrases whose surface order is not specifier-head-complement have undergone syntactic movements that disrupt this underlying order. Others have posited specifier-complement-head as the basic word order. Antisymmetry as a principle of word order is reliant on X-bar notions such as specifier and complement, the existence of order-altering mechanisms such as movement, and disputed by constituency structure theories (as opposed to dependency structure theories). Asymmetric c-command C-command is a relation between tree nodes, as defined by Tanya Reinhart. Kayne uses a simple definition of c-command based on the "first node up". However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
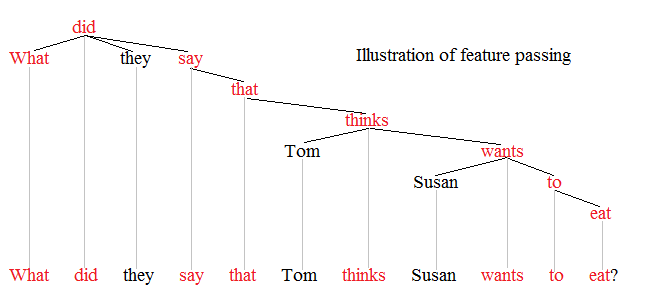
Syntactic Movement
Syntactic movement is the means by which some theories of syntax address discontinuities. Movement was first postulated by structuralist linguists who expressed it in terms of ''discontinuous constituents'' or ''displacement''. Some constituents appear to have been displaced from the position in which they receive important features of interpretation. The concept of movement is controversial and is associated with so-called ''transformational'' or ''derivational'' theories of syntax (such as transformational grammar, government and binding theory, minimalist program). Representational theories (such as head-driven phrase structure grammar, lexical functional grammar, construction grammar, and most dependency grammars), in contrast, reject the notion of movement and often instead address discontinuities with other mechanisms including graph reentrancies, feature passing, and type shifters. Illustration Movement is the traditional means of explaining discontinuities such as wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
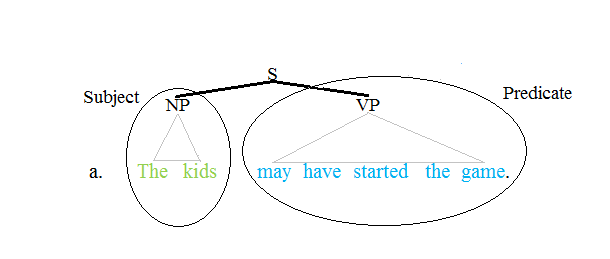
Subject (grammar)
The subject in a simple English sentence such as ''John runs'', ''John is a teacher'', or ''John drives a car'', is the person or thing about whom the statement is made, in this case ''John''. Traditionally the subject is the word or phrase which controls the verb in the clause, that is to say with which the verb agrees (''John is'' but ''John and Mary are''). If there is no verb, as in ''John what an idiot!'', or if the verb has a different subject, as in ''John I can't stand him!'', then 'John' is not considered to be the grammatical subject, but can be described as the ''topic'' of the sentence. While these definitions apply to simple English sentences, defining the subject is more difficult in more complex sentences and in languages other than English. For example, in the sentence ''It is difficult to learn French'', the subject seems to be the word ''it'', and yet arguably the real subject (the thing that is difficult) is ''to learn French''. A sentence such as ''It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predicate (grammar)
The term predicate is used in one of two ways in linguistics and its subfields. The first defines a predicate as everything in a standard declarative sentence except the subject, and the other views it as just the main content verb or associated predicative expression of a clause. Thus, by the first definition the predicate of the sentence ''Frank likes cake'' is ''likes cake''. By the second definition, the predicate of the same sentence is just the content verb ''likes'', whereby ''Frank'' and ''cake'' are the arguments of this predicate. Differences between these two definitions can lead to confusion. Syntax Traditional grammar The notion of a predicate in traditional grammar traces back to Aristotelian logic. A predicate is seen as a property that a subject has or is characterized by. A predicate is therefore an expression that can be ''true of'' something. Thus, the expression "is moving" is true of anything that is moving. This classical understanding of predicate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntactic Expletive
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure ( constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics). There are numerous approaches to syntax that differ in their central assumptions and goals. Etymology The word ''syntax'' comes from Ancient Greek roots: "coordination", which consists of ''syn'', "together", and ''táxis'', "ordering". Topics The field of syntax contains a number of various topics that a syntactic theory is often designed to handle. The relation between the topics is treated differently in different theories, and some of them may not be considered to be distinct but instead to be derived from one another (i.e. word order can be seen as the result of movement rules derived from grammatical relations). S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |