|
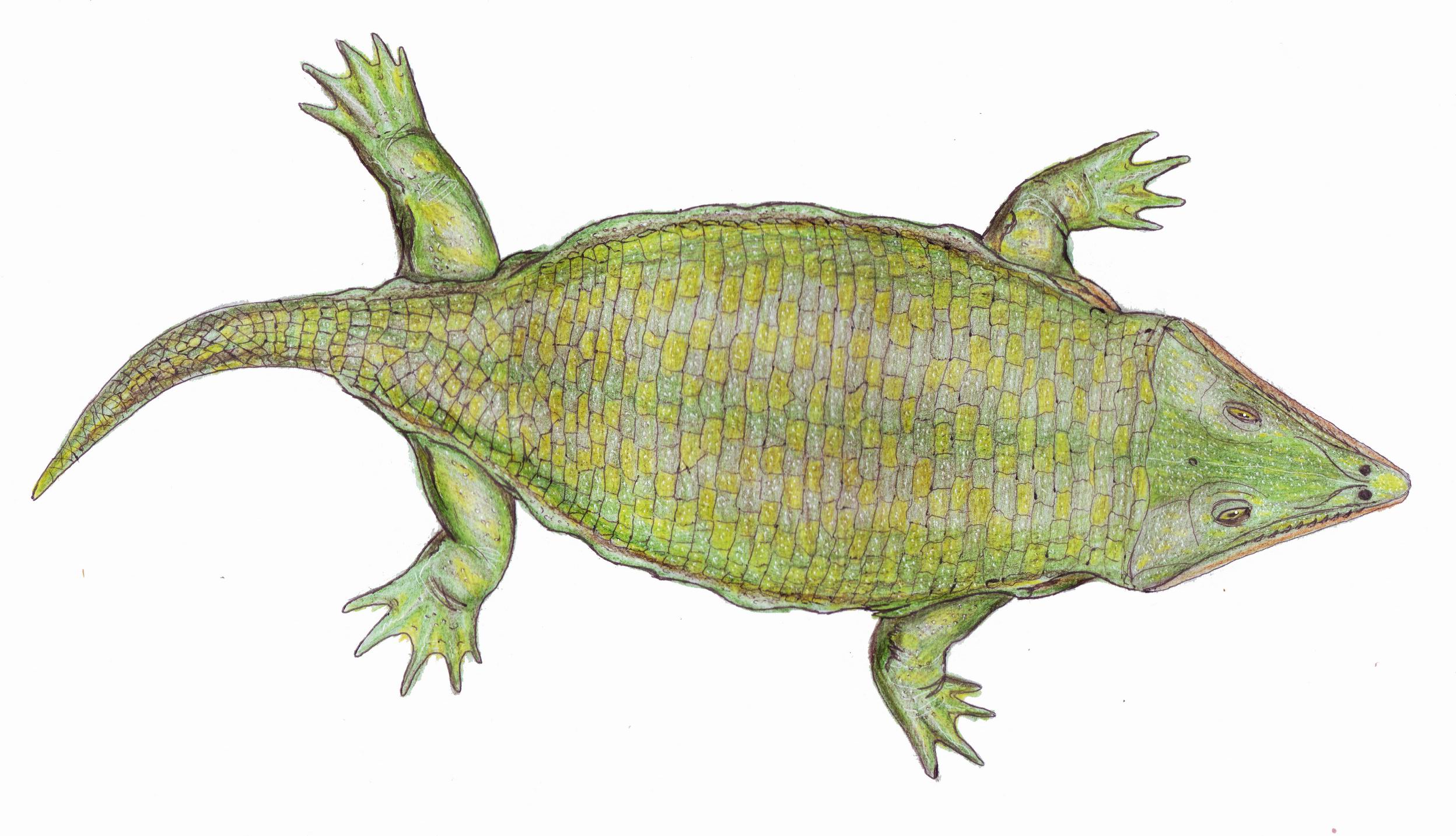
Andersonerpeton
''Andersonerpeton'' is an extinct genus of aïstopod from the Bashkirian (early Pennsylvanian) of Nova Scotia, Canada. It is known from a single jaw, which shares an unusual combination of features from both other aistopods and from stem-tetrapod tetrapodomorph fish. As a result, ''Andersonerpeton'' is significant for supporting a new classification scheme which states that aistopods evolved much earlier than previously expected. The genus contains a single species, ''A. longidentatum'', which was previously believed to have been a species of the microsaur '' Hylerpeton.'' History The type species, ''A. longidentatum'', was initially described by John William Dawson on the basis of RM 2.1129, a left mandible. This fossil hailed from the Joggins fossil cliffs, a site in Nova Scotia famous for fossil deposits dated to the Bashkirian, the first stage of the Pennsylvanian subperiod of the Carboniferous period. ''A. longidentatum'' was originally named ''Hylerpeton longidentatum' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aïstopod
Aistopoda (Greek for " avingnot-visible feet") is an order of highly specialised snake-like stegocephalians known from the Carboniferous and Early Permian of Europe and North America, ranging from tiny forms only , to nearly in length. They first appear in the fossil record in the Mississippian period and continue through to the Early Permian. The skull is small but very specialised, with large orbits, and large fenestrae. The primitive form ''Ophiderpeton'' has a pattern of dermal bones in the skull similar in respects to the temnospondyls. But in the advanced genus ''Phlegethontia'' the skull is very light and open, reduced to a series of struts supporting the braincase against the lower jaw, just as in snakes, and it is possible that the aistopods filled the same ecological niches in the Paleozoic that snakes do today. They had an extremely elongated body, with up to 230 vertebrae. The vertebrae were holospondylous, having only a single ossification per segment. They lac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aistopoda
Aistopoda (Greek for " avingnot-visible feet") is an order of highly specialised snake-like stegocephalians known from the Carboniferous and Early Permian of Europe and North America, ranging from tiny forms only , to nearly in length. They first appear in the fossil record in the Mississippian period and continue through to the Early Permian. The skull is small but very specialised, with large orbits, and large fenestrae. The primitive form ''Ophiderpeton'' has a pattern of dermal bones in the skull similar in respects to the temnospondyls. But in the advanced genus ''Phlegethontia'' the skull is very light and open, reduced to a series of struts supporting the braincase against the lower jaw, just as in snakes, and it is possible that the aistopods filled the same ecological niches in the Paleozoic that snakes do today. They had an extremely elongated body, with up to 230 vertebrae. The vertebrae were holospondylous, having only a single ossification per segment. They la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hylerpeton
''Hylerpeton'' is an extinct genus of leponspondyl amphibian belonging to the family Gymnarthridae from the late Carboniferous period. The nominal species ''"Hylerpeton" longidentatum'' Dawson, 1876 was considered possibly non-microsaurian by Steen (1934) and Carroll (1966), and was eventually recognized as a member of Aistopoda and renamed ''Andersonerpeton ''Andersonerpeton'' is an extinct genus of aïstopod from the Bashkirian (early Pennsylvanian) of Nova Scotia, Canada. It is known from a single jaw, which shares an unusual combination of features from both other aistopods and from stem-tetrap ... longidentatum'' by Pardo and Mann (2018) as the type species of a new genus.Jason D. Pardo and Arjan Mann, 2018. A basal aïstopod from the earliest Pennsylvanian of Canada, and the antiquity of the first limbless tetrapod lineage5Royal Society Open Science http://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.181056 References Gymnarthrids Carboniferous amphibians of North America Fossil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Carboniferous
Late may refer to: * LATE, an acronym which could stand for: ** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia ** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law ** Local average treatment effect, a concept in econometrics Music * ''Late'' (album), a 2000 album by The 77s * Late!, a pseudonym used by Dave Grohl on his '' Pocketwatch'' album * Late (rapper), an underground rapper from Wolverhampton * "Late" (song), a song by Blue Angel * "Late", a song by Kanye West from '' Late Registration'' Other * Late (Tonga), an uninhabited volcanic island southwest of Vavau in the kingdom of Tonga * "Late" (''The Handmaid's Tale''), a television episode * LaTe, Oy Laivateollisuus Ab, a defunct shipbuilding company * Late may refer to a person who is Dead See also * * * '' Lates'', a genus of fish in the lates perch family * Later (other) * Tardiness * Tardiness (scheduling) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coloraderpeton
''Coloraderpeton'' is an extinct genus of aïstopod tetrapodomorphs within the family Oestocephalidae. ''Coloraderpeton'' is known from the Carboniferous Sangre de Cristo Formation of Colorado, and was initially known from vertebrae, ribs, and scales recovered from a UCLA field expedition in 1966. Peter Paul Vaughn described these remains in 1969. A skull was later reported in an unpublished 1983 thesis and formally described by Jason S. Anderson Jason ( ; ) was an ancient Greek mythological hero and leader of the Argonauts, whose quest for the Golden Fleece featured in Greek literature. He was the son of Aeson, the rightful king of Iolcos. He was married to the sorceress Medea. H ... in 2003. References Aistopods Carboniferous amphibians Carboniferous amphibians of North America Fossil taxa described in 1969 {{paleo-amphibian-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboniferous Amphibians
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carboniferous'' means "coal-bearing", from the Latin '' carbō'' (" coal") and '' ferō'' ("bear, carry"), and refers to the many coal beds formed globally during that time. The first of the modern 'system' names, it was coined by geologists William Conybeare and William Phillips in 1822, based on a study of the British rock succession. The Carboniferous is often treated in North America as two geological periods, the earlier Mississippian and the later Pennsylvanian. Terrestrial animal life was well established by the Carboniferous Period. Tetrapods (four limbed vertebrates), which had originated from lobe-finned fish during the preceding Devonian, became pentadactylous in and diversified during the Carboniferous, including early amphibian lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Prehistoric Amphibians
This list of prehistoric amphibians is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be amphibians, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful (''nomina dubia''), or were not formally published ('' nomina nuda''), as well as junior synonyms of more established names, and genera that are no longer considered amphibians. Modern forms are excluded from this list. The list currently includes 454 names. Naming conventions and terminology Naming conventions and terminology follow the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. Technical terms used include: * Junior synonym: A name which describes the same taxon as a previously published name. If two or more genera are formally designated and the type specimens are later assigned to the same genus, the first to be published (in chronological order) is the senior synon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lethiscus
''Lethiscus'' is the earliest known representative of the Aistopoda, a group of very specialised snake-like amphibians known from the early Carboniferous (Mississippian). ''Lethiscus'' is known from only a single specimen from the Holkerian Stage (Middle Viséan) of the Early Carboniferous (Middle Mississippian) of Scotland, and is one of the oldest known post Devonian tetrapods. Despite its very early date, it was already a highly advanced animal. The skull is specialised and light, very like that of ''Ophiderpeton'', with the orbits, far forward, and the cheek region unossified (lacking bone). There are approximately 30 closely spaced teeth on the maxilla and dentary, and a sutural pattern of the skull closely resembles that of the Late Carboniferous aïstopod ''Oestocephalus''. There is no trace of limbs. However, unlike later members of the aïstopod lineage, the vertebrae still possess intercentra, and the pleurocentra are large. ''Lethiscus'' is the only representa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurocranium
In human anatomy, the neurocranium, also known as the braincase, brainpan, or brain-pan is the upper and back part of the skull, which forms a protective case around the brain. In the human skull, the neurocranium includes the calvaria or skullcap. The remainder of the skull is the facial skeleton. In comparative anatomy, neurocranium is sometimes used synonymously with endocranium or chondrocranium. Structure The neurocranium is divided into two portions: * the membranous part, consisting of flat bones, which surround the brain; and * the cartilaginous part, or chondrocranium, which forms bones of the base of the skull. In humans, the neurocranium is usually considered to include the following eight bones: * 1 ethmoid bone * 1 frontal bone * 1 occipital bone * 2 parietal bones * 1 sphenoid bone * 2 temporal bones The ossicles (three on each side) are usually not included as bones of the neurocranium. There may variably also be extra sutural bones present. Below the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant taxon, extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (pelycosaurs, extinct therapsids and all extant mammals). Tetrapods evolved from a clade of primitive semiaquatic animals known as the Tetrapodomorpha which, in turn, evolved from ancient lobe-finned fish (sarcopterygians) around 390 million years ago in the Middle Devonian, Middle Devonian period; their forms were transitional between lobe-finned fishes and true four-limbed tetrapods. Limbed vertebrates (tetrapods in the broad sense of the word) are first known from Middle Devonian trackways, and body fossils became common near the end of the Late Devonian but these were all aquatic. The first crown group, crown-tetrapods (last common ancestors of extant tetrapods capable of terrestrial locomotion) appeared by the very early Mississippian ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |