|
Amnon Neeman
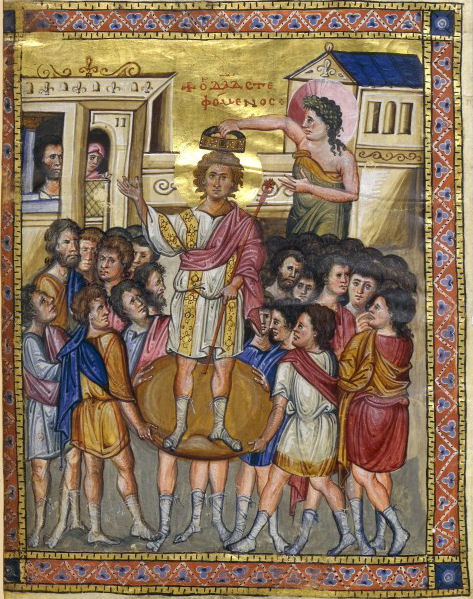
Amnon ( ''’Amnōn'', "faithful") was, in the Hebrew Bible, the oldest son of King David and his second wife, Ahinoam of Jezreel. He was born in Hebron during his father's reign in Judah. He was the heir apparent to the throne of Israel until he was assassinated by his half-brother Absalom to avenge the rape of Absalom's sister Tamar. Biblical account Amnon's background Amnon was born in Hebron to Ahinoam and King David. As the presumptive heir to the throne of Israel, Amnon enjoyed a life of power and privilege. Rape of Tamar Although he was the heir-apparent to David's throne, Amnon is best remembered for the rape of his paternal half-sister Tamar, daughter of David and Maachah. Despite the biblical prohibition on sexual relations between half siblings, Amnon had an overwhelming desire for her. He acted on advice from his cousin, Jonadab son of Shimeah, David's brother, to lure Tamar into his quarters by pretending to be sick and desiring her to cook a special meal for him ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kings Of Israel And Judah
The article deals with the biblical and historical kings of the Land of Israel— Abimelech of Sichem, the three kings of the United Kingdom of Israel and those of its successor states, Israel and Judah, followed in the Second Temple period, part of classical antiquity, by the kingdoms ruled by the Hasmonean and Herodian dynasties. The Hebrew Bible describes a succession of kings of a United Kingdom of Israel, and then of divided kingdoms, Israel and Judah. In contemporary scholarship, the united monarchy is debated, due to a lack of archaeological evidence for it. It is generally accepted that a " House of David" existed, but some scholars believe that David could have only been the king or chieftain of Judah, which was likely small, and that the northern kingdom was a separate development. There are some dissenters to this view, including those who support the traditional narrative, and those who support the united monarchy's existence but believe that the Bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talmai
Talmai (, ; 'my furrows') is a name in the Bible referring to a number of minor people. Its Aramaic version was associated with the Greek Ptolemy (see that article for the list of corresponding names and surnames), and is the origin of Bartholomew. The name "Talmai" (Hebrew: תלמי) is often transliterated as "Tolmai" in Aramaic. While Bartholomew, one of the apostles, is referred to as "Bar-Tolmai," meaning "son of Tolmai," this connection is primarily etymological. It showcases the linguistic roots of the names rather than indicating a direct familial relationship between Bartholomew (the apostle) and the Nephilim. Talmai and his brothers, the Nephilim Talmai, Ahiman and Sheshai were Nephilim, three giant sons of Anak whom Caleb and the spies saw in Mount Hebron (Book of Numbers 13:22) when they went in to explore the land. They were afterwards driven out and slain (Joshua 15:14; Judges 1:10). Talmai, father of Maacah King of Geshur. His daughter Maacah Maacah (or M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Wesley
John Wesley ( ; 2 March 1791) was an English cleric, Christian theology, theologian, and Evangelism, evangelist who was a principal leader of a Christian revival, revival movement within the Church of England known as Methodism. The societies he founded became the dominant form of the independent Methodist movement that continues to this day. Educated at Charterhouse School, Charterhouse and Christ Church, Oxford, Wesley was elected a fellow of Lincoln College, Oxford, in 1726 and ordination, ordained as an Anglican priest two years later. At Oxford, he led the "Holy Club", a society formed for the purpose of the study and the pursuit of a devout Christian life. After an unsuccessful two-year ministry in Savannah, Georgia, he returned to London and joined a religious society led by Moravian Church, Moravian Christians. On 24 May 1738, he experienced what has come to be called his evangelical conversion. He subsequently left the Moravians and began his own ministry. A key step ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methodism
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a Protestant Christianity, Christian Christian tradition, tradition whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's brother Charles Wesley were also significant early leaders in the movement. They were named ''Methodists'' for "the methodical way in which they carried out their Christian faith". Methodism originated as a Christian revival, revival movement within Anglicanism with roots in the Church of England in the 18th century and became a separate denomination after Wesley's death. The movement spread throughout the British Empire, the United States and beyond because of vigorous Christian mission, missionary work, and today has about 80 million adherents worldwide. Most List of Methodist denominations, Methodist denominations are members of the World Methodist Council. Wesleyan theology, which is upheld by the Methodist denominations, focuses on Sanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
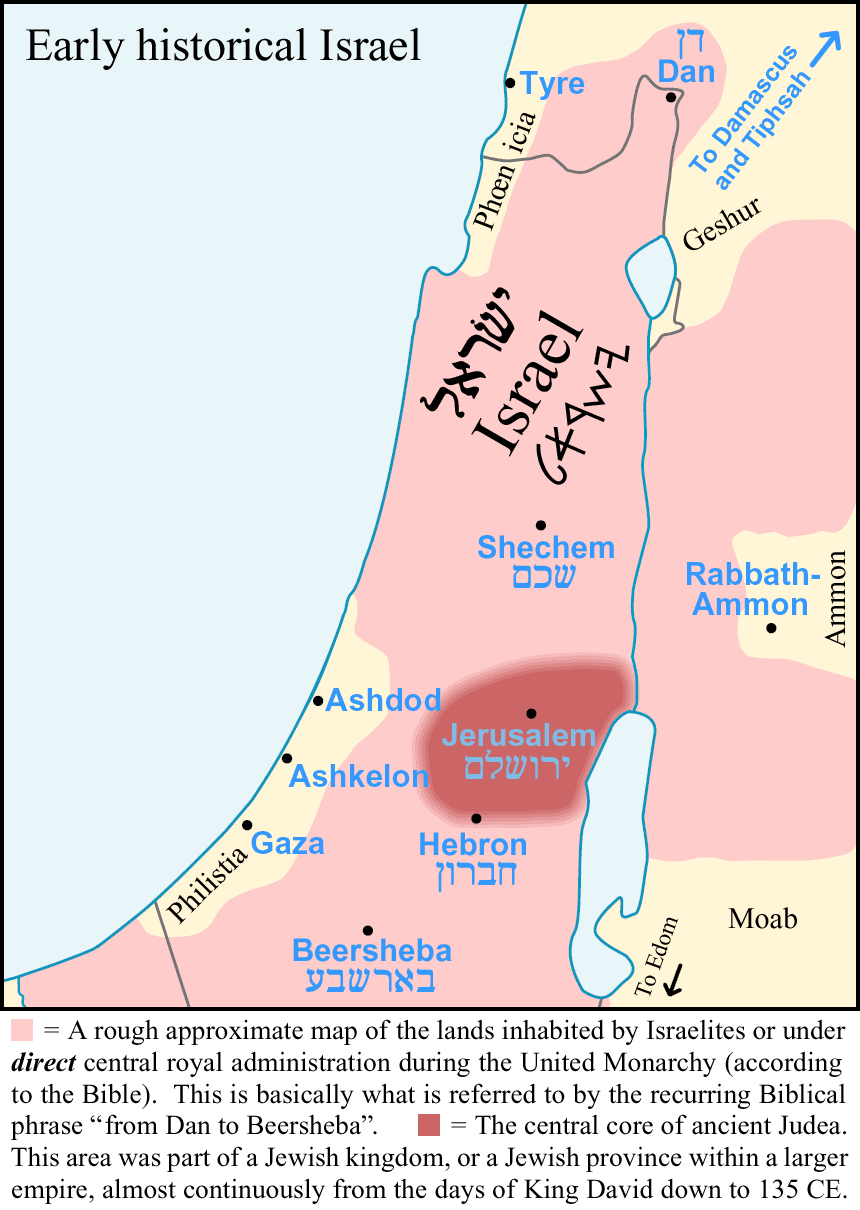
Geshur
Geshur () was a territory in the ancient Levant mentioned in the early books of the Hebrew Bible and possibly in several other ancient sources, located in the region of the modern-day Golan Heights. Some scholars suggest it was established as an independent city-state during the early Iron Age from the middle of the tenth century BCE, maintaining its autonomy for about a century until it was annexed in the third quarter of the eighth century by Tiglath-Pileser III, the king of Assyria. Location Geshur is identified with the area stretching along the eastern shore of the Sea of Galilee and reaching south to the Yarmuk River, in what is now called the Golan Heights. This location places it on one of the routes connecting the region of Bashan with the Phoenician coast. Tel Dover, located southeast of the Sea of Galilee on the Jarmuk (Yarmuk) River, may have been the kingdom's southern border. Surveys conducted within the Golan Heights have not discovered many settlements within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kareth
The Hebrew term ''kareth'' ("cutting off" , ), or extirpation, is a form of punishment for sin, mentioned in the Hebrew Bible and later Jewish writings. The typical Biblical phrase used is "that soul shall be cut off from its people" or a slight variation of this. Several different suggestions have been made for the understanding of this punishment in the Bible and in rabbinic thought. Etymology The word ''kareth'' is derived from the Hebrew verb ''karat'' ("to cut off"). The noun form ''kareth'' does not occur in the Hebrew Bible; rather, verb forms such as ''venichreta'' (" hat soulshall be cut off") are most common. Hebrew Bible In the Hebrew Bible, verbs that underlie the later use of the noun form ''kareth'' refer to forms of punishment including premature death, or else exclusion from the people. The former view is implied by verses stating that the punishment will be inflicted directly by God, while the latter view may be suggested by verses which distinguish between bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leviticus 20
Kedoshim, K'doshim, or Qedoshim (—Hebrew language, Hebrew for "holy ones," the 14th word, and the first distinctive word, in the parashah) is the 30th weekly Torah portion (, ''parashah'') in the annual Judaism, Jewish cycle of Torah reading and the seventh in the Book of Leviticus. It constitutes Leviticus 19:1–20:27. The parashah tells of the laws of holiness and ethical behavior, repeats the Ten Commandments, and describes penalties for sexual transgressions. The parashah is made up of 3,229 Hebrew letters, 868 Hebrew words, 64 Chapters and verses of the Bible, verses, and 109 lines in a Torah Scroll (, ''Sefer Torah''). Jews generally read it in late April or May. The lunisolar calendar, lunisolar Hebrew calendar contains up to 55 weeks, the exact number varying between 50 in common years and 54 or 55 in leap years. In leap years (for example, 2024), Parashat Kedoshim is read separately. In common years (for example, 2025 and 2026), Parashat Kedoshim is combined with the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deuteronomy 27
Ki Tavo, Ki Thavo, Ki Tabo, Ki Thabo, or Ki Savo (—Hebrew language, Hebrew for "when you enter," the second and third words, and the incipit, first distinctive words, in the parashah) is the 50th weekly Torah portion (, ''parashah'') in the annual Judaism, Jewish cycle of Torah reading and the seventh in the Book of Deuteronomy. It comprises Deuteronomy 26:1–29:8. The parashah tells of the ceremony of the First Fruits, first fruits (, ''bikkurim''), tithes, and the blessings from observance and curses (, ''tocheichah'') from violation of the law. The parashah is made up of 6,811 Hebrew letters, 1,747 Hebrew words, 122 Chapters and verses of the Bible, verses, and 261 lines in a Torah Scroll (, ''Sefer Torah''). Jews generally read it in September, or rarely in late August. Readings In traditional Sabbath Torah reading, the parashah is divided into seven readings, (, ''Aliyah (Torah), aliyot''). In the Masoretic Text of the Tanakh (Hebrew Bible), Parashah Ki Tavo has four "ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leviticus 18
Leviticus 18 (the eighteenth chapter of the Book of Leviticus) deals with a number of sexual activities considered abominable, including incest and bestiality. The chapter also condemns Moloch worship. It is part of the Holiness Code (Leviticus 17–26), and its sexual prohibitions are largely paralleled by Leviticus 20, except that chapter 20 has more emphasis on punishment. Leviticus 18:22 is has traditionally been interpreted as prohibiting homosexual acts, but its meaning is debated, with some scholars suggesting it applies only to specific contexts like adultery, rape, or incest and others arguing it evolved over time. Text The original text of Leviticus 18, like that of most of the Hebrew Bible, is written in Hebrew. The oldest extant versions of the text in Hebrew are found in the Dead Sea Scrolls, the Samaritan Pentateuch, and the Masoretic Text. An ancient Greek translation from the third century BCE, the Septuagint, also exists. Since the addition of chapter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael D
Michael D may refer to: * Mike D (born 1965), founding member of the Beastie Boys Arts * Michael D. Cohen (actor) (born 1975), Canadian actor * Michael D. Ellison, African American recording artist * Michael D. Fay, American war artist * Michael D. Ford (1928–2018), English set decorator * Michael D. Roberts, American actor Business * Michael D. Dingman (1931–2017), American businessman * Michael D. Ercolino (1906–1982), American businessman * Michael D. Fascitelli, (born c. 1957), American businessman * Michael D. Penner (born 1969), Canadian lawyer and businessman Education * Michael D. Cohen (academic) (1945–2013), professor of complex systems, information and public policy at the University of Michigan * Michael D. Hanes, American music educator * Michael D. Hurley (born 1976), British Professor of Literature and Theology * Michael D. Johnson, a former President of John Carroll University * Michael D. Knox (born 1946), American antiwar activist and educator * Michael D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |