|
Amiodarone Induced Thyrotoxicosis
Amiodarone induced thyrotoxicosis (AIT) is a form of hyperthyroidism due to treatment with antiarrhythmic drug, amiodarone. Amiodarone induced thyroid dysfunction more commonly results in hypothyroidism, estimated to occur in 6-32% of patients, whereas hyperthyroidism from amiodarone use is estimated at 1-12%. However, the prevalence of AIT varies based on geographical region, and is more common in areas with low dietary iodine intake, where it occurs in 10-12% of patients. In the United States, clinical manifestations of AIT occur in 3-5% of patients. AIT may present clinically early after initiation of amiodarone or can be delayed even up several years. Symptoms associated with AIT are similar to those of other forms of hyperthyroidism, including new-onset or recurrence of arrhythmias, worsening of pre-existing heart conditions such as ischemic heart disease or heart failure, unattributed weight loss, and fever. Development of AIT is associated with an increased risk for major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amiodarone
Amiodarone is an antiarrhythmic medication used to treat and prevent a number of types of cardiac dysrhythmias. This includes ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and wide complex tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, and paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. Evidence in cardiac arrest, however, is poor. It can be given by mouth, intravenously, or intraosseously. When used by mouth, it can take a few weeks for effects to begin. Common side effects include feeling tired, tremor, nausea, and constipation. As amiodarone can have serious side effects, it is mainly recommended only for significant ventricular arrhythmias. Serious side effects include lung toxicity such as interstitial pneumonitis, liver problems, heart arrhythmias, vision problems, thyroid problems, and death. If taken during pregnancy or breastfeeding it can cause problems in the fetus or the infant. It is a class III antiarrhythmic medication. It works partly by increasing the time before a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a condition in which the heart becomes enlarged and cannot pump blood effectively. Symptoms vary from none to feeling tired, leg swelling, and shortness of breath. It may also result in chest pain or fainting. Complications can include heart failure, heart valve disease, or an irregular heartbeat. Causes include genetics, alcohol, cocaine, certain toxins, complications of pregnancy, and certain infections. Coronary artery disease and high blood pressure may play a role, but are not the primary cause. In many cases the cause remains unclear. It is a type of cardiomyopathy, a group of diseases that primarily affects the heart muscle. The diagnosis may be supported by an electrocardiogram, chest X-ray, or echocardiogram. In those with heart failure, treatment may include medications in the ACE inhibitor, beta blocker, and diuretic families. A low salt diet may also be helpful. In those with certain types of irregular heartbeat, blood thinner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
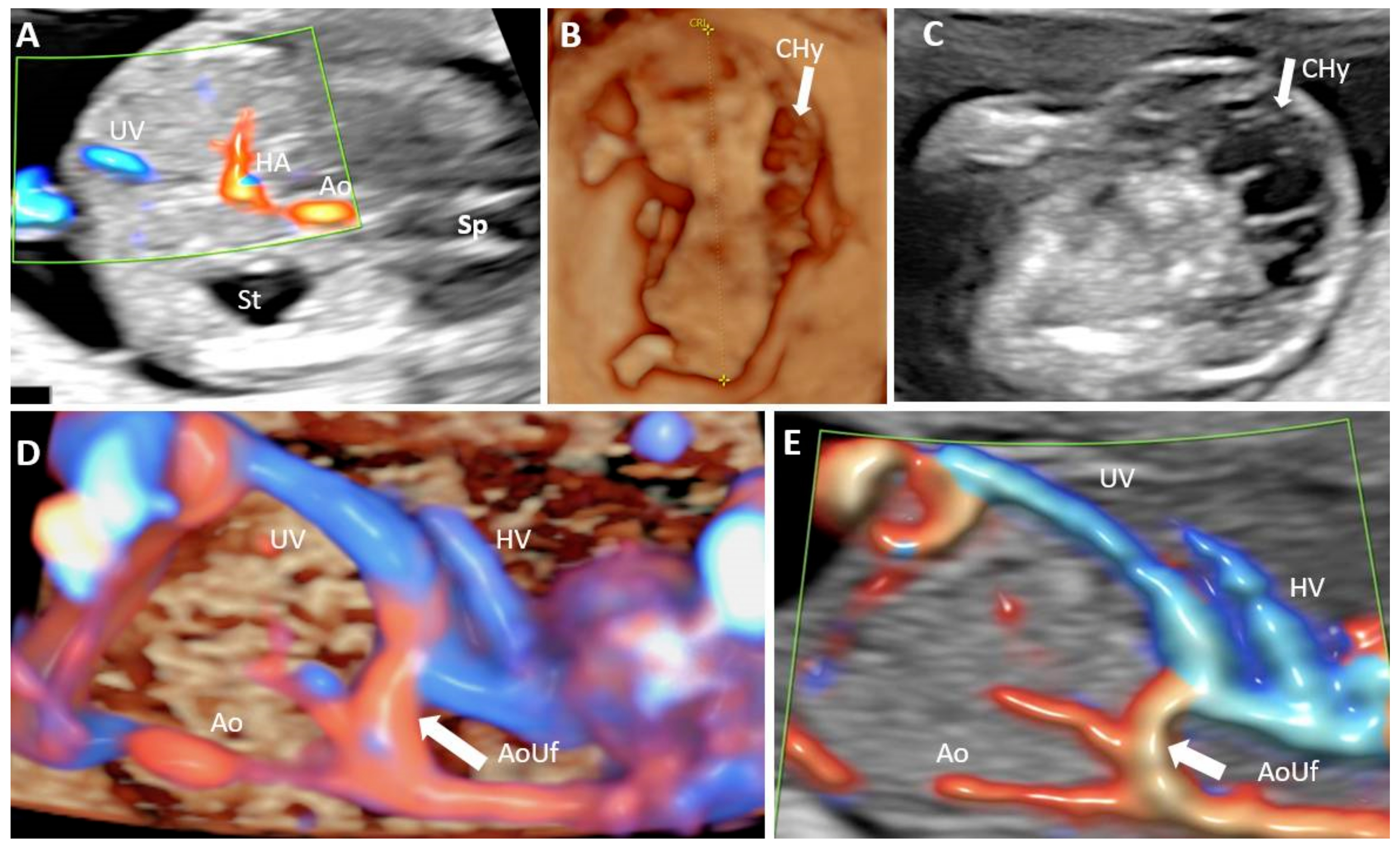
Doppler Ultrasonography
Doppler ultrasonography is medical ultrasonography that employs the Doppler effect to perform imaging of the movement of tissues and body fluids (usually blood), and their relative velocity to the probe. By calculating the frequency shift of a particular sample volume, for example, flow in an artery or a jet of blood flow over a heart valve, its speed and direction can be determined and visualized. Duplex ultrasonography sometimes refers to Doppler ultrasonography or spectral Doppler ultrasonography. Doppler ultrasonography consists of two components: brightness mode (B-mode) showing anatomy of the organs, and Doppler mode (showing blood flow) superimposed on the B-mode. Meanwhile, spectral Doppler ultrasonography consists of three components: B-mode, Doppler mode, and spectral waveform displayed at the lower half of the image. Therefore, "duplex ultrasonography" is a misnomer for spectral Doppler ultrasonography, and more exact name should be "triplex ultrasonography". This is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasonography
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly imaging) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints, blood vessels, and internal organs, to measure some characteristics (e.g., distances and velocities) or to generate an informative audible sound. The usage of ultrasound to produce visual images for medicine is called medical ultrasonography or simply sonography, or echography. The practice of examining pregnant women using ultrasound is called obstetric ultrasonography, and was an early development of clinical ultrasonography. The machine used is called an ultrasound machine, a sonograph or an echograph. The visual image formed using this technique is called an ultrasonogram, a sonogram or an echogram. Ultrasound is composed of sound waves with frequencies greater than 20,000 Hz, which is the approximate upper threshold of human h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technetium (99mTc) Sestamibi
Technetium (99mTc) sestamibi ( INN; commonly sestamibi; USP: technetium Tc 99m sestamibi; trade name Cardiolite) is a pharmaceutical agent used in nuclear medicine imaging. The drug is a coordination complex consisting of the radioisotope technetium-99m bound to six (sesta=6) methoxyisobutylisonitrile (MIBI) ligands. The anion is not defined. The generic drug became available late September 2008. A scan of a patient using MIBI is commonly known as a "MIBI scan". Sestamibi is taken up by tissues with large numbers of mitochondria and negative plasma membrane potentials. Sestamibi is mainly used to image the myocardium (heart muscle). It is also used in the work-up of primary hyperparathyroidism to identify parathyroid adenomas, for radioguided surgery of the parathyroid and in the work-up of possible breast cancer. Cardiac imaging (MIBI scan) A ''MIBI scan'' or ''sestamibi scan'' is now a common method of cardiac imaging. Technetium (99mTc) sestamibi is a lipophilic cation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive Iodine Uptake Test
The radioactive iodine uptake test is a type of scan used in the diagnosis of thyroid problems, particularly hyperthyroidism. It is entirely different from radioactive iodine therapy (RAI therapy), which uses much higher doses to destroy cancerous cells. The RAIU test is also used as a follow-up to RAI therapy to verify that no thyroid cells survived, which could still be cancerous. ThyCa: Thyroid Cancer Survivors' Association, Inc., Radioactive Iodine (RAI). The patient swallows Isotopes of iodine#Notable radioisotopes, a radioisotope of iodine in the form of capsule or fluid, and the absorption (uptake) of this radioactive tracer, radiotracer by the thyroid is studied after 4–6 hours and after 24 hours with the aid of a scintillation counter. The dose is typically 0.15–0.37 Megabecquerel, MBq (4–10 Microcurie, μCi) of Iodine-131, 131I iodide, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radionuclide Imaging
Nuclear medicine (nuclear radiology, nucleology), is a medical specialty involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear imaging is, in a sense, ''radiology done inside out'', because it records radiation emitted from within the body rather than radiation that is transmitted through the body from external sources like X-ray generators. In addition, nuclear medicine scans differ from radiology, as the emphasis is not on imaging anatomy, but on the function. For such reason, it is called a physiological imaging modality. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans are the two most common imaging modalities in nuclear medicine. Diagnostic medical imaging Diagnostic In nuclear medicine imaging, radiopharmaceuticals are taken internally, for example, through inhalation, intravenously, or orally. Then, external detectors (gamma cameras) capture and form images from the radi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunological Defense
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as cancer cells, parasitic worms, and also objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use molecules and cells to perform their functions. Nearly all organisms have some kind of immune system. Bacteria have a rudimentary immune system in the form of enzymes that protect against viral infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient plants and animals and remain in their modern descendants. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circulatory System
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels (from Greek meaning ''heart'', and Latin meaning ''vessels''). The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms ''cardiovascular system'' and ''vascular system'' interchangeably with ''circulatory system''. The network of blood vessels are the great vessels of the heart including large elastic arteries, and large veins; other arteries, smaller arterioles, capillaries that join with venules (small veins), and other veins. The circulatory system is closed in vertebrates, which means that the blood never leaves the network of blood vessels. Many invertebrates such as arthropods have an open circulatory system with a he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore is considered a mechanism of innate immunity, whereas adaptive immunity is specific to each pathogen. Inflammation is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out damaged cells and tissues, and initiate tissue repair. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. bacteria) and compromise the survival of the organism. However inflammation can also have negative effects. Too much inflammation, in the form of chronic inflammation, is associated with variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroiditis
Thyroiditis is the inflammation of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is located on the front of the neck below the laryngeal prominence, and makes hormones that control metabolism. Thyroiditis is a group of disorders that all cause thyroidal inflammation. Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment depend on the cause of thyroiditis. Forms of thyroiditis are Hashimoto's thyroiditis, postpartum thyroiditis, subacute (de Quervain's) thyroiditis, silent thyroiditis, drug-induced thyroiditis, radiation-induced thyroiditis and acute thyroiditis. Types Hashimoto's thyroiditis is an autoimmune disease where the body creates thyroid antibodies. It presents with hypothyroidism due to the destruction of thyroid cells. In Hashimoto's thyroiditis, the hypothyroidism is most often permanent, with symptoms are fatigue, weight gain, depression, dry skin, and constipation. Thyroid hormone replacement is the treatment of hypothyroidism. Silent thyroiditis or painless thyroiditis, also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytotoxicity
Cytotoxicity is the quality of being toxic to cells. Examples of toxic agents are toxic metals, toxic chemicals, microbe neurotoxins, radiation particles and even specific neurotransmitters when the system is out of balance. Also some types of drugs, e.g alcohol, and some venom, e.g. from the puff adder (''Bitis arietans'') or brown recluse spider (''Loxosceles reclusa'') are toxic to cells. Cell physiology Treating cells with the cytotoxic compound can result in a variety of prognoses. The cells may undergo necrosis, in which they lose membrane integrity and die rapidly as a result of cell lysis. The cells can stop actively growing and dividing (a decrease in cell viability), or the cells can activate a genetic program of controlled cell death (apoptosis). Cells undergoing necrosis typically exhibit rapid swelling, lose membrane integrity, shut down metabolism, and release their contents into the environment. Cells that undergo rapid necrosis in vitro do not have sufficient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |