|
Amorolfine
Amorolfine (or amorolfin), is a morpholine antifungal drug that inhibits Δ14-sterol reductase and cholestenol Δ-isomerase, which depletes ergosterol and causes ignosterol to accumulate in the fungal cytoplasmic cell membranes. Marketed as Curanail, Loceryl, Locetar, and Odenil, amorolfine is commonly available in the form of a nail lacquer, containing 5% amorolfine hydrochloride as the active ingredient. It is used to treat onychomycosis (fungal infection of the toe- and fingernails). Amorolfine 5% nail lacquer in once-weekly or twice-weekly applications was shown in two decades-old studies to be between 60% and 71% effective in treating toenail onychomycosis; complete cure rates three months after stopping treatment (after six months of treatment) were 38% and 46%. However, full experimental details of these trials were not available, and since they were first reported in 1992 there have been no subsequent trials. It is a ''topical'' solution for the treatment of toenail in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morpholine
Morpholine is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound having the chemical formula oxygen, O(carbon, Chydrogen, H2CH2)2nitrogen, NH. This heterocycle features both amine and ether functional groups. Because of the amine, morpholine is a base (chemistry), base; its conjugate acid is called morpholinium. For example, treating morpholine with hydrochloric acid generates the salt (chemistry), salt morpholinium chloride. It is a colorless liquid with a weak, ammonia- or fish-like odor. The naming of morpholine is attributed to Ludwig Knorr, who incorrectly believed it to be part of the structure of morphine. Production Morpholine is often produced industrially by the dehydration of diethanolamine with concentrated sulfuric acid. Alternatively, it can be made from bis(2-chloroethyl)ether in a reaction with ammonia, by which also ammonium chloride is formed. Morpholine is also produced industrially from diethylene glycol and ammonia, under high temperature and pressure, in the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antifungal
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as cryptococcal meningitis, and others. Such drugs are usually obtained by a doctor's prescription, but a few are available over the counter (OTC). The evolution of antifungal resistance is a growing threat to health globally. Routes of administration Ocular Indicated when the fungal infection is located in the eye. There is currently only one ocular antifungal available: natamycin. However, various other antifungal agents could be compounded in this formulation. Intrathecal Used occasionally when there's an infection of the central nervous system and other systemic options cannot reach the concentration required in that region for therapeutic benefit. Example(s): amphotericin B. Vaginal This may be used to treat some fungal in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fenpropimorph
Fenpropimorph is a morpholine-derived fungicide used in agriculture, primarily on cereal crops such as wheat. It has been reported to disrupt eukaryotic sterol biosynthesis pathways, notably by inhibiting fungal Δ14 reductases. It has also been reported to inhibit mammalian sterol biosynthesis by affecting lanosterol demethylation. Although used in agriculture for pest management purposes, it has been reported to have a strong adverse effect on sterol biosynthesis in higher-plants by inhibiting the cycloeucalenol-obtusifoliol isomerase. This inhibition was shown to not only alter the lipid composition of the plasma-membrane, but also impact cell division and growth, in plants. In addition to its effects on fungi, fenpropimorph is also a very high affinity ligand of the mammalian sigma receptor. See also * Amorolfine Amorolfine (or amorolfin), is a morpholine antifungal drug that inhibits Δ14-sterol reductase and cholestenol Δ-isomerase, which depletes ergosterol and cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antifungals
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as cryptococcal meningitis, and others. Such drugs are usually obtained by a doctor's prescription, but a few are available over the counter (OTC). The evolution of antifungal resistance is a growing threat to health globally. Routes of administration Ocular Indicated when the fungal infection is located in the eye. There is currently only one ocular antifungal available: natamycin. However, various other antifungal agents could be compounded in this formulation. Intrathecal Used occasionally when there's an infection of the central nervous system and other systemic options cannot reach the concentration required in that region for therapeutic benefit. Example(s): amphotericin B. Vaginal This may be used to treat some fungal in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ergosterol
Ergosterol (ergosta-5,7,22-trien-3β-ol) is a mycosterol found in cell membranes of fungi and protozoa, serving many of the same functions that cholesterol serves in animal cells. Because many fungi and protozoa cannot survive without ergosterol, the enzymes that synthesize it have become important targets for drug discovery. In human nutrition, ergosterol is a provitamin form of vitamin D2; exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light causes a chemical reaction that produces vitamin D2. Role in fungi Ergosterol (ergosta-5,7,22-trien-3β-ol) is a sterol found in fungi, and named after ergot, the common name of members of the fungal genus '' Claviceps'' from which ergosterol was first isolated. Ergosterol is a component of yeast and other fungal cell membranes, serving many of the same functions that cholesterol serves in animal cells. Its specificity in higher fungi is thought to be related to the climatic instabilities (highly varying humidity and moisture conditions) encountered by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasmic
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are the cytosol (a gel-like substance), the cell's internal sub-structures, and various cytoplasmic inclusions. In eukaryotes the cytoplasm also includes the nucleus, and other membrane-bound organelles.The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance, or cytoplasmic matrix, that remains after the exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, plant plastids, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Membranes
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of a cell, being selectively permeable to ions and organic molecule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholestenol Delta-isomerase
In enzymology, a cholestenol Δ-isomerase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :5alpha-cholest-7-en-3beta-ol \rightleftharpoons 5alpha-cholest-8-en-3beta-ol Hence, this enzyme has one substrate, 5alpha-cholest-7-en-3beta-ol, and one product, 5alpha-cholest-8-en-3beta-ol. This enzyme belongs to the family of isomerases, specifically those intramolecular oxidoreductases transposing C=C bonds. The systematic name of this enzyme class is Delta7-cholestenol Delta7-Delta8-isomerase. This enzyme participates in biosynthesis of steroids A steroid is an organic compound with four fused rings (designated A, B, C, and D) arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter memb .... See also * Emopamil binding protein References * EC 5.3.3 Enzymes of unknown structure {{isomerase-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
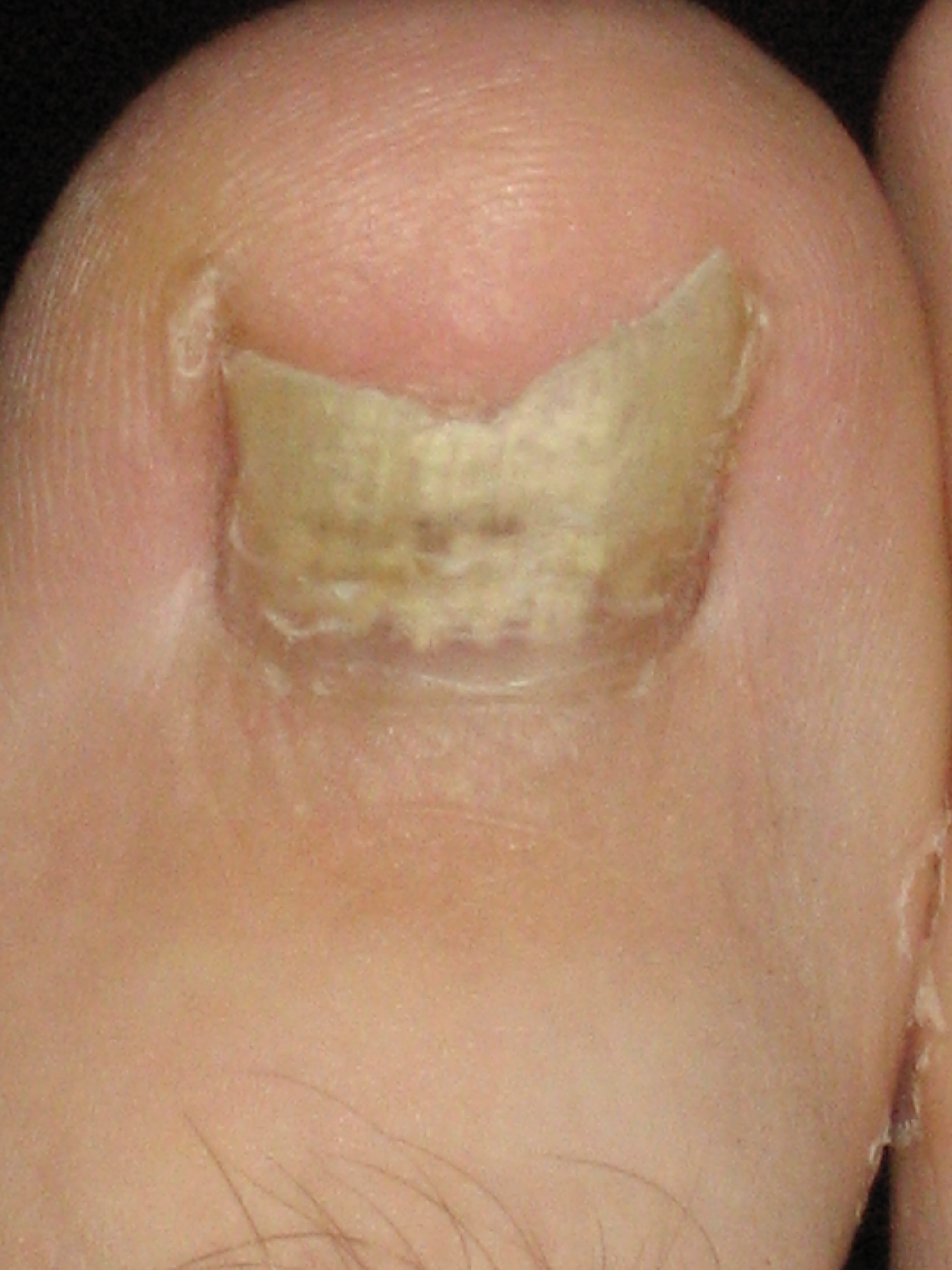
Onychomycosis
Onychomycosis, also known as tinea unguium, is a fungal infection of the nail. Symptoms may include white or yellow nail discoloration, thickening of the nail, and separation of the nail from the nail bed. Fingernails may be affected, but it is more common for toenails. Complications may include cellulitis of the lower leg. A number of different types of fungus can cause onychomycosis, including dermatophytes and ''Fusarium''. Risk factors include athlete's foot, other nail diseases, exposure to someone with the condition, peripheral vascular disease, and poor immune function. The diagnosis is generally suspected based on the appearance and confirmed by laboratory testing. Onychomycosis does not necessarily require treatment. The antifungal medication terbinafine taken by mouth appears to be the most effective but is associated with liver problems. Trimming the affected nails when on treatment also appears useful. There is a ciclopirox-containing nail polish, but there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topical Medication
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surface area, body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes including Cream (pharmaceutical), creams, foams, gels, lotions, and ointments. Many topical medications are epicutaneous, meaning that they are applied directly to the skin. Topical medications may also be insufflation (medicine), inhalational, such as asthma medications, or applied to the surface of tissues other than the skin, such as eye drops applied to the conjunctiva, or ear drops placed in the ear, or medications applied to the surface of a Human tooth, tooth. The word ''topical'' derives from Ancient Greek, Greek wikt:τοπικός, τοπικός ''topikos'', "of a place". Justification Topical drug delivery is a route of administering drugs via the Human skin, skin to provide topical therapeutic effects. As sk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systemic Administration
Systemic administration is a route of administration of medication, nutrition or other substance into the circulatory system so that the entire body is affected. Administration can take place via enteral administration (absorption of the drug through the gastrointestinal tract) or parenteral administration (generally injection, infusion, or implantation). Contrast with topical A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes ... administration where the effect is generally local. References Routes of administration {{pharma-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |