|
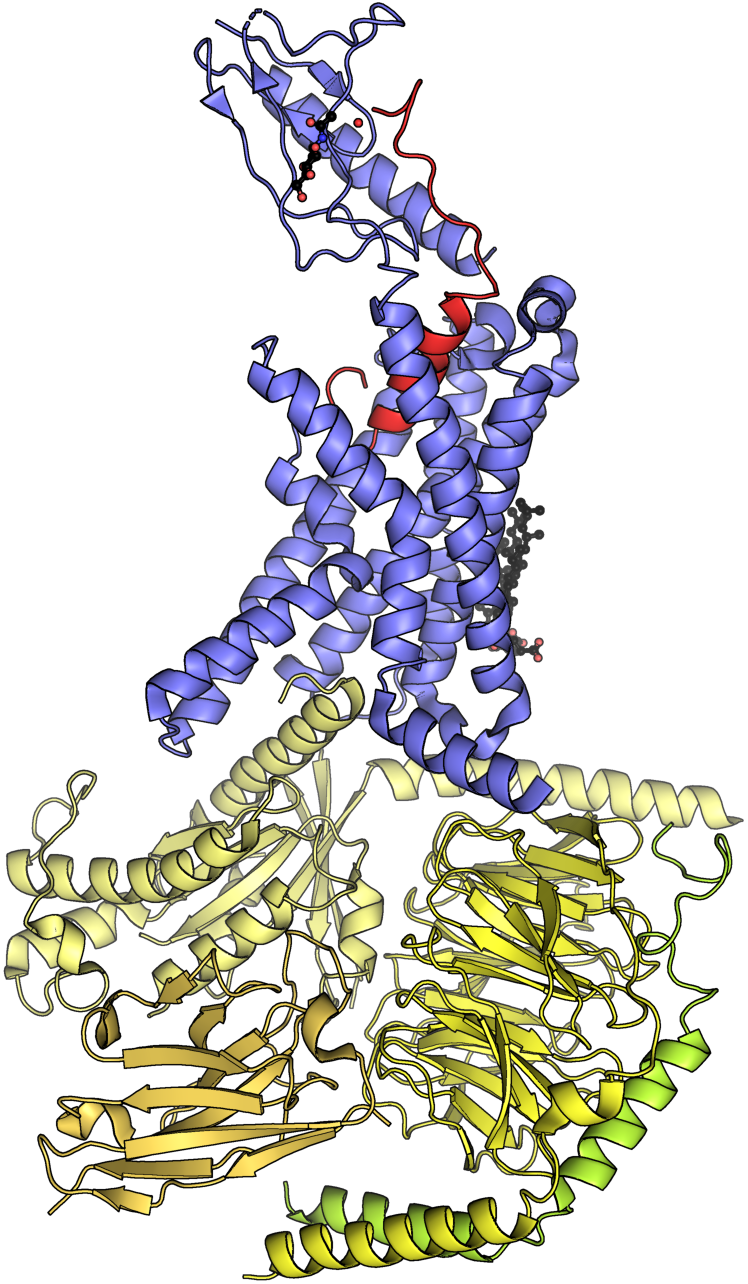
Amylin Receptor
The amylin receptors (AMYRs) are heterodimers of the calcitonin receptor and receptor activity modifying proteins (RAMPs). They are bound to by amylin with high affinity and consist of AMY1, AMY2, and AMY3. Amylin mimetics that are agonists at the amylin receptors are being developed as therapies for diabetes and obesity, and one, pramlintide, has been FDA approved. The AMY1 receptor may be activated by both amylin and the calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and could play a role in the effects of CGRP receptor antagonists developed for migraine. Dual agonists of the amylin and calcitonin receptors (DACRAs) are under development for obesity. Amylin and its receptors are believed to play a role in Alzheimer's disease Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems wit .... Refere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterodimer
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex or multimer formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word ''dimer'' has roots meaning "two parts", '' di-'' + '' -mer''. A protein dimer is a type of protein quaternary structure. A protein homodimer is formed by two identical proteins while a protein heterodimer is formed by two different proteins. Most protein dimers in biochemistry are not connected by covalent bonds. An example of a non-covalent heterodimer is the enzyme reverse transcriptase, which is composed of two different amino acid chains. An exception is dimers that are linked by disulfide bridges such as the homodimeric protein NEMO. Some proteins contain specialized domains to ensure dimerization (dimerization domains) and specificity. The G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptors have the ability to form both homo- and hetero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcitonin Receptor
The calcitonin receptor (CT) is a G protein-coupled receptor that binds the peptide hormone calcitonin and is involved in maintenance of calcium homeostasis, particularly with respect to bone formation and metabolism. CT works by activating the G-proteins Gs alpha subunit, Gs and Gq alpha subunit, Gq often found on osteoclasts, on cells in the kidney, and on cells in a number of regions of the brain. It may also affect the ovaries in women and the testes in men. The function of the CT receptor protein is modified through its interaction with Receptor activity-modifying proteins (RAMPs), forming the multimeric amylin receptors AMY1 (CT + RAMP1), AMY2 (CT + RAMP2), and AMY3 (CT+ RAMP3). Preclinical studies have suggested that dual amylin and calcitonin receptor agonists may be more effective than amylin receptor agonists for obesity and type II diabetes. Interactions Calcitonin receptor has been shown to Protein-protein interaction, interact with Apolipoprotein B and LRP1. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amylin
Amylin, or islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP), is a 37-residue peptide hormone. It is co-secreted with insulin from the pancreatic β-cells in the ratio of approximately 100:1 (insulin:amylin). Amylin plays a role in glycemic regulation by slowing gastric emptying and promoting satiety, thereby preventing post-prandial spikes in blood glucose levels. IAPP is processed from an 89-residue coding sequence. Proislet amyloid polypeptide (proIAPP, proamylin, proislet protein) is produced in the pancreatic beta cells (β-cells) as a 67 amino acid, 7404 Dalton pro-peptide and undergoes post-translational modifications including protease cleavage to produce amylin. Synthesis ProIAPP consists of 67 amino acids, which follow a 22 amino acid signal peptide which is rapidly cleaved after translation of the 89 amino acid coding sequence. The human sequence (from N-terminus to C-terminus) is: (MGILKLQVFLIVLSVALNHLKA) TPIESHQVEKR^ KCNTATCATQRLANFLVHSSNNFGAILSSTNVGSNTYG^ KR^ NAVEVLKREP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAMP1
Receptor activity modifying protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RAMP1'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the RAMP family of single-transmembrane-domain proteins, called receptor (calcitonin) activity modifying proteins (RAMPs). RAMPs are type I transmembrane proteins with an extracellular N terminus and a cytoplasmic C terminus. RAMPs are required to transport calcitonin-receptor-like receptor (CALCRL) to the plasma membrane. CALCRL, a receptor with seven transmembrane domains, can function as either a calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor or an adrenomedullin receptor, depending on which members of the RAMP family are expressed. In combination with the RAMP1 protein, CALCRL functions as the CGRP receptor. The RAMP1 protein is involved in the terminal glycosylation, maturation, and presentation of the CGRP receptor to the cell surface. The RAMP1 protein can also interact with the calcitonin receptor (CT) protein, where heter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are Cell (biology), cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an Receptor antagonist, antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist. Etymology The word originates from the Ancient Greek, Greek word (''agōnistēs''), "contestant; champion; rival" < (''agōn''), "contest, combat; exertion, struggle" < (''agō''), "I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive." Types of agonists Receptor (biochemistry), Receptors can be activated by either endogenous agonists (such as hormones and neurotransmitters) or exogenous agonists (such as medication, drugs), resulting in a biological response. A physiological agonism an ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of the body becoming unresponsive to insulin's effects. Classic symptoms include polydipsia (excessive thirst), polyuria (excessive urination), polyphagia (excessive hunger), weight loss, and blurred vision. If left untreated, the disease can lead to various health complications, including disorders of the cardiovascular system, eye, kidney, and nerves. Diabetes accounts for approximately 4.2 million deaths every year, with an estimated 1.5 million caused by either untreated or poorly treated diabetes. The major types of diabetes are type 1 and type 2. The most common treatment for type 1 is insulin replacement therapy (insulin injections), while anti-diabetic medications (such as metformin and semaglutide) and lifestyle modificatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's weight divided by the square of the person's height—is over ; the range is defined as overweight. Some East Asian countries use lower values to calculate obesity. Obesity is a major cause of disability and is Obesity-associated morbidity, correlated with various diseases and conditions, particularly cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, certain types of cancer, and osteoarthritis. Obesity has individual, socioeconomic, and environmental causes. Some known causes are Western pattern diet, diet, low physical activity, automation, urbanization, quantitative trait locus, genetic susceptibility, medications, mental disorders, Economic policy, economic pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pramlintide
Pramlintide (trade name Symlin) is an injectable amylin analogue drug for diabetes (both type 1 and 2), developed by Amylin Pharmaceuticals (now a wholly owned subsidiary of AstraZeneca). Pramlintide is sold as an acetate salt. Pharmacology Pramlintide is an analogue of amylin, a small peptide hormone that is released into the bloodstream by the β cells of the pancreas along with insulin after a meal. Like insulin, amylin is completely absent in individuals with Type I diabetes. In synergy with endogenous amylin, pramlintide aids in the regulation of blood glucose by slowing gastric emptying, promoting satiety via hypothalamic receptors (different receptors than for GLP-1), and inhibiting inappropriate secretion of glucagon, a catabolic hormone that opposes the effects of insulin and amylin. Pramlintide also has effects in raising the acute first-phase insulin response threshold following a meal. Both a reduction in glycated hemoglobin and weight loss have been shown in insu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcitonin Gene-related Peptide
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) is a neuropeptide that belongs to the calcitonin family. Human CGRP consists of two Protein isoform, isoforms, CGRP alpha (α-CGRP, also known as CGRP I) and CGRP beta (β-CGRP, also known as CGRP II). α-CGRP is a 37-amino acid neuropeptide formed by alternative splicing of the calcitonin/CGRP gene located on chromosome 11. β-CGRP is less studied. In humans, β-CGRP differs from α-CGRP by three amino acids and is encoded in a separate, nearby gene. The CGRP family includes calcitonin (CT), adrenomedullin (AM), and amylin (AMY). Function CGRP is produced in both peripheral and central neurons. It is a potent peptide vasodilator and can function in the transmission of nociception. In the spinal cord, the function and expression of CGRP may differ depending on the location of synthesis. CGRP is derived mainly from the cell bodies of motor neurons when synthesized in the Ventral horn of spinal cord, ventral horn of the spinal cord and may c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcitonin Gene-related Peptide Receptor Antagonist
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonists, commonly known as gepants, are a class of drugs that act as antagonists of the calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor (CGRPR). Several monoclonal antibodies that bind to the CGRP receptor or peptide have been approved for prevention of migraine. Nerve activation triggers the release of CGRP and other neuropeptides, leading to inflammation, pain, and swelling. Three small molecule CGRPR antagonists are approved in the U.S. as antimigraine agents. Drugs of this class have also been investigated for use in osteoarthritis. Examples Non-peptide small molecules * Ubrogepant is approved for acute treatment of migraines * Rimegepant (BMS-927711) is approved for acute and preventative treatment of migraines * Atogepant (AGN-241689) is approved for preventative treatment of migraines * Zavegepant (BHV- 3500) is a nasal spray approved for acute treatment of migraines. * Telcagepant (MK-0974), reached phase III clinical trial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Migraine
Migraine (, ) is a complex neurological disorder characterized by episodes of moderate-to-severe headache, most often unilateral and generally associated with nausea, and light and sound sensitivity. Other characterizing symptoms may include vomiting, cognitive dysfunction, allodynia, and dizziness. Exacerbation or worsening of headache symptoms during physical activity is another distinguishing feature. Up to one-third of people with migraine experience aura, a premonitory period of sensory disturbance widely accepted to be caused by cortical spreading depression at the onset of a migraine attack. Although primarily considered to be a headache disorder, migraine is highly heterogenous in its clinical presentation and is better thought of as a spectrum disease rather than a distinct clinical entity. Disease burden can range from episodic discrete attacks to chronic disease. Migraine is believed to be caused by a mixture of environmental and genetic factors that influe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease and the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with language, disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the average life expectancy following diagnosis is three to twelve years. The causes of Alzheimer's disease remain poorly understood. There are many environmental and genetic risk factors associated with its development. The strongest genetic risk factor is from an allele of apolipoprotein E. Other risk factors include a history of head injury, clinical depression, and high blood pressure. The progression of the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |