|
Anatra Anakle
Anatra () was an aircraft manufacturer founded by Artur Antonovich Anatra () at Odesa, Ukraine, then Russian Empire in 1913 which manufactured aircraft until 1917. Artur Anatra had previously helped fund the purchase of the first aircraft to arrive in the Russian Empire, in 1909. The factory began as a naval workshop producing foreign designs, and they constructed approximately twenty aircraft from 1909 through 1912. Anatra licensed designs by Farman, Morane-Saulnier, Nieuport, and Voisin, ultimately building at a rate of as many as sixty per month by 1917.Gunston, 1995, p.1 They also manufactured their own designs for the Russian army during World War I.Gunston, 1993, p.24 Both of its factories were taken over and operated by the Soviets, until eventually being closed in 1922, after having produced 1056 aircraft in Odesa, and 50 at a second location they had opened away, in Simferopol, in Crimea.Durkota, 1995, p.338 Aircraft Anatra started by producing foreign designs under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artur Antonovich Anatra
Artur is a cognate (etymology), cognate to the common male given name Arthur meaning "bear-like", or “of honour”. It is believed to possibly be descended from the Ancient Rome, Roman surname Artoria gens, Artorius or the Celtic bear-goddess Artio or more probably from the Celtic word ''artos'' ("bear"). Other Celtic languages have similar first names, such as Irish language, Old Irish ''Art, Artúur'', Welsh language, Welsh ''Arth'' - which may also be the source for the modern name. ''Art'' is also a diminutive form of the common name Arthur. In Estonian language, Estonian, and many Romance, Slavic and Germanic languages the name is spelled as Artur. The Finnish versions are Artturi and Arttu. Avestan '/arta and its Vedic Sanskrit, Vedic equivalent ''rta, '' both derive from Proto-Indo-Iranian ''*ṛtá-'' "truth", which in turn continues PIE, Proto-Indo-European ''*'' "properly joined, right, true", from the root ''*''. The word is attested in Old Persian as '. People nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farman III
The Farman III, also known as the Henry Farman 1909 biplane, was an early French aircraft designed and built by Henry Farman in 1909. Its design was widely imitated, so much so that aircraft of similar layout were generally referred to as being of the "Farman" type. Background Henry Farman's first aircraft had been bought from the Voisin brothers in 1907. Soon after his first flights, Farman began to modify and improve the design of the aircraft, which was known as either the Farman I or Voisin-Farman I. During 1908, Farman re-covered the aircraft with 'Continental' rubberized fabric and added the side-curtains, and it was re-designated the Farman I-bis. Following the Wilbur Wright-piloted flying demonstrations at Le Mans in August 1908, Farman fitted ailerons to the aircraft. The Voisin brothers built another aircraft, to be called the Farman II, incorporating refinements of the design to Farman's specification. Voisin later sold this aircraft to J.T.C. Moore-Brabazon. Brabaz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatra Anamon
The Anatra Anamon was a Russian prototype monoplane fighter built by the A.A. Anatra factory in World War I. Design The Anamon was a single-seat monoplane fighter of slim plywood fuselage and mid-placed trapezoid wing with cut out viewing aperture. The landing gear was similar to that designed for the Anatra D. Test flights of the Anatra Anamon began June 16, 1916, but pilots complained about the 'long' (150m) takeoff and landing Roll as well as steep gliding. The deep pilot's position also was not appreciated. Improvements were suggested, but after minor damage such plans were axed. Specifications References External links {{Anatra aircraft Anamon Biplanes Single-engined tractor aircraft 1910s Russian military reconnaissance aircraft Aircraft first flown in 1916 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fighter Aircraft
Fighter aircraft (early on also ''pursuit aircraft'') are military aircraft designed primarily for air-to-air combat. In military conflict, the role of fighter aircraft is to establish air supremacy, air superiority of the battlespace. Domination of the airspace above a battlefield permits bombers and attack aircraft to engage in tactical bombing, tactical and strategic bombing of enemy targets, and helps prevent the enemy from doing the same. The key performance features of a fighter include not only its firepower but also its high speed and maneuverability relative to the target aircraft. The success or failure of a combatant's efforts to gain air superiority hinges on several factors including the skill of its pilots, the tactical soundness of its doctrine for deploying its fighters, and the numbers and performance of those fighters. Many modern fighter aircraft also have secondary capabilities such as ground-attack aircraft, ground attack and some types, such as fighter-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
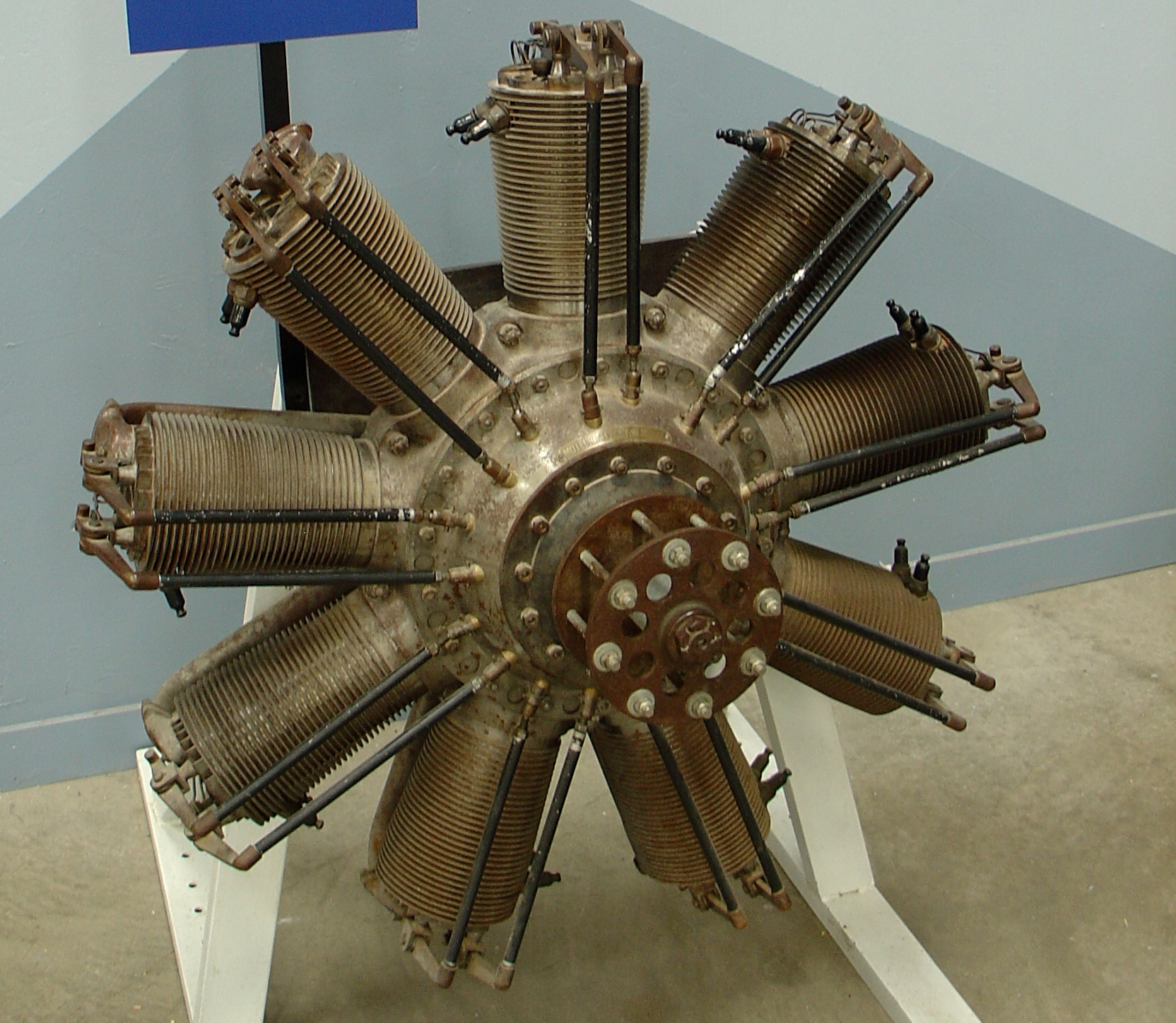
Salmson 9R
The Salmson water-cooled aero-engines, produced in France by Société des Moteurs Salmson from 1908 until 1920, were a series of pioneering aero-engines: unusually combining water-cooling with the radial arrangement of their cylinders. History Henri Salmson, a manufacturer of water pumps, was engaged by Georges Marius Henri-Georges Canton and Pierre Unné, a pair of Swiss engineers, to produce engines to their design. Their initial efforts were on barrel engines, but these failed to meet expectations due to low reliability and high fuel consumption caused by internal friction. A new 7-cylinder water-cooled radial design was then developed by Canton and Unné. The range was expanded to produce 9-cylinder models, and also two-row 14-cylinder and 18-cylinder engines. By 1912 the Salmson A9 was producing around 120 brake horsepower; while competitive with rival designs from French companies, Salmson, Canton and Unné decided to develop more powerful engines as their rivals were c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatra DS
The Anatra DS or Anasal was a two-seat reconnaissance aircraft developed from the Anatra D (Anade). It was built in the Anatra factory in Odessa in the Russian Empire and flown during World War I by both sides during the Russian Civil War. The main difference from the previous model was the replacement of a 100 hp rotary engine with a much more powerful 150 hp Salmson radial engine, which improved performance. The engine was unusual, being one of the few water-cooled radial engines, hence the plane had a water radiator in front of the upper wing. This engine was license-built in Russia. The forward fuselage was similar to its predecessor, with a partial engine cowling, open at the bottom, with characteristic holes. The plane was also slightly larger and more heavily armed, adding a synchronised forward-firing machine gun for the pilot in addition to the observer's weapon. The plane, named Anasal (short for Anatra Salmson) was first flown on 7 August 1916Andrzej Ki� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clerget 9Z
Clerget was the name given to a series of early rotary aircraft engine types of the World War I era that were designed by Pierre Clerget( fr). Manufactured in France by Clerget-Blin and in Great Britain by Gwynnes Limited they were used on such aircraft as the Sopwith Camel and Vickers Gunbus. In the 1920s Pierre Clerget turned his attention to diesel radial engines and finally produced a H-16 engine before he died in 1943. Rotary engine development (spark ignition) What distinguished the Clerget rotary engine from its rivals (Gnome and Le Rhône) was that the Clerget had normal intake and exhaust valves unlike the Gnome, and the connecting rod arrangement was much simpler than the Le Rhone. A source of failure among the Clerget engines were the special-purpose piston rings, called obturator rings. These were located below the gudgeon or wrist pin, to block heat transfer from the combustion area to the lower part of the cylinder and overcome their subsequent distortion. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Russian Air Force
The Imperial Russian Air Service () was an air force founded in 1912 for Imperial Russia."''12 августа 1912 года приказом по военному ведомству вопросы воздухоплавания и авиации были изъяты из ведения Главного инженерного управления и переданы специально созданному органу: в воздухоплавательную часть Генерального штаба. Эта дата считается днём образования военной авиации России''"12 августа 1912 года // "Щит и меч", No. 29 (1333) от 9 августа 2012 года, стр.8 The Air Service operated for five years and only saw combat in World War I before being reorganized and renamed in 1917 following the Russian Revolution. With the onset of the Russian Civil War, some former IRAS pilots joined Alexander Kolchak on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reconnaissance
In military operations, military reconnaissance () or scouting is the exploration of an area by military forces to obtain information about enemy forces, the terrain, and civil activities in the area of operations. In military jargon, reconnaissance is abbreviated to ''recce'' (in British, Canadian, Australian English) and to ''recon'' (in American English), both derived from the root word ''reconnoitre'' / ''reconnoitering''. The types of reconnaissance include patrolling the local area of operations and long-range reconnaissance patrols, which are tasks usually realized in the United States of America by U.S. Army Rangers, cavalry scouts, and military intelligence specialists, using navy ships and submarines, Aerial reconnaissance, reconnaissance aircraft, satellites to collect raw intelligence; and establishing observation posts. Moreover, espionage is different from reconnaissance, because spies work as civilians in enemy territory. Etymology The word is derived from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatra D
The Anatra D or Anade was a two-seat reconnaissance aircraft built in Odessa, Russian Empire and flown during World War I. It was a two-bay biplane of conventional configuration that seated the pilot and observer in tandem, open cockpits. Test flights revealed a number of design flaws, including weak wing structure that would later kill the company test pilot on 21 July 1917 and poor stability. Despite the problems, the aircraft was ordered into production by the Army, and deliveries commenced in May 1916 after revisions had been made to correct the aircraft's centre of gravity in the hope of addressing the worst handling problems. The type continued in limited service after the war, eventually being used as a trainer until about 1919. Operators *Imperial Russian Air Service acquired 170 aircraft, initial deliveries began on 16 May 1916 *Soviet Air Forces *Ukrainian People's Republic Air Fleet The Air Fleet of the UPR was the air force of the Ukrainian People's Republi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
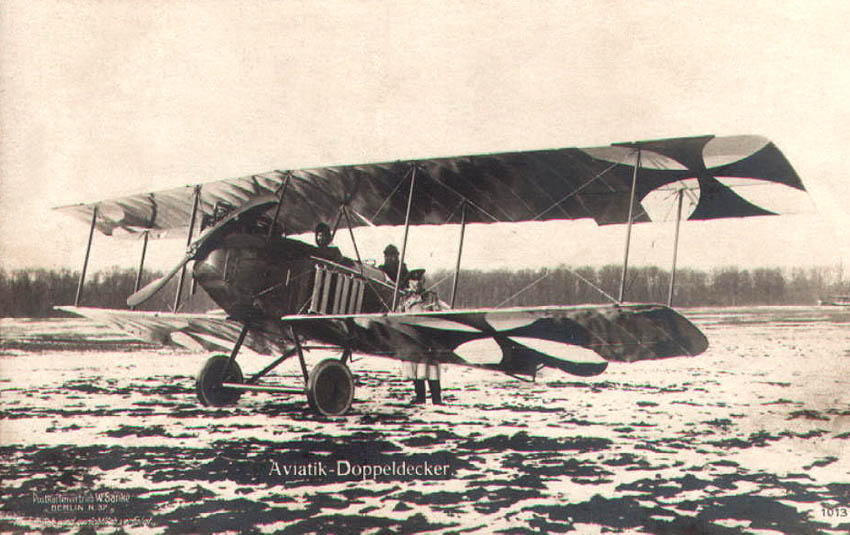
Aviatik
Automobil und Aviatik AG was a German aircraft manufacturer during World War I. The company was established at Mülhausen (today in France) in 1909 and soon became one of the country's leading producers of aircraft. It relocated to Freiburg in 1914 and to Leipzig in 1916 and established a subsidiary in Vienna as Österreichisch-Ungarische Flugzeugfabrik Aviatik. During the war, the company became best known for its reconnaissance aircraft, the B.I and B.II, although the Austro-Hungarian subsidiary also produced a number of its own designs, including fighters such as the D.I. History The company was founded in December 1909 by the Alsatian Georges Chatel. II cover page It started with the license-production of French aircraft; Hanriot monoplanes and Farman biplanes. From 1912, the factory started building its own successful biplanes, designed by Robert Wild. Just at the beginning of World War One, on 1 August 1914 the company was relocated to Freiburg due to French threat, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatra V
Anatra () was an aircraft manufacturer founded by Artur Antonovich Anatra () at Odesa, Ukraine, then Russian Empire in 1913 which manufactured aircraft until 1917. Artur Anatra had previously helped fund the purchase of the first aircraft to arrive in the Russian Empire, in 1909. The factory began as a naval workshop producing foreign designs, and they constructed approximately twenty aircraft from 1909 through 1912. Anatra licensed designs by Farman, Morane-Saulnier, Nieuport, and Voisin, ultimately building at a rate of as many as sixty per month by 1917.Gunston, 1995, p.1 They also manufactured their own designs for the Russian army during World War I.Gunston, 1993, p.24 Both of its factories were taken over and operated by the Soviets, until eventually being closed in 1922, after having produced 1056 aircraft in Odesa, and 50 at a second location they had opened away, in Simferopol, in Crimea.Durkota, 1995, p.338 Aircraft Anatra started by producing foreign designs under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |