|
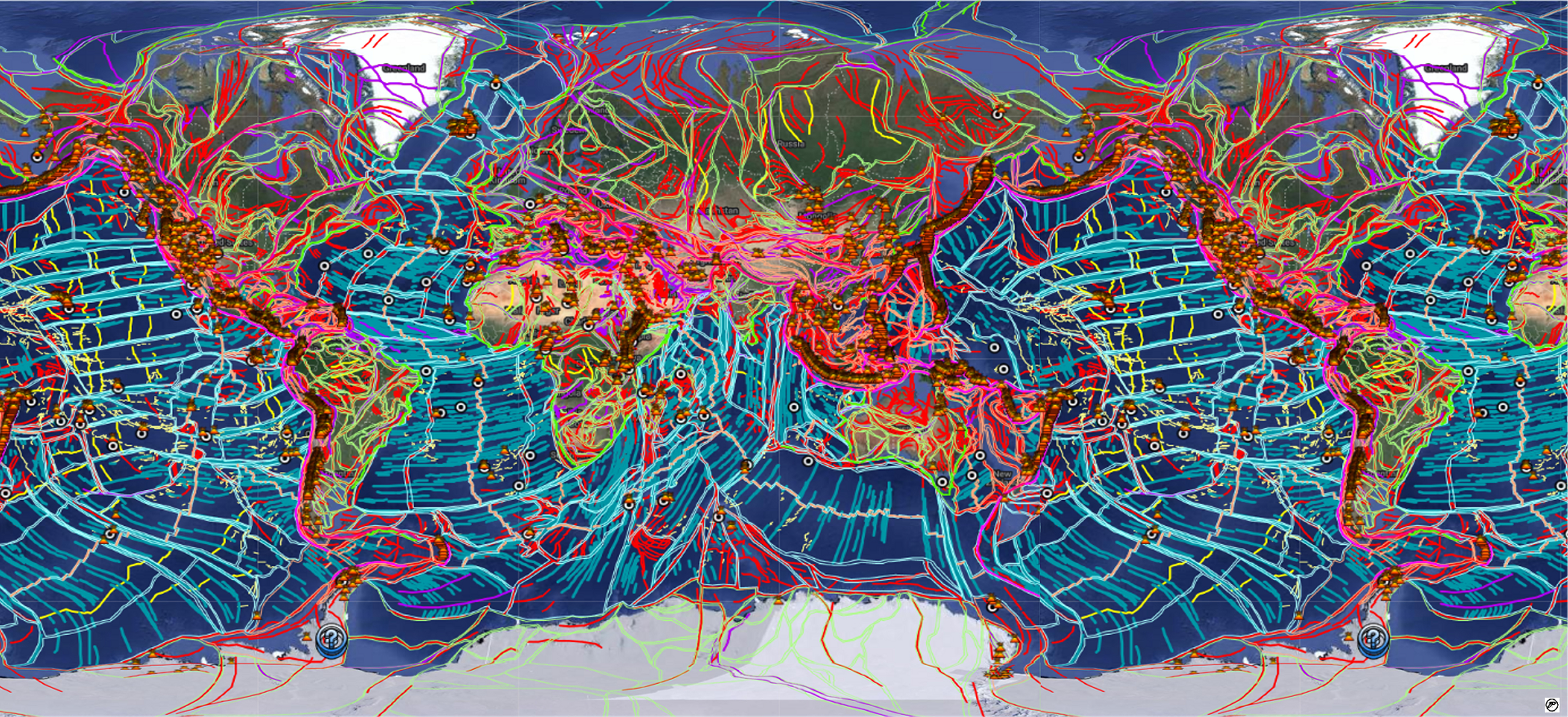
Anatolian Plate
The Anatolian plate is a continental tectonic plate lying under Asiatic part of Turkey, known as Anatolia. Most of the country of Turkey is located on the Anatolian plate. The plate is separated from the Eurasian plate and the Arabian plate by the North Anatolian Fault and the East Anatolian Fault respectively. According to the American Museum of Natural History, the Anatolian transform fault system is "probably the most active in the world". Most significant earthquakes in the region have historically occurred along the northern fault, such as the 1939 Erzincan earthquake. The northern edge is a transform boundary with the Eurasian plate, forming the North Anatolian Fault zone (NAFZ). The East Anatolian Fault, a left lateral transform fault, forms a boundary with the Arabian plate. The devastating 2023 Turkey–Syria earthquakes occurred along the active East Anatolian Fault at a strike-slip fault where the Arabian plate is sliding past the Anatolian plate horizont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Tectonic Plates
This is a list of tectonic plates on Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. Plate tectonics, Tectonic plates are pieces of Earth's crust and uppermost mantle (geology), mantle, together referred to as the lithosphere. The plates are around thick and consist of two principal types of material: oceanic crust (also called ''Sima (geology), sima'' from silicon and magnesium) and continental crust (''sial'' from silicon and aluminium). The composition of the two types of crust differs markedly, with mafic basaltic rocks dominating oceanic crust, while continental crust consists principally of lower-density felsic granite, granitic rocks. Current plates Geologists generally agree that the following tectonic plates currently exist on Earth#Surface, Earth's surface with roughly definable boundaries. Tectonic plates are sometimes subdivided into three fairly arbitrary categories: ''major'' (or ''primary'') ''plates'', ''minor'' (or ''secondary'') ''plates'', and ''microplates'' (or ''tertiary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2023 Turkey–Syria Earthquakes
On 6 February 2023, at 04:17 Time in Turkey, TRT (01:17 Coordinated Universal Time, UTC), a 7.8 earthquake struck southern and central Turkey and northern and western Ba'athist Syria, Syria. The epicenter was west–northwest of Gaziantep. The earthquake had a maximum Modified Mercalli intensity scale, Mercalli intensity of XII (''Extreme'') around the epicenter and in Antakya. It was followed by a 7.7 earthquake at 13:24. This earthquake was centered north-northeast from the first. There was widespread damage and tens of thousands of fatalities. The 7.8 earthquake is the largest in Turkey since the 1939 Erzincan earthquake of the same magnitude, and jointly the second-largest in the country, after larger estimates for the 1668 North Anatolia earthquake. It is also one of the List of earthquakes in the Levant, strongest earthquakes ever recorded in the Levant. It was felt as far as Egypt and the Black Sea coast of Turkey. There were more than List of aftershoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some . In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea, which in turn connects to the Black Sea, by the straits of the Dardanelles and the Bosphorus, respectively. The Aegean Islands are located within the sea and some bound it on its southern periphery, including Crete and Rhodes. The sea reaches a maximum depth of 2,639 m (8,658 ft) to the west of Karpathos. The Thracian Sea and the Sea of Crete are main subdivisions of the Aegean Sea. The Aegean Islands can be divided into several island groups, including the Dodecanese, the Cyclades, the Sporades, the Saronic Islands, Saronic islands and the North Aegean islands, North Aegean Islands, as well as Crete and its surrounding islands. The Dodecanese, located to the southeast, includes the islands of Rhodes, Kos, and Patmos; the islands of Delos and Naxos are wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based hyperbolic navigation system owned by the United States Space Force and operated by Mission Delta 31. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provide geolocation and time information to a GPS receiver anywhere on or near the Earth where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites. It does not require the user to transmit any data, and operates independently of any telephone or Internet reception, though these technologies can enhance the usefulness of the GPS positioning information. It provides critical positioning capabilities to military, civil, and commercial users around the world. Although the United States government created, controls, and maintains the GPS system, it is freely accessible to anyone with a GPS receiver. Overview The GPS project was started by the U.S. Department of Defense in 1973. The first prototype spacecraft was launched in 1978 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyprus Arc
The Cyprus Arc is a curved plate boundary zone in the Eastern Mediterranean extending from the eastern edge of the Hellenic arc to the triple junction of the Anatolian Plate, Arabian Plate and African Plate. Unlike simpler plate margins, the Cyprus Arc accommodates simultaneous compression, extension and strike-slip movements along different segments, reflecting the complex interaction of three major plates. The arc is linked into the Latakia Ridge to the west via the East Anatolian Fault (EAF). Tectonic regime Early models portrayed the Cyprus Arc as a straightforward zone of compression, where northward subduction of the Neo-Tethys oceanic lithosphere beneath the Anatolian Plate closed the eastern Mediterranean basin. In that view, the Eratosthenes Seamount—a promontory of extended continental crust—was thrust northward under the arc, uplifting the Troodos and eventually obducting slices of oceanic crust (ophiolite) onto the seamount's continental edge. GPS measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellenic Arc
The Hellenic arc or Aegean arc is an arcuate mountain chain of the southern Aegean Sea located on the southern margin of the Aegean Sea plate. Geologically it results from the subduction of the African plate under it along the Hellenic subduction zone. The Hellenic Trench trends parallel to its southern side. The Aegean Sea plate, a microplate, is often considered part of the Eurasian plate from which it is in the process of diverging. The arc itself is mainly marine, the mountaintops appearing as islands in the Ionian Sea, Crete and its environs, or in the Dodecanese group. It encroaches on mainland terrain in the Peloponnesus, on Crete, on Rhodes, and on the southern coast of Anatolia, thus being encompassed by both Greece and Turkey. The direction of subduction is northward. Locations on the arc or near it on the north side are therefore called "outer" as they are at the outer margin of the plate. Locations further north are "inner." Generally the motion of subduction is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere and some continental lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at the convergent boundaries between tectonic plates. Where one tectonic plate converges with a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the other and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with rates of convergence as high as 11 cm/year. Subduction is possible because the cold and rigid oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of the dense subducting lithosphere. The down-going slab sinks into the mantle largely under its own ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the west almost by the Morocco–Spain border. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only wide. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The sea was an important rout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convergent Boundary
A convergent boundary (also known as a destructive boundary) is an area on Earth where two or more lithospheric plates collide. One plate eventually slides beneath the other, a process known as subduction. The subduction zone can be defined by a plane where many earthquakes occur, called the Wadati–Benioff zone. These collisions happen on scales of millions to tens of millions of years and can lead to volcanism, earthquakes, orogenesis, destruction of lithosphere, and deformation. Convergent boundaries occur between oceanic-oceanic lithosphere, oceanic-continental lithosphere, and continental-continental lithosphere. The geologic features related to convergent boundaries vary depending on crust types. Plate tectonics is driven by convection cells in the mantle. Convection cells are the result of heat generated by the radioactive decay of elements in the mantle escaping to the surface and the return of cool materials from the surface to the mantle. These convection cells bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasian & Anatolian Plate
Eurasia ( , ) is a continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. According to some geographers, physiographically, Eurasia is a single supercontinent. The concept of Europe and Asia as distinct continents dates back to antiquity, but their borders have historically been subject to change. For example, the ancient Greeks originally included Africa in Asia but classified Europe as separate land. Eurasia is connected to Africa at the Suez Canal, and the two are sometimes combined to describe the largest contiguous landmass on Earth, Afro-Eurasia. History Eurasia has been the host of many ancient civilizations, including those based in Mesopotamia, Egypt, the Indus Valley and China. In the Axial Age (mid-first millennium BCE), a continuous belt of civilizations stretched through the Eurasian subtropical zone from the Atlantic to the Pacific. This belt became the mainstream of world history for two millennia. New connections emerged between the subregions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strike-slip Fault
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A '' fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geological maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |