|
Ammianus
Ammianus Marcellinus, occasionally anglicized as Ammian (Greek: Αμμιανός Μαρκελλίνος; born , died 400), was a Greek and Roman soldier and historian who wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from antiquity (preceding Procopius). Written in Latin and known as the '' Res gestae'', his work chronicled the history of Rome from the accession of Emperor Nerva in 96 to the death of Valens at the Battle of Adrianople in 378. Only the sections covering the period 353 to 378 survive. Biography Ammianus was born in the East Mediterranean, possibly in Syria or Phoenicia, around 330, into a noble family of Greek origin. Since he calls himself ''Graecus'' ( Greek), he was most likely born in a Greek-speaking area of the empire. His native language was Greek, but he also knew Latin. The surviving books of his history cover the years 353 to 378. Ammianus began his career as a military officer in the Praetorian Guard, where he gained firsthand experience in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Res Gestae (Ammianus Marcellinus)
The ''Rerum gestarum libri XXXI'' (commonly abbreviated as ''Res gestae'') is a historical work written by the Roman officer Ammianus Marcellinus beginning around 380 and likely completed by 392. The title is not original. The term ''Res gestae'' was later used by Priscian of Caesarea. and translates to "The Things Accomplished." The manuscript ''Vaticanus Latinus 1873'' labels it ''Rerum gestarum libri'', though a more accurate title might be ''Rerum gestarum libri ab excessu Neruae''. Content Part of the 31 books of the work was published in 391, while those from Book XXVI onward appeared in subsequent years, possibly by 394. Many scholars suggest a later date, with evidence indicating Books XX to XXII were released between 388 and 390. Only Books XIV to XXXI survive, covering the period from 353 to 378, during which Ammianus, as a member of the imperial guard, was an eyewitness. In 1998, Timothy Barnes proposed that the ''Res Gestae'' were organized in groups of six books ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantius II
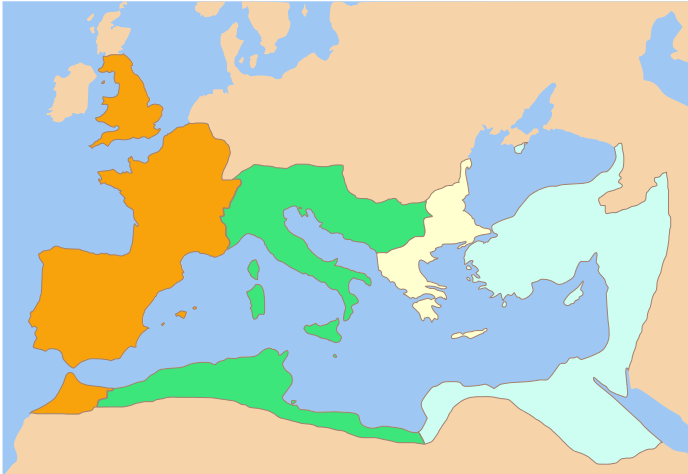
Constantius II (; ; 7 August 317 – 3 November 361) was Roman emperor from 337 to 361. His reign saw constant warfare on the borders against the Sasanian Empire and Germanic peoples, while internally the Roman Empire went through repeated civil wars, court intrigues, and usurpations. His religious policies inflamed domestic conflicts that would continue after his death. Constantius was a son of Constantine the Great, who elevated him to the imperial rank of '' Caesar'' on 8 November 324 and after whose death Constantius became ''Augustus'' together with his brothers, Constantine II and Constans on 9 September 337. He promptly oversaw the massacre of his father-in-law, an uncle, and several cousins, consolidating his hold on power. The brothers divided the empire among themselves, with Constantius receiving Greece, Thrace, the Asian provinces, and Egypt in the east. For the following decade a costly and inconclusive war against Persia took most of Constantius's time and at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julian (emperor)
Julian (; ; 331 – 26 June 363) was the Caesar (title), Caesar of the West from 355 to 360 and Roman emperor from 361 to 363, as well as a notable philosopher and author in Ancient Greek, Greek. His rejection of Christianity, and his promotion of Neoplatonic Hellenistic religion, Hellenism in its place, caused him to be remembered as Julian the Apostate in the Christian tradition. A nephew of Constantine the Great, Julian was one of few in the imperial family to survive the purges and civil wars during the reign of Constantius II, his cousin. Julian became an orphan as a child after his father was executed in 337, and spent much of his life under Constantius's close supervision. However, the emperor allowed Julian freedom to pursue an education in the Greek-speaking east. In 355, Constantius II summoned Julian to court and appointed him to rule Roman Gaul, Gaul. Julian was successful in his rule, defeating and counterattacking Germanic peoples, Germanic raids across the Rhine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silvanus (magister Peditum)
Silvanus (died 7 September 355) was a Roman general and usurper of Frankish descent. He revolted in Gaul against Emperor Constantius II, claiming the imperial title for 28 days in AD 355. Origin and career Silvanus was born in Gaul, the son of Bonitus, a Laetic Frankish general who had supported Constantine I in the civil war against Licinius. Like so many other Franks of his times, and like his father before him, he was a loyal and thoroughly Romanized "barbarian" in the military service of the Empire. In AD 351, he held the rank of tribune in the army of the rebel Magnentius, and in this role he defected to Emperor Constantius II at the Battle of Mursa Major. Silvanus was soon promoted to the post of ''magister peditum'' in Gaul in 353. Gaul had been subject to raiding and looting by Alemanni tribesmen; Constantius entrusted Silvanus with the difficult task of driving the invaders back beyond the Rhine, and restoring the fast-eroding Roman authority in the province. Silvanus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Adrianople
The Battle of Adrianople also known as Battle of Hadrianopolis was fought between the Eastern Roman army led by the Roman emperor Valens and Gothic rebels (largely Thervings as well as Greutungs, non-Gothic Alans, and various local rebels) led by Fritigern. The battle took place on 9 August 378 in the vicinity of Adrianople, in the Roman province of Thracia (modern Edirne in European Turkey). It ended with an overwhelming victory for the Goths and the death of Emperor Valens.Zosimus, ''Historia Nova'', book 4. As part of the Gothic War of 376–382, the battle is often considered the start of the events which led to the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century. A detailed contemporary account of the lead-up to the battle from the Roman perspective was written by Ammianus Marcellinus and forms the culminating point at the end of his history. Background In 376, the Goths, led by Alavivus and Fritigern, asked to be allowed to settle in the Eastern Roman Empir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ursicinus (magister Equitum)
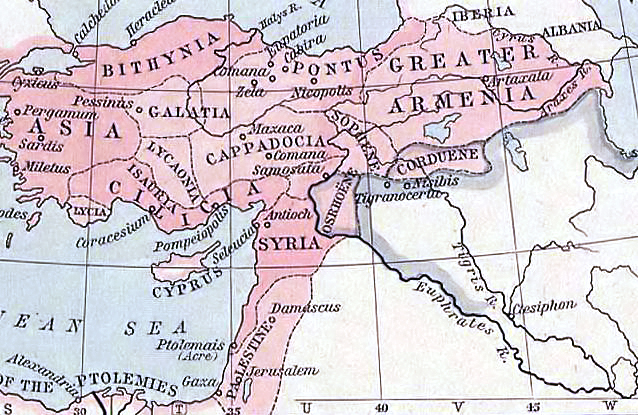
Ursicinus was a Roman senior military officer, holding the rank of ''Magister Equitum per Orientem'' (Master of Horse of the East) and even ''Magister Peditum Praesentalis'' in the later Roman Empire ''c.'' 349–359. He was a citizen of Antioch and was well connected in the Eastern part of the Roman Empire. Career From AD 349 to 359 he served as Magister Equitum in the East. In 351 or 352 he was entrusted with the suppression of the Jewish revolt against Constantius Gallus led by Patricius and Isaac of Diocesarea. Tiberias and Diospolis, two of the cities conquered by the rebels, were almost completely destroyed, while Diocaesarea was razed to the ground. Ursicinus also was ordered to kill several thousand rebels, even young ones.Jerome, ''Chronica'', 15-21; Theophanes, AM 5843. Service with Ammianus Marcellinus In 353, historian Ammianus Marcellinus was attached to the command of Ursicinus at his headquarters in Nisibis, where he remained until recalled in 354 by Gallus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valens
Valens (; ; 328 – 9 August 378) was Roman emperor from 364 to 378. Following a largely unremarkable military career, he was named co-emperor by his elder brother Valentinian I, who gave him the Byzantine Empire, eastern half of the Roman Empire to rule. In 378, Valens was defeated and killed at the Battle of Adrianople against the invading Goths, which astonished contemporaries and marked the beginning of barbarian encroachment into Roman territory. As emperor, Valens continually faced threats both internal and external. He defeated, after some dithering, the usurper Procopius (usurper), Procopius in 366, and campaigned against the Goths across the Danube in 367 and 369. In the following years, Valens focused on the eastern frontier, where he faced the perennial threat of Sasanian Empire, Persia, particularly in Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Armenia, as well as additional conflicts with the Saracens and Isaurians. Domestically, he inaugurated the Aqueduct of Valens in Cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; , ) "Antioch on Daphne"; or "Antioch the Great"; ; ; ; ; ; ; . was a Hellenistic Greek city founded by Seleucus I Nicator in 300 BC. One of the most important Greek cities of the Hellenistic period, it served as the capital of the Seleucid Empire and later as regional capital to both the Roman and Byzantine Empire. During the Crusades, Antioch served as the capital of the Principality of Antioch, one of four Crusader states that were founded in the Levant. Its inhabitants were known as ''Antiochenes''. The remains of the ancient city of Antioch are mostly buried beneath alluvial deposits from the Orontes River. The modern city of Antakya, in Hatay Province of Turkey, lies in its place. Antioch was founded near the end of the fourth century BC by Seleucus I Nicator, one of Alexander the Great's generals, as one of the tetrapoleis of Seleucis of Syria. Seleucus encouraged Greeks from all over the Mediterranean to settle in the city. The ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
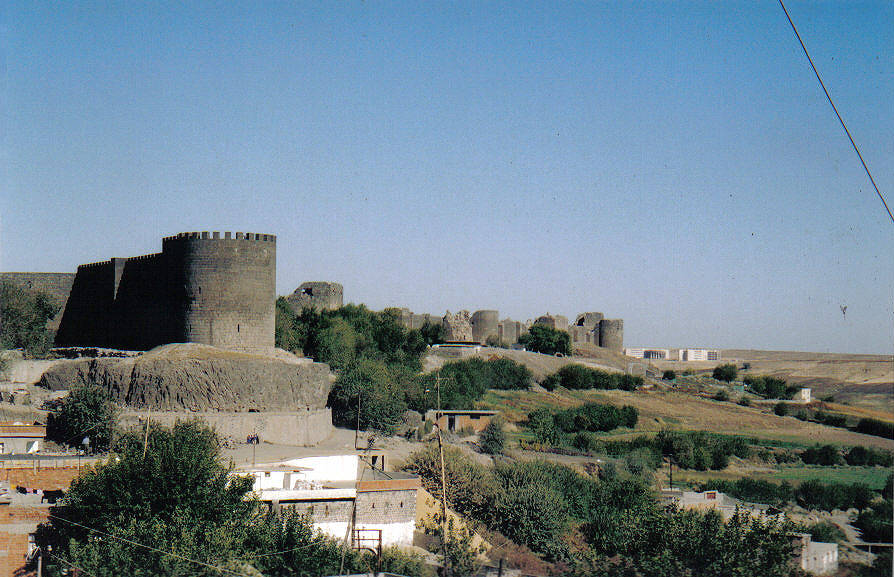
Nisibis
Nusaybin () is a municipality and Districts of Turkey, district of Mardin Province, Turkey. Its area is 1,079 km2, and its population is 115,586 (2022). The city is populated by Kurds of different tribal affiliation. Nusaybin is separated from the larger Kurds, Kurdish-majority city of Qamishli by the Syria–Turkey border. The city is at the foot of the Mount Izla escarpment at the southern edge of the Tur Abdin hills, standing on the banks of the Jaghjagh River (), the ancient Mygdonius (). The city existed in the Assyrian Empire and is recorded in Akkadian language, Akkadian inscriptions as ''Naṣibīna''. Having been part of the Achaemenid Empire, in the Hellenistic period the settlement was re-founded as a ''polis'' named "Antioch on the Mygdonius" by the Seleucid dynasty after the conquests of Alexander the Great. A part of first the Roman Republic and then the Roman Empire, the city (; ) was mainly Syriac language, Syriac-speaking, and control of it was contested be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenice (Roman Province)
Phoenice ( ; ) was a province of the Roman Empire, encompassing the historical region of Phoenicia. It was officially created in 194 AD and after , Phoenice Syria was divided into Phoenice proper or Phoenice Paralia, and Phoenice Libanensis, a division that persisted until the region was conquered by the Muslim Arabs in the 630s. Administrative history Background Phoenicia came under Roman rule in 64 BC, when Pompey created the province of Syria. With the exception of a brief period in 36–30 BC, when Mark Antony gave the region to Ptolemaic Egypt, Phoenicia remained part of the province of Syria thereafter. Emperor Hadrian (reigned 117–138) is said to have considered a division of the overly large Syrian province in 123–124 AD. Creation It was not until shortly after c. 194 AD that Septimius Severus (r. 193–211) actually undertook this, dividing the province into Syria Coele in the north and Syria Phoenice in the south. The province was much larger than the area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amioun
Amioun (; ) is the capital of the predominantly Greek Orthodox Christianity in Lebanon, Greek Orthodox Koura District (i.e. χώρα, "country" in Greek) in North Lebanon. Etymology The town of Amioun derives its name from the Aramaic language, meaning "'am Yawan" "place of the Greeks", with a possible alternative root ''fortified town'' with Roman temples. Amioun is located on the top of an ancient hill dating back to before the 2nd millennium B.C., and the town was called "Amia" during this period. The word ''Amia'' was cited in the letters of Tell el Amarna, which were sent in the 14th century B.C. by local governors to their overlords, the pharaohs of Ancient Egypt, Egypt. In his etymological study of the names of Lebanon's towns and villages, historian Anis Freiha asserted that ''Amia'' is in turn derived from the Semitic word ''emun'', meaning "invincible fort". Demographics Amioun had a population of 2,673 in 1953. In 2014, Christianity in Lebanon, Christians made u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domesticus (Roman Empire)
The origins of the word ''domesticus'' can be traced to the late 3rd century of the Late Roman army. They often held high ranks in various fields, whether it was the servants of a noble house on the civilian side, or a high-ranking military position. After serving under the emperor for a certain duration, the Domestici would be able to become leaders themselves and potentially command their own regiment of legionaries in the military. Relatively, the most important offices were the “Comes Domesticorum” also known as, “Commander of the Protectores Domestici,” and “Comes rei Militaris” or General. Origin The domestici rose to prominence during the Crisis of the 3rd Century, the myriad of societal catastrophes nearly led to the collapse of the Roman Empire. The accession of Diocletian and his subsequent reforms ended the continual strife and unstable leadership Ancient Rome had faced during this period. The title of “Domesticus” was developed to advocate for bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |