|
Amyntas Of Galatia
Amyntas (), Tetrarch of the Trocmi was a King of Galatia and of several adjacent countries between 36 and 25 BC, mentioned by StraboStrabo, '' Geographia'', xii as contemporary with himself. He was the son of Brogitarus, king of Galatia, and Adobogiona, daughter of king Deiotarus Philoromaeus. Amyntas seems to have first possessed Lycaonia, where he maintained more than 300 flocks. To this he added the territory of Derbe by the murder of its prince, Antipater of Derbe, the friend of Cicero, and Isaura and Cappadocia by Roman favour. Originally he had been the king of Cappadocia Deiotarus secretary (), and was made by Amyntas commander in chief () of the Galatian auxiliaries sent to help Brutus and Cassius against the Triumvires, but deserted to Mark Anthony just before the battle of Philippi in 42 BC. After the death of Deiotarus, Amyntas was made king of Cappadocia in 37 as a client ruler of Mark Antony. Plutarch enumerates him among the adherents of Mark Antony a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decimus Junius Brutus Albinus
Decimus Junius Brutus Albinus (27 April 81 BC – September 43 BC) was a Ancient Rome, Roman general and politician of the crisis of the Roman Republic, late republican period and one of the leading instigators of Julius Caesar's Assassination of Julius Caesar, assassination. He had previously been an important supporter of Caesar in the Gallic Wars and in Caesar's civil war, the civil war against Pompey. Decimus Brutus is often confused with his distant cousin and fellow conspirator, Marcus Junius Brutus. Biography Early life Decimus was probably son of the Roman senator Decimus Junius Brutus (consul 77 BC), Decimus Junius Brutus and his notorious wife Sempronia (wife of Decimus Junius Brutus), Sempronia, one of the participants in the conspiracy of Catilina in 63 BC. His birthday seems to have been 27 April, and he was probably born in the year 81 BC, perhaps slightly earlier. Decimus was of distinguished ancestry: his father, Decimus Junius Brutus Callaicus, grandfather and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acmonia
Acmonia or Akmonia () is an ancient city of Phrygia Pacatiana, in Asia Minor, now known as Ahat Köyü in the district of Banaz, Uşak Province. It is mentioned by Cicero and was a point on the road between Dorylaeum and Philadelphia. Under the Romans, it was within the conventus iuridicus of Apamea. Bishopric Acmonia was the seat of a bishop in antiquity. It appears in the ''Notitiae Episcopatuum'' from the 10th to the 12th or 13th century. The first bishop whose name is known is Optimus, who was transferred to the metropolitan see of Antiochia in Pisidia before 381. Gennadius took part in the Council of Chalcedon in 451. Theotimus signed in 459 the decree of Patriarch Gennadius I of Constantinople against the simoniacs. Paulus was at the Second Council of Nicaea in 787. Eustathius was a both the Council of Constantinople (869) and the Council of Constantinople (879). Somewhat less certain is the attribution to this diocese of Basilius, who participated in the T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amyntas, Tetrarch Of The Tectosagii
Amyntas () was Tetrarch of the Tectosages and King of Cilicia Trachea between 36 BC and 25 BC. He was the predecessor of Polemon I of Pontus as King of Cilicia Trachea. Amyntas was a son of Dytilaos, Tetrarch of the Tectosagii. Amyntas was the father of a Princess of the Tectosagii who married Artemidoros of the Trocmii, son of Amyntas, Tetrarch of the Trocmii, King of Galatia. Through his daughter and her husband he was grandfather of Gaius Julius Severus, a nobleman from Akmonia at Galatia, in turn the father of Gaius Julius Bassus, Proconsul in Bithynia in 98, and Gaius Julius Severus, a Tribune in Legio VI ''Ferrata''. References {{Reflist *Christian Settipani Christian Settipani (born 31 January 1961) is a French genealogist, historian and IT professional, currently working as the Technical Director of a company in Paris. Biography Settipani holds a Master of Advanced Studies from the Paris-Sorb ..., Les Ancêtres de Charlemagne (France: Éditions Christian, 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
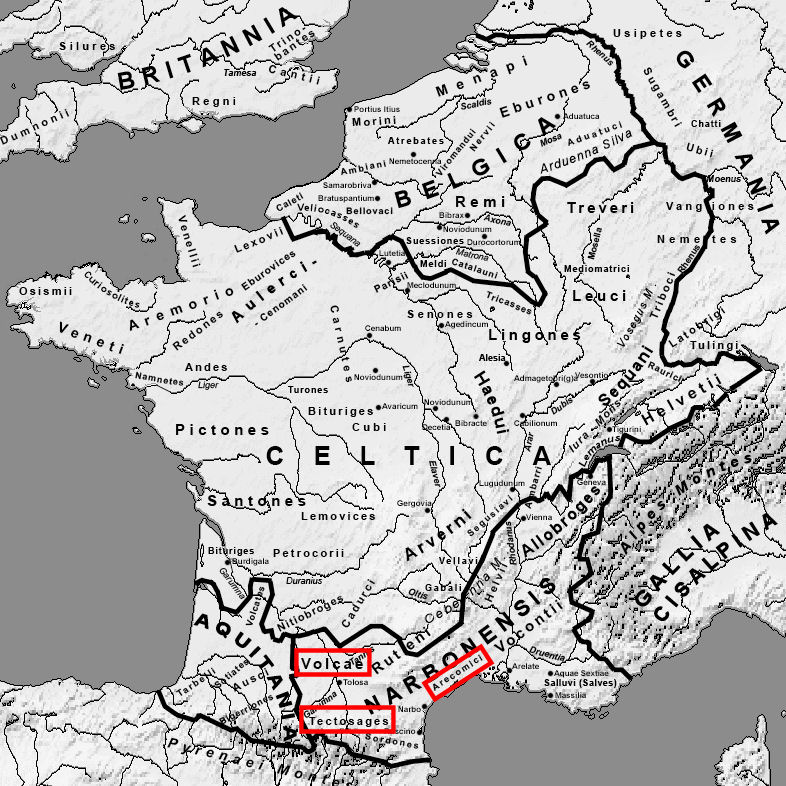
Volcae
The Volcae () were a Gallic tribal confederation constituted before the raid of combined Gauls that invaded Macedonia c. 270 BC and fought the assembled Greeks at the Battle of Thermopylae in 279 BC. Tribes known by the name Volcae were found simultaneously in southern Gaul, Moravia, the Ebro valley of the Iberian Peninsula, and Galatia in Anatolia. The Volcae appear to have been part of the late La Tène material culture, and a Celtic identity has been attributed to the Volcae, based on mentions in Greek and Latin sources as well as onomastic evidence. Driven by highly mobile groups operating outside the tribal system and comprising diverse elements, the Volcae were one of the new ethnic entities formed during the Celtic military expansion at the beginning of the 3rd century BC. Collecting in the famous excursion into the Balkans, ostensibly, from the Greek point of view, to raid Delphi, a branch of the Volcae split from the main group on the way into the Balkans and joined t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History (Pliny)
The ''Natural History'' () is a Latin work by Pliny the Elder. The largest single work to have survived from the Roman Empire to the modern day, the ''Natural History'' compiles information gleaned from other ancient authors. Despite the work's title, its subject area is not limited to what is today understood by natural history; Pliny himself defines his scope as "the natural world, or life". It is encyclopedic in scope, but its structure is not like that of a modern encyclopedia. It is the only work by Pliny to have survived, and the last that he published. He published the first 10 books in AD 77, but had not made a final revision of the remainder at the time of Pliny the Elder#Death, his death during the Eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD, AD 79 eruption of Vesuvius. The rest was published posthumously by Pliny's nephew, Pliny the Younger. The work is divided into 37 books, organised into 10 volumes. These cover topics including astronomy, mathematics, geography, ethn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliny The Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic (''Natural History''), a comprehensive thirty-seven-volume work covering a vast array of topics on human knowledge and the natural world, which became an editorial model for encyclopedias. He spent most of his spare time studying, writing, and investigating natural and geographic phenomena in the field. Among Pliny's greatest works was the twenty-volume ''Bella Germaniae'' ("The History of the German Wars"), which is Lost literary work, no longer extant. ''Bella Germaniae'', which began where Aufidius Bassus' ''Libri Belli Germanici'' ("The War with the Germans") left off, was used as a source by other prominent Roman historians, including Plutarch, Tacitus, and Suetonius. Tacitus may have used ''Bella Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Lives
* Culture of ancient Greece Culture of ancient Rome Ancient Greek biographical works Ethics literature History books about ancient Rome Cultural depictions of Gaius Marius Cultural depictions of Mark Antony Cultural depictions of Cicero Depictions of Julius Caesar in literature Cultural depictions of Pompey Cultural depictions of Marcus Junius Brutus Cultural depictions of Marcus Licinius Crassus Cultural depictions of Theseus Cultural depictions of Romulus and Remus Cultural depictions of Cato the Younger Cultural depictions of Sulla Cultural depictions of Alexander the Great The ''Parallel Lives'' (, ''Bíoi Parállēloi''; ) is a series of 48 biographies of famous men written in Greek by the Greco-Roman philosopher, historian, and Apollonian priest Plutarch, probably at the beginning of the second century. The lives are arranged in pairs to illuminate their common moral virtues or failings. While any historically valuable similarities are often forced, these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. The reign of Augustus initiated an Roman imperial cult, imperial cult and an era of regional hegemony, imperial peace (the or ) in which the Roman world was largely free of armed conflict. The Principate system of government was established during his reign and lasted until the Crisis of the Third Century. Octavian was born into an equites, equestrian branch of the plebeian Octavia gens, Octavia. Following his maternal great-uncle Julius Caesar's assassination of Julius Caesar, assassination in 44 BC, Octavian was named in Caesar's will as his Adoption in ancient Rome, adopted son and heir, and inherited Caesar's name, estate, and the loyalty of his legions. He, Mark Antony, and Marcus Lepidus formed the Second Triumvirat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Actium
The Battle of Actium was a naval battle fought between Octavian's maritime fleet, led by Marcus Agrippa, and the combined fleets of both Mark Antony and Cleopatra. The battle took place on 2 September 31 BC in the Ionian Sea, near the former Roman Republic, Roman colony of Actium, Greece, and was the climax of over a decade of rivalry between Octavian and Mark Antony. In early 31 BC, the year of the battle, Antony and Cleopatra were temporarily stationed in Greece. Mark Antony possessed 500 ships and 70,000 infantry, and made his camp at Actium, and Octavian, with 400 ships and 80,000 infantry, arrived from the north and occupied Patras, Patrae and Corinth, where he managed to cut Antony's southward communications with Egypt (via the Peloponnese) with help from Marcus Agrippa. Octavian previously gained a preliminary victory in Greece, where his navy successfully ferried troops across the Adriatic Sea under the command of Agrippa. Octavian landed on mainland Greece, opposite o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutarch
Plutarch (; , ''Ploútarchos'', ; – 120s) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo (Delphi), Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', a series of biographies of illustrious Greeks and Romans, and ''Moralia'', a collection of essays and speeches. Upon becoming a Roman citizen, he was possibly named Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus (). Family Plutarch was born to a prominent family in the small town of Chaeronea, about east of Delphi, in the Greek region of Boeotia. His family was long established in the town; his father was named Autobulus and his grandfather was named Lamprias. His brothers, Timon and Lamprias, are frequently mentioned in his essays and dialogues, which speak of Timon in particular in the most affectionate terms. Studies and life Plutarch studied mathematics and philosophy in Athens under Ammonius of Athens, Ammonius from AD 66 to 67. He attended th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Philippi
The Battle of Philippi was the final battle in the Liberators' civil war between the forces of Mark Antony and Octavian (of the Second Triumvirate) and the leaders of Julius Caesar's assassination, Brutus and Cassius, in 42 BC, at Philippi in Macedonia. The Second Triumvirate declared the civil war ostensibly to avenge Julius Caesar's assassination in 44 BC, but the underlying cause was a long-brewing conflict between the Optimates and the Populares. The battle, involving up to 200,000 men in one of the largest of the Roman civil wars, consisted of two engagements in the plain west of the ancient city of Philippi. The first occurred in the first week of October; Brutus faced Octavian, and Antony's forces fought those of Cassius. The Roman armies fought poorly, with low discipline, nonexistent tactical coordination and amateurish lack of command experience evident in abundance with neither side able to exploit opportunities as they developed. At first, Brutus pushed back Octa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |