|
Ancient Greek Funerary Vases
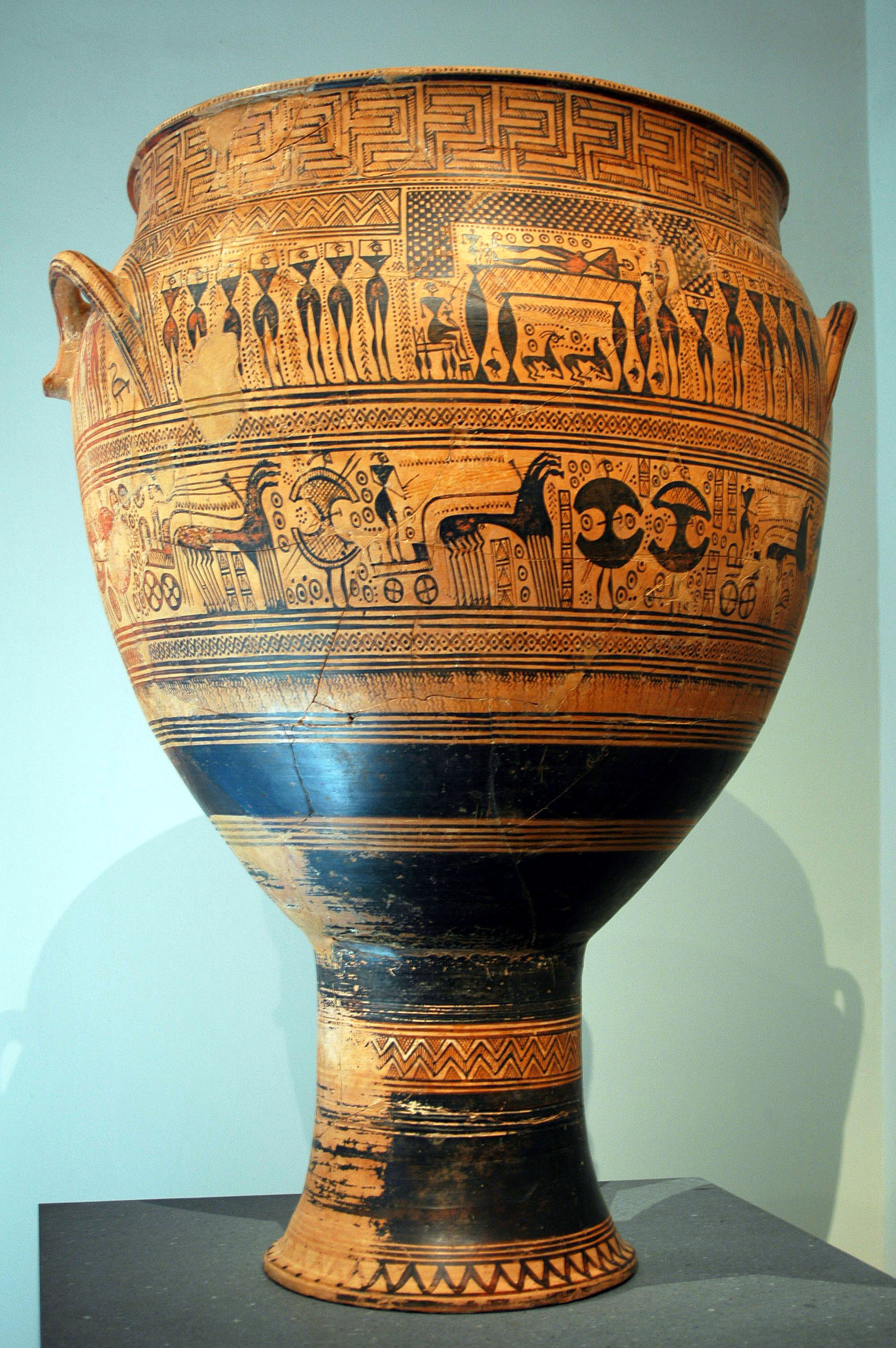
Ancient Greek funerary vases are decorative grave markers made in ancient Greece that were designed to resemble liquid-holding vessels. These decorated vases were placed on grave sites as a mark of elite status. There are many types of funerary vases, such as amphorae, kraters, oinochoe, and kylix cups, among others. One famous example is the Dipylon Amphora, Dipylon amphora. Every-day vases were often not painted, but wealthy Greeks could afford luxuriously painted ones. Funerary vases on male graves might have themes of military prowess, or athletics. However, allusions to death in Greek tragedies was a popular motif. Famous centers of vase styles include Corinth, Lakonia, Ionia, South Italy, and Athens. Uses One major type of funerary vase was the krater, a mixing bowl for wine and water used by elite Greek males at symposiums. Symposiums were an eastern influence in which the aristocracy would lie down and drink; many Greek painters referenced this lifestyle in their art. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WLA Metmuseum Krater Hirschfeld Workshop
WLA may refer to: *Airwaves Airlink (ICAO: WLA), a Zambian airline *Harley-Davidson WLA, a motorcycle produced during World War 2 *Washington Library Association *Weak-Link Approach, a molecular assembly methodology *West Los Angeles, Los Angeles, California, a region within the Westside of Los Angeles County, a much larger area often referred to by the same name *Western Lacrosse Association, a Senior A box lacrosse league in British Columbia, Canada *White Ladies Aston, a village and civil parish in Worcestershire, England *Winnebago Lutheran Academy, a Lutheran high school in Fond du Lac, Wisconsin *Wisconsin Library Association *Wyoming Library Association *Women's Land Army, the name for several groups of women recruited in wartime to work in agriculture *Workload automation, Workload Automation, an Information Technology tool used to automate IT and business processes. *World Literature Assignment 1 and 2 in IB Group 1 subjects in the IB Diploma Programme {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achilles Painter
The Achilles Painter was a vase-painter active ca. 470–425 BC. His name vase is an amphora, Vatican 16571, in the Vatican Museums depicting Achilles and dated 450–445 BC. An armed and armored Achilles gazes pensively to the right with one hand on his hip. The other hand holds a spear. On the opposite surface a woman performs libation. J. D. Beazley attributed over 200 vases to his hand, the largest share being red-figure and white-ground lekythoi. In his middle phase (ca. 450–445 BC), he decorates more open forms. The Achilles Painter was a late pupil of the Berlin Painter. The Phiale Painter became the Achilles Painter's most prominent student after he assumed the Berlin Painter's workshop. Almost a dozen other recognizable painters passed through the Achilles Painter's workshop as well. Notable painters include the Westreenen Painter, the Persephone Painter, the Clio Painter, Loeb Painter, and the Dwarf Painter. The Kleophon Painter, the Sabouroff Painter, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thanatos
In Greek mythology, Thanatos (; , ''Thánatos'', pronounced in "Death", from θνῄσκω ''thnēskō'' "(I) die, am dying") was the Personifications of death, personification of death. He was a minor figure in Greek mythology, often referred to but rarely appearing in person. His name is transliterated in Latin as ''Thanatus'', but his counterpart in Roman mythology is Mors (mythology), Mors or Letum. In myth and poetry The Greece, Greek poet Hesiod established in his ''Theogony'' that Thánatos has no father, but is the son of Nyx (mythology), Nyx (Night) and brother of Hypnos (Sleep).Hesiod, ''Theogony'' 758 ff, trans. Evelyn-White, Greek epic 8th or 7th century BC Homer earlier described Hypnos and Thanatos as twin brothers in his epic poem, the ''Iliad'', where they were charged by Zeus via Apollo with the swift delivery of the slain hero Sarpedon (Trojan War hero), Sarpedon to his homeland of Lycia. Counted among Thanatos' siblings were other negative personifica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipylon Amphora Close Front (Prothesis)
The Dipylon (, "Two-Gated") was the main gate in the city wall of Classical Athens. Located in the modern suburb of Kerameikos, it led to the namesake ancient cemetery, and to the roads connecting Athens with the rest of Greece. The gate was of major ceremonial significance as the starting point of the procession of the Great Panathenaea, and accordingly it was a large, monumental structure, "the largest gate of the ancient world". Erected in 478 BC as part of Themistocles' fortification of Athens and rebuilt in the 300s BC, it remained standing and in use until the 3rd century AD. History The Dipylon gate was built, along with the neighbouring Sacred Gate, in 478 BC as part of Themistocles' fortification of Athens following the Persian Wars. The new circuit was much wider than the old one that was destroyed by the Persians, and many of the graves and monuments of the already existing Kerameikos cemetery were used in its construction, a fact which earned Themistocles the hostilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bier
A bier is a stand on which a corpse, coffin, or casket containing a corpse is placed to lie in state or to be carried to its final disposition.''The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language'' (American Heritage Publishing Co., Inc., New York, 1973), s.v., "bier" In Christian burial, the bier is often placed in the centre of the nave with candles surrounding it, and remains in place during the funeral. The bier is a flat frame, traditionally wooden but sometimes of other materials. In antiquity it was often a wooden board on which the dead were placed, covered with a shroud. In modern times, the corpse is rarely carried on the bier without being first placed in a coffin or casket, though the coffin or casket is sometimes kept open. A bier is often draped with cloth to lend dignity to the funeral service. The modern funeral industry uses a collapsible aluminium bier on wheels, known as a "church truck" to move the coffin to and from the church or funeral home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shroud
Shroud usually refers to an item, such as a cloth, that covers or protects some other object. The term is most often used in reference to ''burial sheets'', mound shroud, grave clothes, winding-cloths or winding-sheets, such as the Jewish '' tachrichim'' or Muslim ''kaffan'', that the body is wrapped in for burial. A famous example of this is the Shroud of Turin. A traditional Jewish shroud consists of a tunic; a hood; pants that are extra-long and sewn shut at the bottom, so that separate foot coverings are not required; and a belt, which is tied in a knot shaped like the Hebrew letter ''shin'', mnemonic of one of God's names, Shaddai. Traditionally, mound shrouds are made of white cotton, wool or linen, though any material can be used so long as it is made of natural fibre. Intermixture of two or more such fibres is forbidden, due to the prohibition of Shaatnez. A pious Jewish man may next be enwrapped in either his kittel or his tallit, one tassel of which is defaced t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Art
Geometric art is a phase of Greek art, characterized largely by geometric Motif (visual arts), motifs in Pottery, vase painting, that flourished towards the end of the Greek Dark Ages and a little later, . Its center was in ancient Athens, Athens, and from there the style spread among the trading cities of the Aegean Islands, Aegean. The so-called Greek Dark Ages were considered to last from and include the phases from the Protogeometric style, Protogeometric period to the Middle Geometric I period, which Knodell (2021) calls Prehistoric Iron Age. The vases had various uses or purposes within Greek society, including, but not limited to, Ancient Greek funerary vases, funerary vases and symposium vases. Usage Funerals Large funerary vases (often Dipylon kraters for men, and belly-handled Amphora, amphorae for women) not only depicted funerary scenes, but they also Ancient Greek funeral and burial practices, had practical purposes, either holding the ashes or being used as grave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swastikas
The swastika (卐 or 卍, ) is a symbol used in various Eurasian religions and cultures, as well as a few Indigenous peoples of Africa, African and Indigenous peoples of the Americas, American cultures. In the Western world, it is widely recognized as a symbol of the German Nazi Party who Cultural appropriation, appropriated it for their party insignia starting in the early 20th century. The appropriation continues with its use by Neo-Nazism, neo-Nazis around the world. The swastika was and continues to be used as a symbol of divinity and spirituality in Indian religions, including Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism. It generally takes the form of a cross, the arms of which are of equal length and perpendicular to the adjacent arms, each bent midway at a right angle. The word ''swastika'' comes from , meaning 'conducive to well-being'. In Hinduism, the right-facing symbol (clockwise) () is called , symbolizing ('sun'), prosperity and good luck, while the left-facing symbol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphronios Krater (8254576758)2
The Euphronios Krater (or Sarpedon Krater) is an ancient Greek terra cotta calyx-krater, a bowl used for mixing wine with water. Created around the year 515 BC, it is the only complete example of the surviving 27 vases painted by the renowned Euphronios and is considered one of the finest Ancient Greek vases in existence. Illegally excavated from an Etruscan cemetery near Cerveteri, it was part of the collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York from 1972 to 2008, until repatriated to Italy under an agreement negotiated in February 2006. It is now in the collection of the as part of a policy of returning stolen works of art to their place of origin. Description The Euphronios Krater stands in height and has a diameter of . It can hold about . The style of the vase is red-figure pottery, in which figure outlines, details, and the background are painted with an opaque black slip while the figures themselves are left in the color of the unpainted terracotta ceramic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regina Vasorum
The ''Regina Vasorum'' or ''Queen of Vases'' is a 4th-century BC hydria from Cumae depicting Eleusinian divinities with gilded flesh in polychrome relief. It is held in the collections of the Hermitage Museum, St. Petersburg. In addition to its aesthetic qualities, it is valued as an iconographical source for ancient Greek religion. The ''Regina Vasorum'' is a "spectacular" and unusually large example of technical experimentation among Greek potters after the red-figure style had run its course.Harvey Alan Shapiro, Carlos A. Picón, Gerry D. Scott, "Introduction to South Italian Vases," in ''Greek Vases'' (San Antonio Museum of Art, 1995), p. 25online./ref> The figures were made separately, painted, and gilded, then attached to the vase with slip, possibly by sprigging. See also * South Italian ancient Greek pottery South Italian is a designation for ancient Greek pottery fabricated in Magna Graecia largely during the 4th century BC. The fact that Greek Southern Italy produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydria
The hydria (; : hydriai) is a form of Greek pottery from between the Geometric art, late Geometric period (7th century BC) and the Hellenistic period (3rd century BC). The etymology of the word hydria was first noted when it was stamped on a hydria itself, its direct translation meaning 'jug'. It is a type of water-carrying vessel, but it had many other purposes. As time progressed the hydria developed into many forms, some of which were smaller or of a different material. These variants were decorated with detailed figures to represent Greek mythological stories, as well as scenes of daily life, providing extensive insight into Culture of ancient Greece, Ancient Greek culture and society. Function Originally, the hydria's purpose was for the collection of water, but it also held oil and the votes of judges. The design of the hydria allowed for the efficient collecting and pouring of liquids as it possessed three handles: two horizontal ones at its sides and a vertical one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |