|
Anchor (climbing)
In rock climbing, an anchor can be any device or method for attaching a climber, rope, or load to a climbing surfacetypically rock, ice, steep dirt, or a buildingeither permanently or temporarily. The intention of an anchor is case-specific but is usually for fall protection, primarily fall arrest and fall restraint. Climbing anchors are also used for hoisting, holding static loads, or redirecting (also called deviating) a rope. Types Depending on the surface being climbed, there are many types of protection that can be used to construct an anchor, including natural protection such as boulders and trees, or artificial protection such as cams, nuts, bolts or pitons. Natural A natural anchor is a secure natural feature that can serve as a climbing anchor by attaching a sling, lanyard, or cordelette and a carabiner. Examples of natural anchors include trees, boulders, lodged chockstones, horns, icicles, and protrusions. Artificial An artificial anchor consists of man-made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Climbing
Rock climbing is a climbing sports discipline that involves ascending climbing routes, routes consisting of natural rock in an outdoor environment, or on artificial resin climbing walls in a mostly indoor environment. Routes are documented in climbing guidebook, guidebooks, and on online databases, detailing how to climb the route (called the beta (climbing), beta), and who made the first ascent (or FA) and the coveted First ascent#In rock climbing, first free ascent (or FFA). Climbers will try to ascend a route onsight, however, a climber can spend years projecting (climbing), projecting a route before they make a redpoint (climbing), redpoint ascent. Routes range from a few metres to over a in height, and traverse (climbing), traverses can reach in length. They include slab climbing, slabs, face climbing, faces, crack climbing, cracks and overhang (climbing), overhangs/roofs. Popular rock types are granite (e.g. El Capitan), limestone (e.g. Verdon Gorge), and sandstone (e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
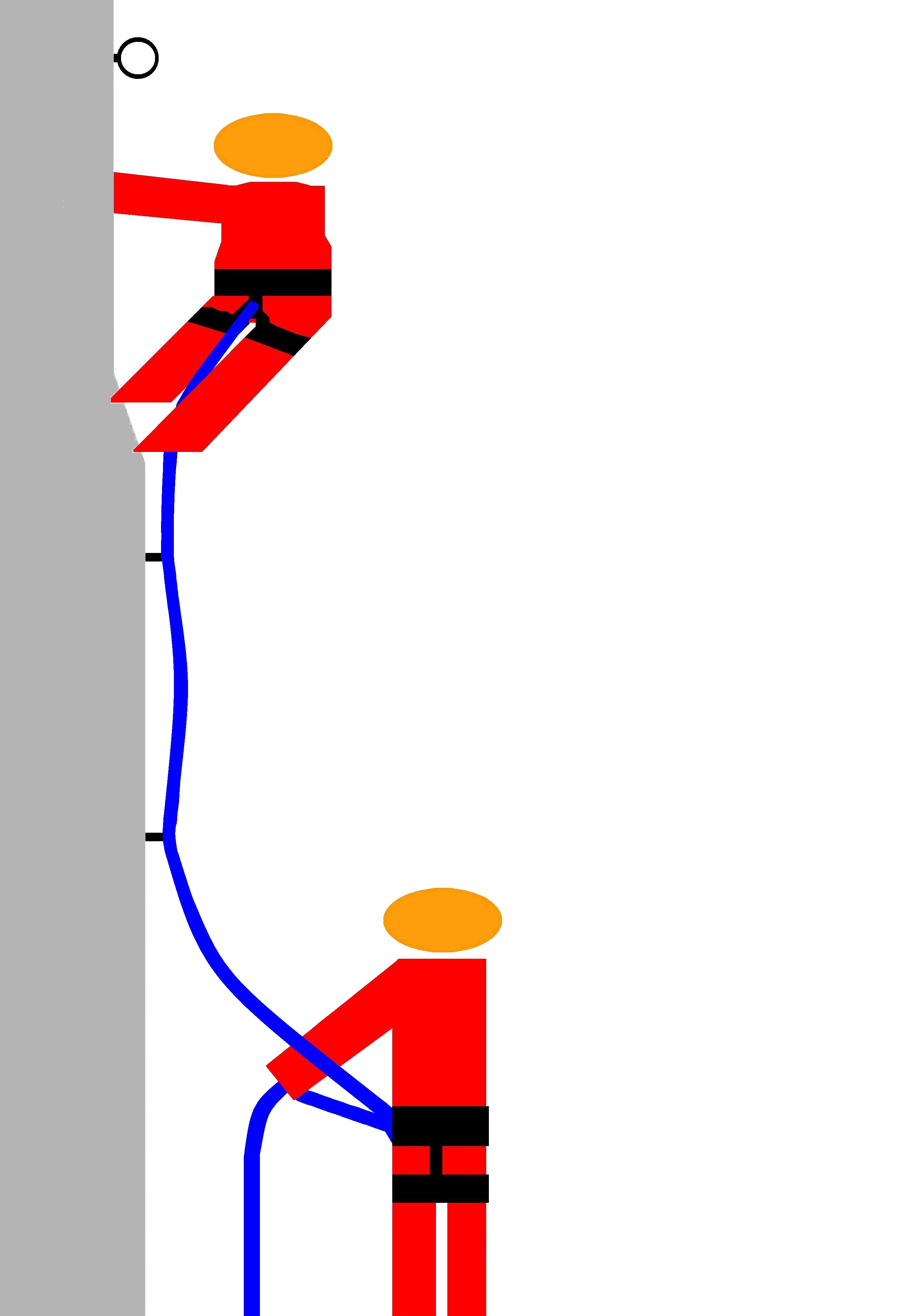
Lead Climbing
Lead climbing (or leading) is a technique in rock climbing where the 'lead climber' Glossary of climbing terms#clip in, clips their rope to the climbing protection as they ascend a pitch (climbing), pitch of the climbing route, while their 'second' (or 'belayer') remains at the base of the route belaying the rope to protect the 'lead climber' in the event that they fall. The term is used to distinguish between the two roles, and the greater effort and increased risk, of the role of the 'lead climber'. Leading a climb is in contrast with top roping a climb, where even though there is still a 'second' belaying the rope, the 'lead climber' faces little or no risk in the event of a fall and does not need to clip into any protection as the rope is already Anchor (climbing), anchored to the top of the route (i.e. if they fall off, they just hang from the rope). Leading a climbing route is a Rock climbing#Description, core activity in rock climbing, and most first ascents and first fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euclidean Vector
In mathematics, physics, and engineering, a Euclidean vector or simply a vector (sometimes called a geometric vector or spatial vector) is a geometric object that has magnitude (or length) and direction. Euclidean vectors can be added and scaled to form a vector space. A '' vector quantity'' is a vector-valued physical quantity, including units of measurement and possibly a support, formulated as a '' directed line segment''. A vector is frequently depicted graphically as an arrow connecting an ''initial point'' ''A'' with a ''terminal point'' ''B'', and denoted by \stackrel \longrightarrow. A vector is what is needed to "carry" the point ''A'' to the point ''B''; the Latin word means 'carrier'. It was first used by 18th century astronomers investigating planetary revolution around the Sun. The magnitude of the vector is the distance between the two points, and the direction refers to the direction of displacement from ''A'' to ''B''. Many algebraic operations on real numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Load Sharing Anchors
Load or LOAD may refer to: Aeronautics and transportation *Load factor (aeronautics), the ratio of the lift of an aircraft to its weight *Passenger load factor, the ratio of revenue passenger miles to available seat miles of a particular transportation operation (e.g. a flight) Biology and medicine *Afterload, the maximum effect of a heartbeat driving blood mass out of the heart into the aorta and pulmonary arteries *Genetic load, of a population *Late-onset Alzheimer's disease (acronym: LOAD), a chronic neurodegenerative disease *Parasite load, of an organism *Viral load, of organisms and populations Computing and electricity *Load (computing), a measure of how much processing a computer performs *Electrical load, a device connected to the output of a circuit * Electronic load, a simulated electrical load used for testing purposes *Invade-a-Load, was a fast loader routine used in software for the Commodore 64 computer; it was used in commercial computer games *Load balancing (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Best Practices
A best practice is a method or technique that has been generally accepted as superior to alternatives because it tends to produce superior results. Best practices are used to achieve quality as an alternative to mandatory standards. Best practices can be based on self-assessment or benchmarking. Best practice is a feature of accredited management standards such as ISO 9000 and ISO 14001. Some consulting firms specialize in the area of best practice and offer ready-made templates to standardize business process documentation. Sometimes a best practice is not applicable or is inappropriate for a particular organization's needs. A key strategic talent required when applying best practice to organizations is the ability to balance the unique qualities of an organization with the practices that it has in common with others. Good operating practice is a strategic management term. More specific uses of the term include good agricultural practices, good manufacturing practice, good l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fall Factor
In lead climbing using a dynamic rope, the fall factor (''f'') is the ratio of the height (''h'') a climber falls before the climber's rope begins to stretch and the rope length (''L'') available to absorb the energy of the fall, :f = \frac. It is the main factor determining the violence of the forces acting on the climber and the gear. As a numerical example, consider a fall of 20 feet that occurs with 10 feet of rope out (i.e., the climber has placed no protection and falls from 10 feet above the belayer to 10 feet below—a factor 2 fall). This fall produces far more force on the climber and the gear than if a similar 20 foot fall had occurred 100 feet above the belayer. In the latter case (a fall factor of 0.2), the rope acts like a bigger, longer rubber band, and its stretch more effectively cushions the fall. Sizes of fall factors The smallest possible fall factor is zero. This occurs, for example, in top-rope a fall onto a rope with no slack. The rope stretches, so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Hitch
The Munter hitch, also known as the Italian hitch, mezzo barcaiolo is a simple adjustable knot, commonly used by climbers, cavers, and rescuers to control friction in a life-lining or belay system. It is often mistakenly identified as the crossing hitch, however in the cross hitch the line does not return along its original path. To climbers, this hitch is also known as HMS, the abbreviation for the German term , meaning ''half clove hitch belay''. This technique can be used with a special "pear-shaped" HMS locking carabiner, or any locking carabiner wide enough to take two turns of the rope. In the late 1950s, three Italian climbers, Mario Bisaccia, Franco Garda and Pietro Gilardoni developed a new belay technique called the "Mezzo Barcaiolo" (MB) meaning; "a half of the knot, which is used by the sailors to secure a boat to a bollard in a harbor." The "MB" came to be known as the Munter hitch after Werner Munter, a Swiss mountain guide popularized its use in mountaineer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quickdraw
QuickDraw was the 2D graphics library and associated application programming interface (API) which is a core part of classic Mac OS. It was initially written by Bill Atkinson and Andy Hertzfeld. QuickDraw still existed as part of the libraries of Mac OS X, but had been largely superseded by the more modern Quartz graphics system. In Mac OS X Tiger, QuickDraw has been officially deprecated. In Mac OS X Leopard applications using QuickDraw cannot make use of the added 64-bit support. In OS X Mountain Lion, QuickDraw header support was removed from the operating system. Applications using QuickDraw still ran under OS X Mountain Lion to macOS High Sierra; however, the current versions of Xcode and the macOS SDK do not contain the header files to compile such programs. Principles of QuickDraw QuickDraw was grounded in the Apple Lisa's LisaGraf of the early 1980s and was designed to fit well with the Pascal-based interfaces and development environments of the early Apple syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
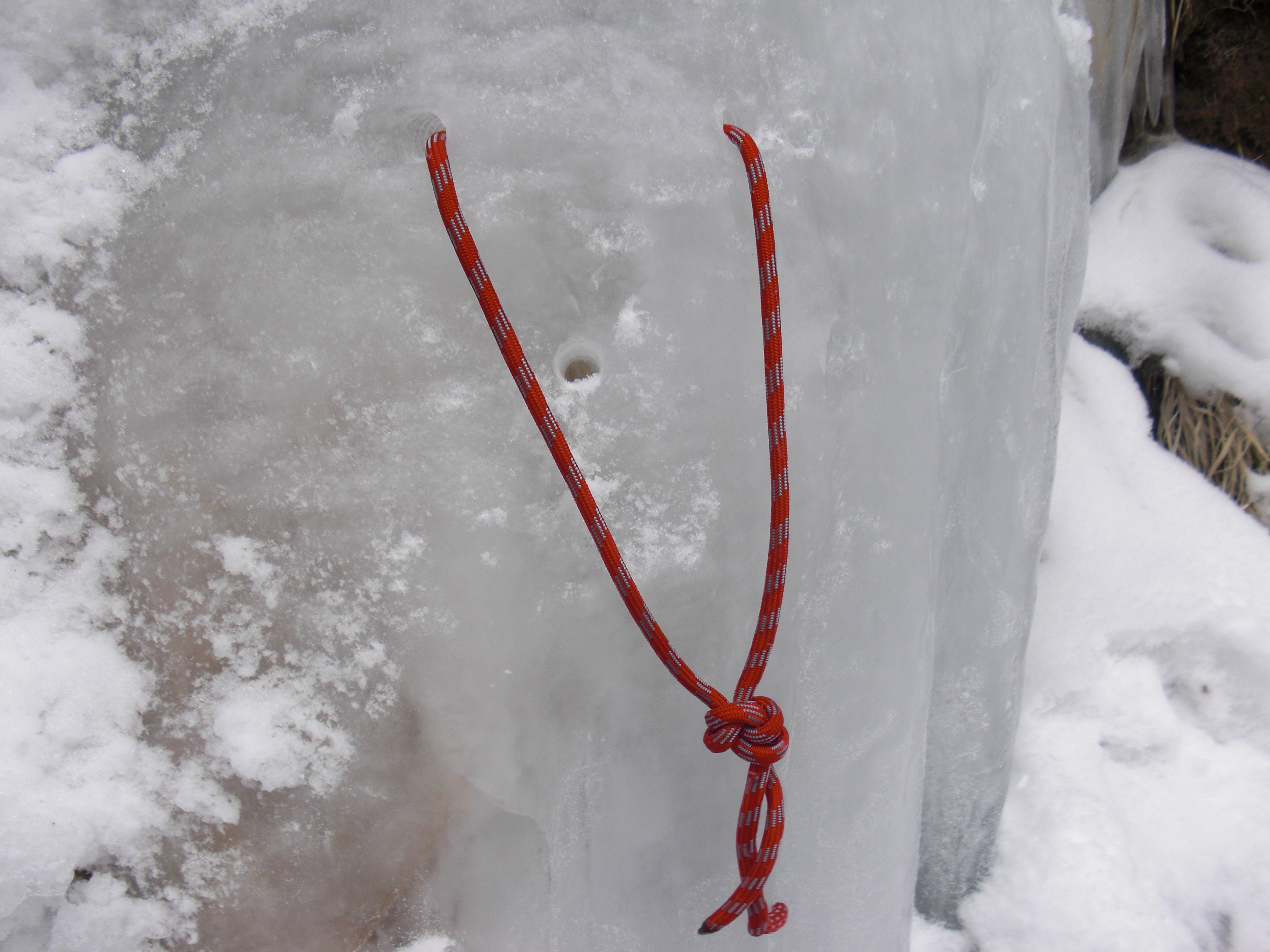
Abalakov Thread
250px, Abseiling with an Abalakov thread The Abalakov thread, also known as a V-thread, A-thread, or 0-thread (zero thread), is an ice protection technique named after its inventor, Soviet climber Vitaly Abalakov. The Abalakov thread is a common method of protecting oneself while ice climbing because it is easy to create, does not require the sacrifice of expensive gear, and can be very safe when used properly. An Abalakov thread is often used in multi-pitch ice climbing routes. Because of its safety and convenience, the Abalakov thread is considered one of the most significant innovations in ice climbing. It significantly expanded the scope of possible routes and abseiling safety. Description An Abalakov thread can be constructed using an ice screw, of appropriate strength cord or webbing, and hook-like Abalakov threading device. Two holes are drilled in the ice, which interconnect at the ends to form a v-like channel in the ice. The cord or webbing is then threaded throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Climbing
Ice climbing is a climbing discipline that involves ascending routes consisting entirely of frozen water. To ascend, the ice climber uses specialist equipment, particularly double ice axes (or the more modern ice tools) and rigid crampons. To protect the route, the ice climber uses steel ice screws that require skill to employ safely and rely on the ice holding firm in any fall. Ice climbing routes can vary significantly by type, and include seasonally frozen waterfalls, high permanently frozen alpine couloirs, and large hanging icicles. From the 1970s, ice climbing developed as a standalone skill from alpine climbing (where ice climbing skills are used on ice and snow). Ice climbing grades peak at WI6 to WI7 as ice tends to hang vertically at its most severe. WI7 is very rare and usually attributed to overhanging ice with serious risk issues (i.e. unstable ice, little protection, and a risk of death). Mixed climbing has pushed the technical difficulty of ice climbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Screw
An ice screw is a threaded tubular Screw fastener, screw used as a running belay or anchor by climbing, climbers on steep ice surface such as steep waterfall ice or alpine ice during ice climbing or crevasse rescue, to hold the climber in the event of a fall, and at belays as anchor points. Design Ice screws may come with one or more of the following: an in-built or separate ratchet mechanism to speed up placement, conical centre-hole to aid removal of ice cores, different lengths, different numbers of cutting teeth, different cutting angles, different surface finishes, and different size clip holes. Price and durability are usually design considerations too, as a usable rack of ice screws will be a significant financial investment for many climbers. Many titanium ice screws were initially made in the former Soviet Union using Cold War-era missile technology, but were generally too brittle, and so the majority of ice screws are now made of 41xx steel, chromoly steel. As of 2011, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |