|
Ancient Northern East Asian
In archaeogenetics, the term Ancient Northern East Asian (ANEA), also known as Northern East Asian (NEA), is used to summarize the related ancestral components that represent the Ancient Northern East Asian peoples, extending from the Baikal region to the Yellow River and the Qinling-Huaihe Line in present-day central China. They are inferred to have diverged from Ancient Southern East Asians (ASEA) around 20,000 to 26,000 BCE. The ANEA can be differentiated into broadly three sub-groups, namely the “Ancient Northeast Asians“ (ANA), “Neo-Siberians", and "Yellow River farmers". The ANEA are to be distinguished from the namely similar "Ancient Northeast Asian" (ANA) lineage, which is alternatively also known as "Amur ancestry", and which forms a sub-group of the ANEA grouping, specifically ancestral to hunter-gatherer people of the 7th-4th millennia before present, in the Amur region and later expanding to far-eastern Siberia, Mongolia and the Baikal regions, but which ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Northeast Asian
In archaeogenetics, the term Ancient Northeast Asian (ANA), also known as Amur ancestry, is the name given to an ancestral component that represents the lineage of the hunter-gatherer people of the 7th-4th millennia before present, in far-eastern Siberia, Mongolia and the Baikal regions. They are inferred to have diverged from Ancient East Asians about 24kya ago, and are represented by several ancient human specimens found in archaeological excavations east of the Altai Mountains. They are a sub-group of the Ancient Northern East Asians (ANEA). Neolithic populations The Prehistoric populations of Eastern Siberia are poorly understood, mainly due to the lack of archaeological specimens. So far, the oldest populations for which genomic data have been obtained are the Upper Paleolithic Ancient North Eurasians (c. 24,000 BP) from Central Siberia, and Upper-Paleolithic populations related to the "Basal-East Asian" Tianyuan man (c. 40,000 BP), specifically the Salkhit (c. 34,000 BP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altai-Sayan Region
The Altai-Sayan region is an area of Inner Asia proximate to the Altai Mountains and the Sayan Mountains, near to where Russia, China, Mongolia and Kazakhstan come together. This region is one of the world centers of temperate plant diversity. Its biological, landscape, historical, cultural and religious diversity is unique. 3,726 species of vascular plants are registered in the region including 700 threatened or rare species, 317 of which are endemic; fauna consists of 680 species, 6% of which are endemic. Its ecosystem is comparatively unchanged since the last ice age, and it is the host of endangered species that include the saiga, nerpa, and snow leopard. It is the focus of ongoing international and regional environmental conservation initiatives. The area is also culturally diverse, with four language groups ( Russian, Mongolian, Sinitic and Turkic, formerly Samoyedic and Yeniseian as well) and more than 20 indigenous ethnic groups practicing traditional land use syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
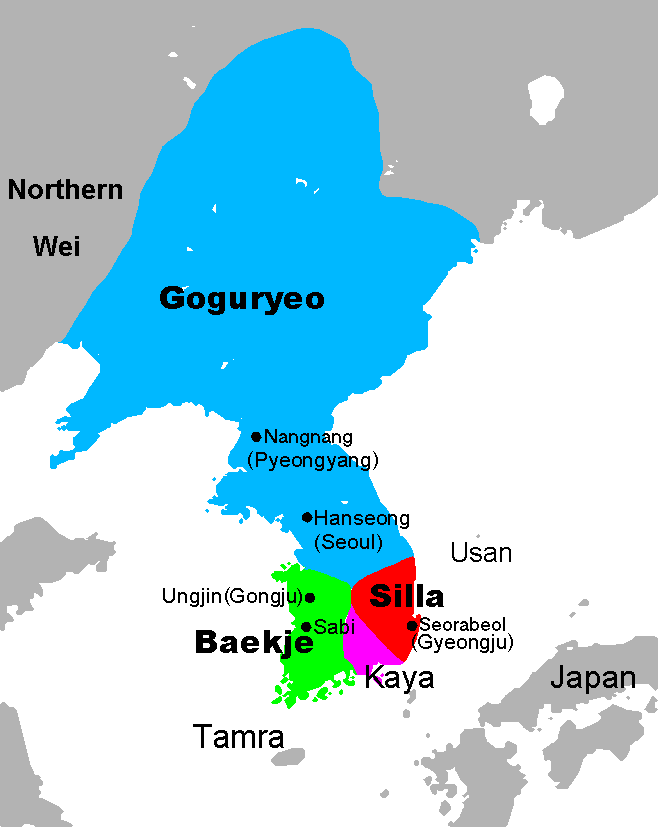
History Of East Asia
The History of East Asia generally encompasses the histories of China, Japan, Korea, Mongolia, and Taiwan from prehistoric times to the present. East Asia is not a uniform term and each of its countries has a different national history, but East Asian Studies scholars maintain that the region is also characterized by a distinct pattern of historical development. This is evident in the interrelationship among traditional East Asian civilizations, which not only involve the sum total of historical patterns but also a specific set of patterns that has affected all or most of traditional East Asia in successive layers. Background The study of East Asian history as an area study is a part of the rise of East Asian studies as an academic field in the Western World. The teaching and studying of East Asian history began in the West during the late 19th century. In the United States, Asian Americans around the time of the Vietnam War believed that most history courses were Euroc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeogenetic Lineages
Archaeogenetics is the study of ancient DNA using various molecular genetic methods and DNA resources. This form of genetic analysis can be applied to human, animal, and plant specimens. Ancient DNA can be extracted from various fossilized specimens including bones, eggshells, and artificially preserved tissues in human and animal specimens. In plants, Ancient DNA can be extracted from seeds and tissue. Archaeogenetics provides us with genetic evidence of ancient population group migrations, domestication events, and plant and animal evolution. The ancient DNA cross referenced with the DNA of relative modern genetic populations allows researchers to run comparison studies that provide a more complete analysis when ancient DNA is compromised. Archaeogenetics receives its name from the Greek word ''arkhaios'', meaning "ancient", and the term ''genetics'', meaning "the study of heredity". The term archaeogenetics was conceived by archaeologist Colin Renfrew. In February 2021, scienti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal (, russian: Oзеро Байкал, Ozero Baykal ); mn, Байгал нуур, Baigal nuur) is a rift lake in Russia. It is situated in southern Siberia, between the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast, Irkutsk Oblasts of Russia, Oblast to the northwest and the Republic of Buryatia to the southeast. With of water, Lake Baikal is the world's List of lakes by volume, largest freshwater lake by volume, containing 22–23% of the world's fresh surface water, more than all of the North American Great Lakes combined. It is also the world's List of lakes by depth, deepest lake, with a maximum depth of , and the world's ancient lake, oldest lake, at 25–30 million years. At —slightly larger than Belgium—Lake Baikal is the world's List of lakes by area, seventh-largest lake by surface area. It is among the world's clearest lakes. Lake Baikal is home to thousands of species of Plant, plants and animals, many of them endemic to the region. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region. Shandong has played a major role in Chinese history since the beginning of Chinese civilization along the lower reaches of the Yellow River. It has served as a pivotal cultural and religious center for Taoism, Chinese Buddhism and Confucianism. Shandong's Mount Tai is the most revered mountain of Taoism and a site with one of the longest histories of continuous religious worship in the world. The Buddhist temples in the mountains to the south of the provincial capital of Jinan were once among the foremost Buddhist sites in China. The city of Qufu is the birthplace of Confucius and was later established as the center of Confucianism. Confucianism developed from what was later called the Hundred Schools of Thought from the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius. Shandong's location at the intersection of ancient and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chertovy Vorota Cave
Chertovy Vorota Cave (known as Devil's Gate Cave in English) is a Neolithic archaeological site located in the Sikhote-Alin mountains, about from the town of Dalnegorsk in Primorsky Krai, Russia. The karst cave is located on a limestone cliff and lies about above the Krivaya River, a tributary of the Rudnaya River, below. Chertovy Vorota provides secure evidence for some of the oldest surviving textiles found in the archaeological record. Description The cave consists of a main chamber, measuring around in length, and several smaller galleries behind it. The site was looted several times before the first archaeological excavations were performed in 1973. Around 600 lithic, osteological and shell artefacts, 700 pottery fragments, and over 700 animal bones were recovered from the site. A .6 cm thick jade disk made from brownish-green jade and measuring in diameter was also recovered from Chertovy Vorota. The remains of racoon dog, brown bear, Asian black bear, wild boar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungusic Languages
The Tungusic languages (also known as Manchu-Tungus and Tungus) form a language family spoken in Eastern Siberia and Manchuria by Tungusic peoples. Many Tungusic languages are endangered. There are approximately 75,000 native speakers of the dozen living languages of the Tungusic language family. Some linguists consider Tungusic to be part of the controversial Altaic language family, along with Turkic, Mongolic, and sometimes Koreanic and Japonic. The term "Tungusic" is from an exonym for the Evenk people (Ewenki) used by the Yakuts ("tongus"). It was borrowed into Russian as "тунгус", and ultimately transliterated into English as "Tungus". Classification Linguists working on Tungusic have proposed a number of different classifications based on different criteria, including morphological, lexical, and phonological characteristics. Some scholars have criticized the tree-based model of Tungusic classification, arguing the long history of contact among the Tungusic langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongolic Languages
The Mongolic languages are a language family spoken by the Mongolic peoples in Eastern Europe, Central Asia, North Asia and East Asia, mostly in Mongolia and surrounding areas and in Kalmykia and Buryatia. The best-known member of this language family, Mongolian, is the primary language of most of the residents of Mongolia and the Mongol residents of Inner Mongolia, with an estimated 5.7+ million speakers. Classification The Mongolic languages have no convincingly established living relatives. The closest relatives of the Mongolic languages appear to be the para-Mongolic languages, which include the extinct Khitan, Tuyuhun, and possibly also Tuoba languages. A few linguists have grouped Mongolic with Turkic, Tungusic and possibly Koreanic and Japonic as part of the widely discredited Altaic family. History The stages of Historical Mongolic are: * Pre-Proto-Mongolic, from approximately the 4th century AD until the 12th century AD, influenced by Common Turkic, and prev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic Languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of over 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and Western Asia. The Turkic languages originated in a region of East Asia spanning from Mongolia to Northwest China, where Proto-Turkic is thought to have been spoken, from where they expanded to Central Asia and farther west during the first millennium. They are characterized as a dialect continuum. Turkic languages are spoken by some 200 million people. The Turkic language with the greatest number of speakers is Turkish, spoken mainly in Anatolia and the Balkans; its native speakers account for about 38% of all Turkic speakers. Characteristic features such as vowel harmony, agglutination, subject-object-verb order, and lack of grammatical gender, are almost universal within the Turkic family. There is a high degree of mutual intelligibility, upon moderate expo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeniseian Languages
The Yeniseian languages (sometimes known as Yeniseic or Yenisei-Ostyak;" Ostyak" is a concept of areal rather than genetic linguistics. In addition to the Yeniseian languages it also includes the Uralic languages Khanty and Selkup. occasionally spelled with -ss-) are a family of languages that are spoken by the Yeniseian people in the Yenisei River region of central Siberia. As part of the proposed Dené–Yeniseian language family, the Yeniseian languages have been argued to be part of "the first demonstration of a genealogical link between Old World and New World language families that meets the standards of traditional comparative-historical linguistics". The only surviving language of the group today is Ket. From hydronymic and genetic data, it is suggested that the Yeniseian languages were spoken in a much greater area in ancient times, including parts of northern China and Mongolia.Vajda, Edward J. (2013). Yeniseian Peoples and Languages: A History of Yeniseian Studie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glazkovo Culture
Glazkov culture is an archaeological culture of possibly proto-Tungusic tribes in the Bronze Age (18th-13th centuries BCE), spread in the Baikal area. The Glazkov culture came to Siberia from the south, displacing Yukagir tribes. Glazkovs is a conditional name for the group of the ancient tribes inhabiting Siberia in the 2nd millennium BCE (Glazkov time) the headwaters of Angara river.Gumilev L.N., ''"History of Hun People"'', Moscow, 'Science', Ch.2, http://gumilevica.kulichki.net/HPH/hph02.htm (In Russian) Glazkov culture is named after a suburb of the city Irkutsk, where it was first found. Areal Archeologists distinguish in the 2nd millennium BCE Southern Siberia two synchronous independent cultures: Glazkov in the east and the Andronovo culture in the west. "In the Baikal territory lived a Glazkov group of related tribes, most likely the ancestors of modern Evenks, Evens or Yukagirs. Their culture was very close to the culture of the inhabitants of the upper Amur and Nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |