|
Amundsen Sea
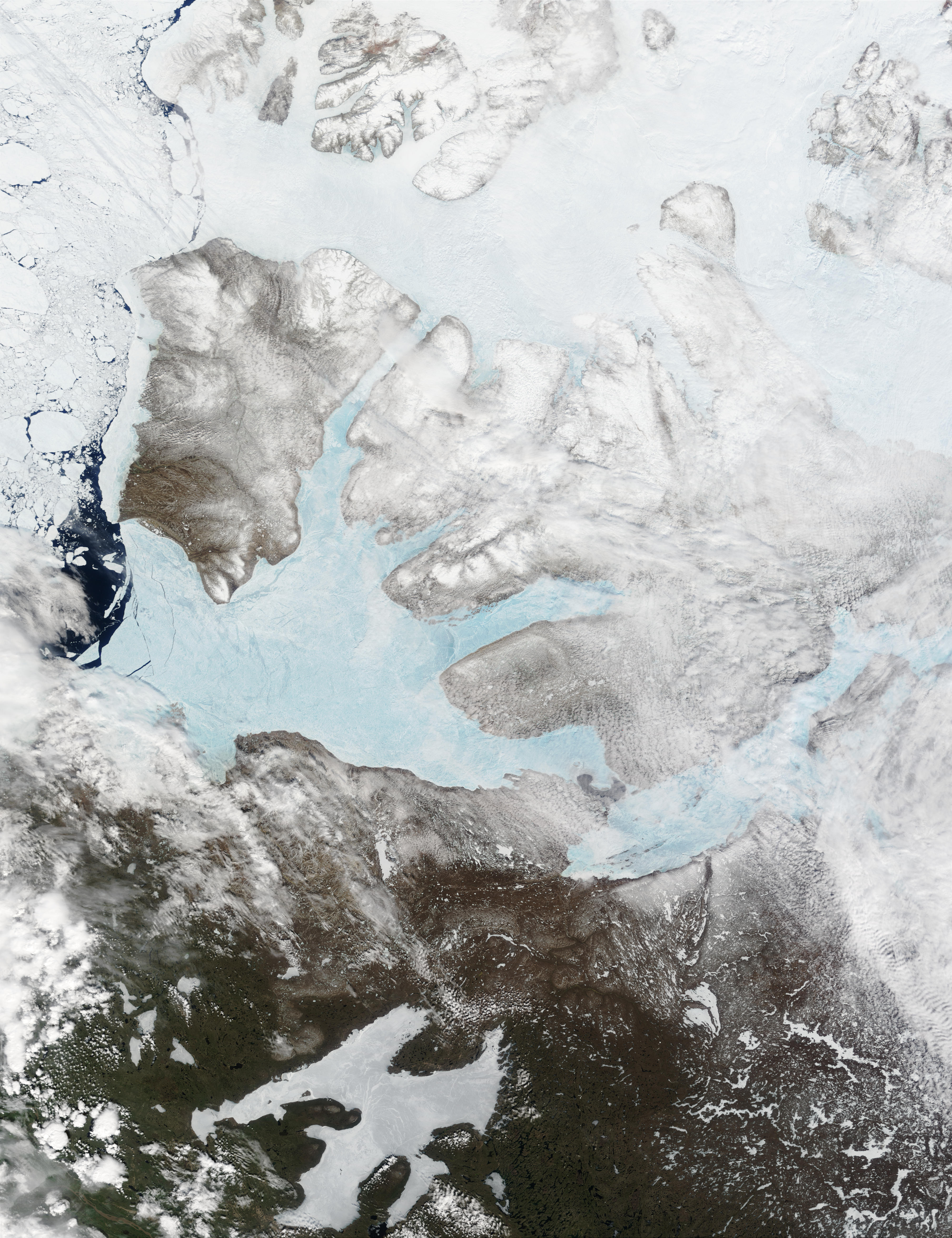
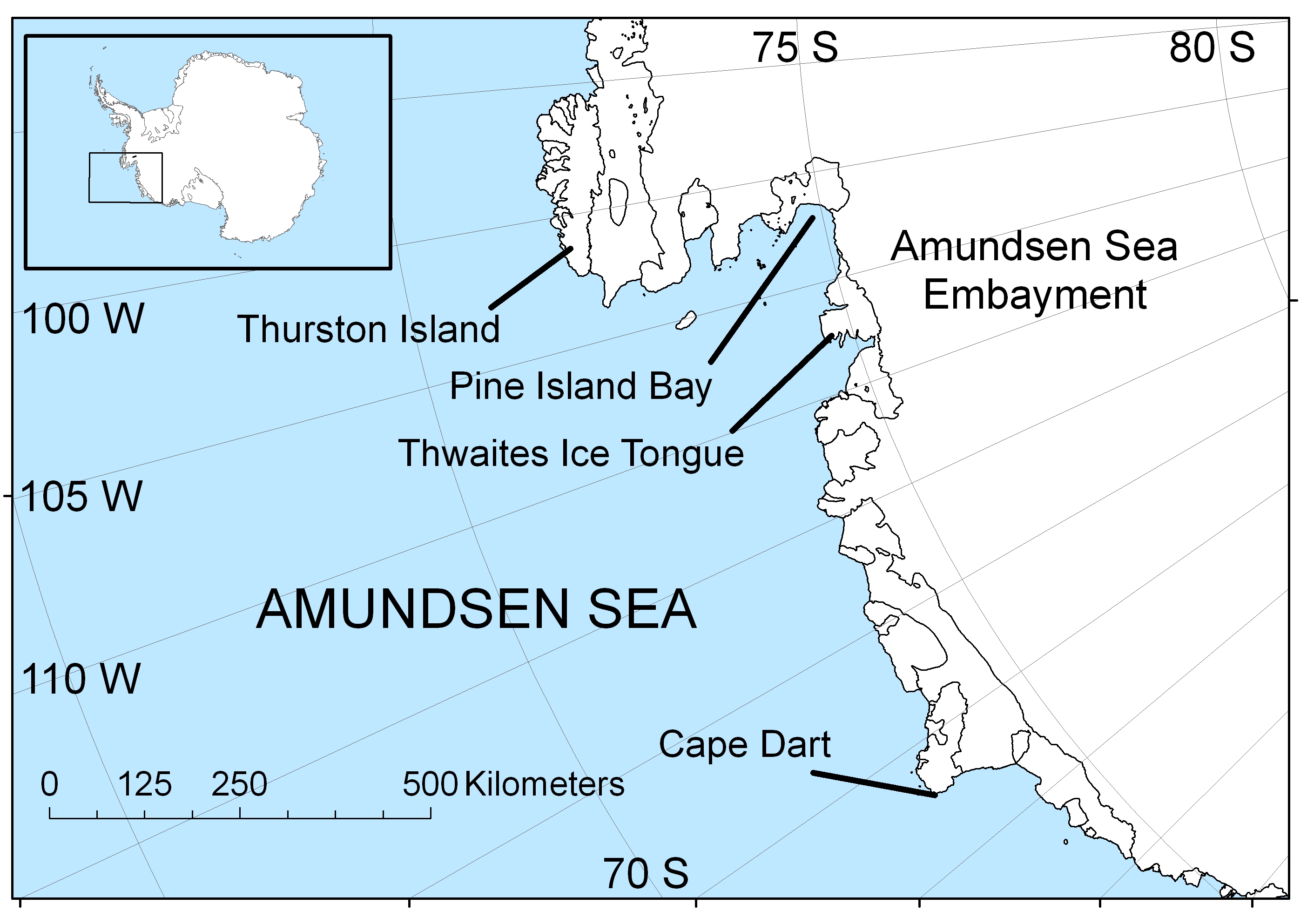
The Amundsen Sea is an arm of the Southern Ocean off Marie Byrd Land in western Antarctica. It lies between Cape Flying Fish (the northwestern tip of Thurston Island) to the east and Cape Dart on Siple Island to the west. Cape Flying Fish marks the boundary between the Amundsen Sea and the Bellingshausen Sea. West of Cape Dart there is no named marginal sea of the Southern Ocean between the Amundsen and Ross Seas. The Norwegian expedition of 1928–1929 under Captain Nils Larsen named the body of water for the Norwegian polar explorer Roald Amundsen while exploring this area in February 1929. The sea is mostly ice-covered, and the Thwaites Ice Tongue protrudes into it. The ice sheet which drains into the Amundsen Sea averages about in thickness; roughly the size of the state of Texas, this area is known as the Amundsen Sea Embayment (ASE); it forms one of the three major ice-drainage basins of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. Embayment The ice sheet that drains in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Antarctic Ice Sheet
The West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS) is the segment of the Antarctic ice sheet, continental ice sheet that covers West Antarctica, the portion of Antarctica on the side of the Transantarctic Mountains that lies in the Western Hemisphere. It is classified as a marine-based ice sheet, meaning that its bed lies well below sea level and its edges flow into floating ice shelves. The WAIS is bounded by the Ross Ice Shelf, the Ronne Ice Shelf, and outlet glaciers that drain into the Amundsen Sea. As a smaller part of Antarctica, WAIS is also more strongly affected by climate change. There has been warming over the ice sheet since the 1950s, and a substantial retreat of its coastal glaciers since at least the 1990s. Estimates suggest it added around to the global sea level rise between 1992 and 2017, and has been losing ice in the 2010s at a rate equivalent to of annual sea level rise. While some of its losses are offset by the growth of the East Antarctic ice sheet, Antarctica as a whol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amundsen Gulf
Amundsen Gulf is a gulf located mainly in the Inuvik Region, Northwest Territories, Canada with a small section in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut. It lies between Banks Island and Victoria Island (Canada), Victoria Island and the mainland. It is approximately in length and about across where it meets the Beaufort Sea. The Amundsen Gulf was explored by Norwegian explorer Roald Amundsen between 1903 and 1906. The gulf is at the western end of the famous Northwest Passage, a route from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean, Pacific. Few people live along the shores of the gulf, but there are a few towns and communities, including Sachs Harbour, Ulukhaktok, and Paulatuk. Heading north in the gulf one would find the Prince of Wales Strait. Heading southeast and east, the gulf leads through the Dolphin and Union Strait, past Simpson Bay and into the Coronation Gulf. From there one would go through the Dease Strait and into the Queen Maud Gulf, and eventually head northeast into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global temperatures is driven by human activities, especially fossil fuel burning since the Industrial Revolution. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices release greenhouse gases. These gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight, warming the lower atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, the primary gas driving global warming, has increased in concentration by about 50% since the pre-industrial era to levels not seen for millions of years. Climate change has an increasingly large impact on the environment. Deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Amplified warming in the Arctic has c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effects Of Global Warming On Oceans
There are many effects of climate change on oceans. One of the most important is an increase in ocean temperatures. More frequent marine heatwaves are linked to this. The rising temperature contributes to a rise in sea levels due to the expansion of water as it warms and the melting of ice sheets on land. Other effects on oceans include sea ice decline, reducing pH values and oxygen levels, as well as increased ocean stratification. All this can lead to changes of ocean currents, for example a weakening of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC). The main cause of these changes are the emissions of greenhouse gases from human activities, mainly burning of fossil fuels and deforestation. Carbon dioxide and methane are examples of greenhouse gases. The additional greenhouse effect leads to ocean warming because the ocean takes up most of the additional heat in the climate system. The ocean also absorbs some of the extra carbon dioxide that is in the atmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Ash
Volcanic ash consists of fragments of rock, mineral crystals, and volcanic glass, produced during volcanic eruptions and measuring less than 2 mm (0.079 inches) in diameter. The term volcanic ash is also often loosely used to refer to all explosive eruption products (correctly referred to as '' tephra''), including particles larger than 2 mm. Volcanic ash is formed during explosive volcanic eruptions when dissolved gases in magma expand and escape violently into the atmosphere. The force of the gases shatters the magma and propels it into the atmosphere where it solidifies into fragments of volcanic rock and glass. Ash is also produced when magma comes into contact with water during phreatomagmatic eruptions, causing the water to explosively flash to steam leading to shattering of magma. Once in the air, ash is transported by wind up to thousands of kilometres away. Due to its wide dispersal, ash can have a number of impacts on society, including animal a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson Mountains
The Hudson Mountains are a mountain range in western Ellsworth Land just east of Pine Island Bay at the Walgreen Coast of the Amundsen Sea. They are of volcanic origin, consisting of low scattered mountains and nunataks that protrude through the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. The Hudson Mountains are bounded on the north by Cosgrove Ice Shelf and on the south by Pine Island Glacier. The mountains were volcanically active during the Miocene and Pliocene, but there is evidence for an eruption about two millennia ago and uncertain indications of activity in the 20th century. Geography and geomorphology The Hudson Mountains rise in western Ellsworth Land of West Antarctica and were discovered in 1940 by the United States Antarctic Service Expedition. The mountains lie at some distance from the Amundsen Sea's Walgreen Coast, facing Pine Island Bay. The Cosgrove Ice Shelf lies north of the Hudson Mountains. The mountains are remote and visits are rare. In 1991, they were prospe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcano
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and because most of Earth's plate boundaries are underwater, most volcanoes are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes resulting from divergent tectonic activity are usually non-explosive whereas those resulting from convergent tectonic activity cause violent eruptions."Mid-ocean ridge tectonics, volcanism and geomorphology." Geology 26, no. 455 (2001): 458. https://macdonald.faculty.geol.ucsb.edu/papers/Macdonald%20Mid-Ocean%20Ridge%20Tectonics.pdf Volcanoes can also form where there is str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Antarctic Survey
The British Antarctic Survey (BAS) is the United Kingdom's national polar research institute. It has a dual purpose, to conduct polar science, enabling better understanding of list of global issues, global issues, and to provide an active presence in the Antarctic on behalf of the UK. It is part of the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC). With over 400 staff, BAS takes an active role in Antarctic affairs, operating five research stations, one ship and five aircraft in both polar regions, as well as addressing key global and regional issues. This involves joint research projects with over 40 UK universities and more than 120 national and international collaborations. Having taken shape from activities during World War II, it was known as the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey until 1962. History Operation Tabarin was a small British expedition in 1943 to establish permanently occupied bases in the Antarctic. It was a joint undertaking by the British Admiralty, Admiralt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Antarctic Ice Sheet
The East Antarctic Ice Sheet (EAIS) lies between 45th meridian west, 45° west and 168th meridian east, 168° east longitudinally. It was first formed around 34 million years ago, and it is the largest ice sheet on the entire planet, with far greater volume than the Greenland ice sheet or the West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS), from which it is separated by the Transantarctic Mountains. The ice sheet is around thick on average and is at its thickest point. It is also home to the geographic South Pole, South Magnetic Pole and the Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station. The surface of the EAIS is the driest, windiest, and coldest place on Earth. Lack of moisture in the air, high albedo from the snow as well as the surface's consistently high elevation results in the reported cold temperature records of nearly . It is the only place on Earth cold enough for atmospheric temperature inversion to occur consistently. That is, while the atmosphere is typically warmest near the surface and bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current Sea Level Rise
The sea level has been rising from the end of the last ice age, which was around 20,000 years ago. Between 1901 and 2018, the average sea level rose by , with an increase of per year since the 1970s. This was faster than the sea level had ever risen over at least the past 3,000 years. The rate accelerated to /yr for the decade 2013–2022. Climate change due to human activities is the main cause. Between 1993 and 2018, melting ice sheets and glaciers accounted for 44% of sea level rise, with another 42% resulting from thermal expansion of water. Sea level rise lags behind changes in the Earth's temperature by decades, and sea level rise will therefore continue to accelerate between now and 2050 in response to warming that has already happened. What happens after that depends on future human greenhouse gas emissions. If there are very deep cuts in emissions, sea level rise would slow between 2050 and 2100. The reported factors of increase in flood hazard potential are often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pine Island Glacier
Pine Island Glacier (PIG) is a large ice stream, and the fastest melting glacier in Antarctica. responsible for about 13% of Antarctica's ice loss. The glacier flows west-northwest along the south side of the Hudson Mountains into Pine Island Bay, part of the Amundsen Sea. The area drained by Pine Island Glacier comprises about 10% of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. Satellite measurements have shown that the Pine Island Glacier Basin has a greater net contribution of ice to the sea than any other ice drainage basin in the world and this has increased due to recent acceleration of the ice stream. In recent years, the flow of the glacier has accelerated and the grounding line has retreated. Since 2015, the calving of very large icebergs from the Pine Island Glacier has become a roughly annual event. The largest such iceberg, Iceberg B-46, had an initial size of . The glacier is extremely remote, but scientists have surveyed the ice with radar, GPS, and seismic sensors. Most of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |