|
Amoebidiales
Amoebidiidae is a family of single-celled eukaryotes, previously thought to be zygomycete fungi belonging to the clasTrichomycetes but molecular phylogenetic analysesBenny, G. L., and O'Donnell, K. 2000. ''Amoebidium parasiticum'' is a protozoan, not a Trichomycete. ''Mycologia'' 92: 1133-1137.Ustinova, I, Krienitz, L., and Huss, V. A. R. 2000. ''Hyaloraphidium curvatum'' is not a green alga, but a lower fungus; ''Amoebidium parasiticum'' is not a fungus, but a member of the DRIPS. ''Protist'' 151: 253-262.Cafaro, M. 2005. Eccrinales (Trichomycetes) are not fungi, but a clade of protists at the early divergence of animals and fungi. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 35: 21-34. place the family with the opisthokont group MesomycetozoeaMendoza L, Taylor JW, Ajello L (October 2002)"The class mesomycetozoea: a heterogeneous group of microorganisms at the animal-fungal boundary" ''Annu. Rev. Microbiol''. 56: 315–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.56.012302.160950 (= Ichthyosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paramoebidium
''Paramoebidium'' is a genus of unicellular, symbiotic eukaryotes that inhabit the digestive tract of immature freshwater arthropod hosts (e.g. black fly larvae, mayfly and stonefly nymphs).Lichtwardt, R.W., M.J. Cafaro, M.M. White. 2001. The Trichomycetes: Fungal Associates of Arthropods Revised Edition. Published online http://www.nhm.ku.edu/%7Efungi/Monograph/Text/Mono.htm ''Paramoebidium'' is classified in the opisthokont class Mesomycetozoea (= Ichthyosporea), and is the sole genus in the family Paramoebidiidae. Prior to 2005, ''Paramoebidium'' species were tentatively placed with the fungal group Trichomycetes due to their habitation of arthropod guts, host overlap between various ''Paramoebidium'' and fungal trichomycete taxa, and similar vegetative growth form.Moss, S.T., 1979. Commensalism of Trichomycetes. In L. R. Batra, ed. ''Insect-Fungus Symbiosis Nutrition, Mutualism, and Commensalism''. Montclair: Allanheld, Osmun & Co. Publishers, Inc., pp. 175–227. Etymology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
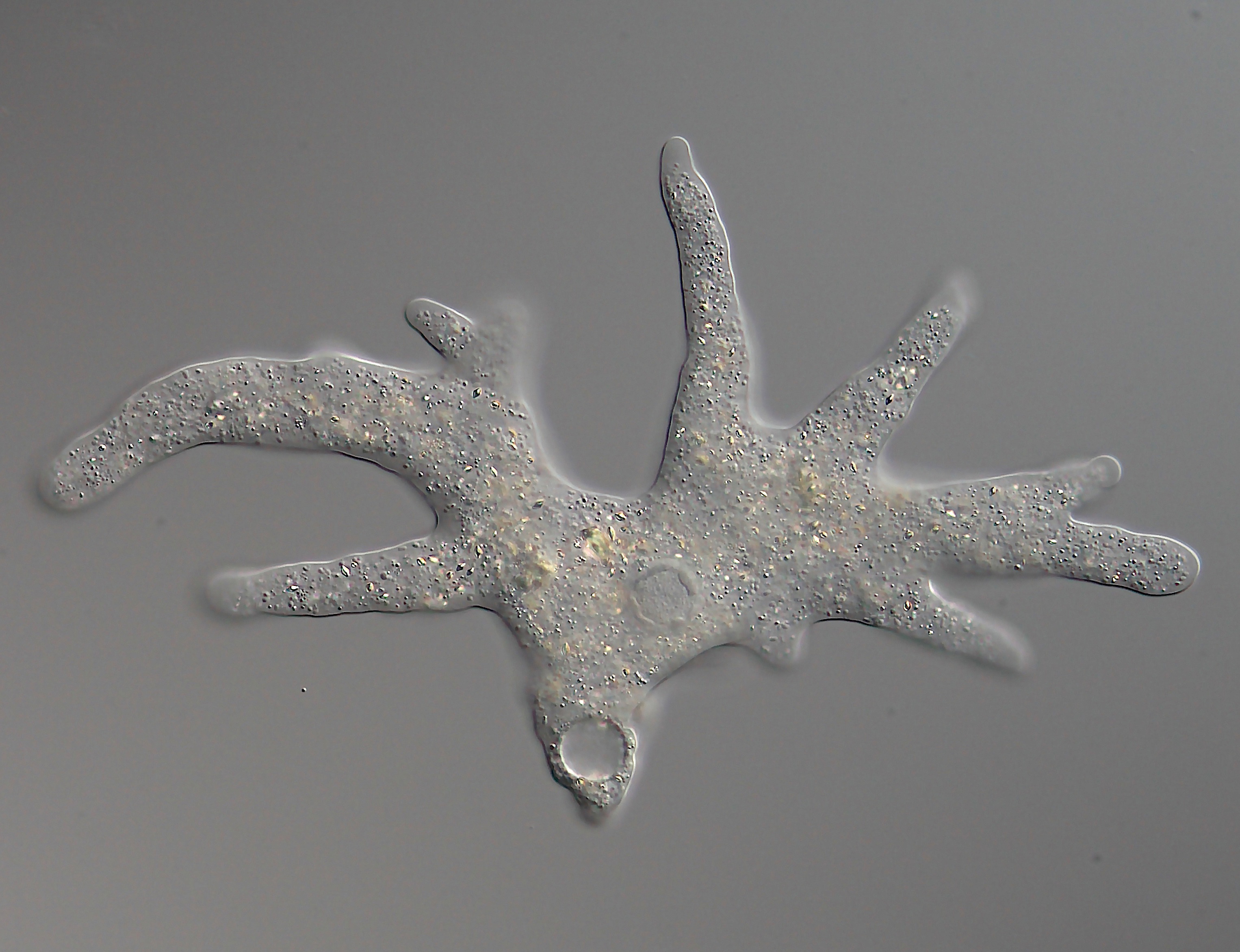
Amoebidium Parasiticum
''Amoebidium'' is a genus of unicellular, symbiotic eukaryotes in the Opisthokont group Mesomycetozoea, family Amoebidiidae.Reynolds, N.K., M.E. Smith, E.D. Tretter, J. Gause, D. Heeney, M.J. Cafaro, J.F. Smith, S.J. Novak, W.A. Bourland, M.M. White. 2017. Resolving relationships at the animal-fungal divergence: A molecular phylogenetic study of the protist trichomycetes (Ichthyosporea, Eccrinida). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 109, 447-464. ''Amoebidium'' species attach to the exoskeleton of freshwater aquatic arthropods such as midge larvae and water fleas (''Daphnia'').Lichtwardt, R.W., M.J. Cafaro, M.M. White. 2001. The Trichomycetes: Fungal Associates of Arthropods Revised Edition. Published online http://www.nhm.ku.edu/%7Efungi/Monograph/Text/Mono.htm The type species is Amoebidium parasiticum', which is also one of the only species to be cultured axenically.Whisler, H.C., 1960. Pure culture of the Trichomycete, Amoebidium parasiticum. Nature 186, 732-733. Etymo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the kingdom (biology)#Six kingdoms (1998), traditional eukaryotic kingdoms, along with Animalia, Plantae, and either Protista or Protozoa and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichomycetes
Trichomycetes refers to a group of fungi in the division Zygomycota that grow in the guts of arthropods living in aquatic habitats. The name is obsolete, having not been validly published. Species formerly placed in the Trichomycetes are now placed in the orders Harpellales and Asellariales, both in the subdivision Kickxellomycotina, while Amoebidiales and Eccrinales Eccrinales are an order of eukaryotes, previously thought to be zygomycete fungi A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), ... are included in Opisthokonta. References Zygomycota Obsolete fungus taxa {{zygomycota-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyosporea
The Ichthyosporea (or DRIP clade, or Mesomycetozoea) are a small group of Opisthokonta in Eukaryota (formerly protists), mostly parasites of fish and other animals. Significance They are not particularly distinctive morphologically, appearing in host tissues as enlarged spheres or ovals containing spores, and most were originally classified in various groups as fungi, protozoa, or colorless algae. However, they form a coherent group on molecular trees, closely related to both animals and fungi and so of interest to biologists studying their origins. In a 2008 study they emerge robustly as the sibling-group of the clade Filozoa, which includes the animals. Huldtgren et al., following x-ray tomography of microfossils of the Ediacaran The Ediacaran ( ) is a geological period of the Neoproterozoic geologic era, Era that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period at 635 Million years ago, Mya to the beginning of the Cambrian Period at 538.8 Mya. It is the las ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyophonida
Ichthyophonida is an order of parasitic eukaryote The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ..., especially in the parasitizing of animals. Phylogeny Taxonomy Members of Ichthyophonida include: * Suborder Sphaeroformina Cavalier-Smith 2012 ** Family Creolimacidae Cavalier-Smith 2012 *** Genus '' Anurofeca'' Baker, Beebee & Ragan 1999 *** Genus '' Creolimax'' Marschall et al. 2008 *** Genus '' Sphaeroforma'' Jostensen et al. 2002 'Pseudoperkinsus'' Figueras et al. 2000** Family Psorospermidae Cavalier-Smith 2012 *** Genus '' Psorospermis'' Cavalier-Smith 2012 Psorospermium.html" ;"title="'Psorospermium">'Psorospermium'' Hilgendorf 1883 non Eimer 1870 ** Family Piridae Cavalier-Smith 2012 *** Genus ''Caullerya'' Chatton 1907 *** Genus ''Abeoforma'' Marshall & Berbee 2011 * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoeba
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; : amoebas (less commonly, amebas) or amoebae (amebae) ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of Cell (biology), cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudopodia, pseudopods. Amoebae do not form a single Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic group; instead, they are found in every major Lineage (evolution), lineage of eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms. Amoeboid cells occur not only among the protozoa, but also in fungi, algae, and animals. Microbiologists often use the terms "amoeboid" and "amoeba" interchangeably for any organism that exhibits amoeboid movement. In older classification systems, most amoebae were placed in the Class (biology), class or subphylum Sarcodina, a grouping of Unicellular organism, single-celled organisms that possess pseudopods or move by protoplasmic flow. However, molecular phylogenetic studies have shown that Sarcodina is not a monophyletic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesomycetozoea
The Ichthyosporea (or DRIP clade, or Mesomycetozoea) are a small group of Opisthokonta in Eukaryota (formerly protists), mostly parasites of fish and other animals. Significance They are not particularly distinctive morphologically, appearing in host tissues as enlarged spheres or ovals containing spores, and most were originally classified in various groups as fungi, protozoa, or colorless algae. However, they form a coherent group on molecular trees, closely related to both animals and fungi and so of interest to biologists studying their origins. In a 2008 study they emerge robustly as the sibling-group of the clade Filozoa, which includes the animals. Huldtgren et al., following x-ray tomography of microfossils of the Ediacaran Doushantuo Formation, has interpreted them as mesomycetozoan spore capsules. Terminology The name DRIP is an acronym for the first protozoa identified as members of the group, Cavalier-Smith Thomas (Tom) Cavalier-Smith, Royal Society, FRS, R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opisthokont
The opisthokonts () are a broad group of eukaryotes, including both the animal and fungus kingdoms. The opisthokonts, previously called the "Fungi/Metazoa group", are generally recognized as a clade. Opisthokonts together with Apusomonadida and Breviata comprise the larger clade Obazoa. Flagella and other characteristics A common characteristic of opisthokonts is that flagellate cells, such as the sperm of most animals and the spores of the chytrid fungi, propel themselves with a single ''posterior'' flagellum. It is this feature that gives the group its name. In contrast, flagellate cells in other eukaryote groups propel themselves with one or more ''anterior'' flagella. Flagellate cells however have been secondarily lost in some opisthokont groups, including most of the fungi. Opisthokont characteristics include synthesis of extracellular chitin in exoskeleton, cyst/spore wall, or cell wall of filamentous growth and hyphae; the extracellular digestion of substrates with os ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thallus
Thallus (: thalli), from Latinized Greek (), meaning "a green shoot" or "twig", is the vegetative tissue of some organisms in diverse groups such as algae, fungi, some liverworts, lichens, and the Myxogastria. A thallus usually names the entire body of a multicellular non-moving organism in which there is no organization of the tissues into organs. Many of these organisms were previously known as the thallophytes, a polyphyletic group of distantly related organisms. An organism or structure resembling a thallus is called thalloid, thalloidal, thalliform, thalline, or thallose. Even though thalli do not have organized and distinct parts ( leaves, roots, and stems) as do the vascular plants, they may have analogous structures that resemble their vascular "equivalents". The analogous structures have similar function or macroscopic structure, but different microscopic structure; for example, no thallus has vascular tissue. In exceptional cases such as the Lemnoideae, where th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, Thorax (insect anatomy), thorax and abdomen (insect anatomy), abdomen), three pairs of jointed Arthropod leg, legs, compound eyes, and a pair of antenna (biology), antennae. Insects are the most diverse group of animals, with more than a million described species; they represent more than half of all animal species. The insect nervous system consists of a insect brain, brain and a ventral nerve cord. Most insects reproduce Oviparous, by laying eggs. Insects Respiratory system of insects, breathe air through a system of Spiracle (arthropods), paired openings along their sides, connected to Trachea#Invertebrates, small tubes that take air directly to the tissues. The blood therefore does not carry oxygen; it is only partly contained in ves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |