|
Amia Basiloides
''Amia basiloides'' is an extinct species of giant bowfin that inhabited western North America during the Middle or Late Paleocene, about 5-10 million years after the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event. The species name originates from the Ancient Greek βασιλεύς (''basileus''), meaning "king", referencing its immense size. Discovery It is known from a holotype comprising nearly complete skull with a partial skeleton found in the Fort Union Formation in Montana Montana ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota to the east, South Dakota to the southeast, Wyoming to the south, an ..., USA. This specimen was previously assigned to the species ''Amia uintaensis'', a taxon now considered a ''nomen vanum''. An isolated vertebra is also known from another Fort Union Formation locality, which appears to represent an individual 20 to 30 percent la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleocene
The Paleocene ( ), or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 mya (unit), million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''palaiós'' meaning "old" and the Eocene Epoch (which succeeds the Paleocene), translating to "the old part of the Eocene". The epoch is bracketed by two major events in Earth's history. The K–Pg extinction event, brought on by an asteroid impact (Chicxulub impact) and possibly volcanism (Deccan Traps), marked the beginning of the Paleocene and killed off 75% of species, most famously the non-avian dinosaurs. The end of the epoch was marked by the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), which was a major climatic event wherein about 2,500–4,500 gigatons of carbon were released into the atmosphere and ocean systems, causing a spike in global temperatures and ocean acidification. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holostei
Holostei is a group of ray-finned bony fish. It is divided into two major clades, the Halecomorphi, represented by the single living genus, '' Amia'' with two species, the bowfins (''Amia calva'' and '' Amia ocellicauda''), as well as the Ginglymodi, the sole living representatives being the gars (Lepisosteidae), represented by seven living species in two genera ('' Atractosteus'', '' Lepisosteus''). The earliest members of the clade, which are putative " semionotiforms" such as '' Acentrophorus'' and '' Archaeolepidotus'', are known from the Middle to Late Permian and are among the earliest known neopterygians. Holostei was thought to be regarded as paraphyletic. However, a recent study provided evidence that the Holostei are the closest living relatives of the Teleostei, both within the Neopterygii. This was found from the morphology of the Holostei, for example presence of a paired vomer. Holosteans are closer to teleosts than are the chondrosteans, the other group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils Of Montana
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of ''Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of Canada. Paleontology includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleogene Fish Of North America
The Paleogene Period ( ; also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene) is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Neogene Period Ma. It is the first period of the Cenozoic Era, the tenth period of the Phanerozoic and is divided into the Paleocene, Eocene, and Oligocene epochs. The earlier term Tertiary Period was used to define the time now covered by the Paleogene Period and subsequent Neogene Period; despite no longer being recognized as a formal stratigraphic term, "Tertiary" still sometimes remains in informal use. Paleogene is often abbreviated "Pg", although the United States Geological Survey uses the abbreviation "" for the Paleogene on the Survey's geologic maps. Much of the world's modern vertebrate diversity originated in a rapid surge of diversification in the early Paleogene, as survivors of the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event took advantage of empty ecologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleocene Fish
The Paleocene ( ), or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''palaiós'' meaning "old" and the Eocene Epoch (which succeeds the Paleocene), translating to "the old part of the Eocene". The epoch is bracketed by two major events in Earth's history. The K–Pg extinction event, brought on by an asteroid impact (Chicxulub impact) and possibly volcanism (Deccan Traps), marked the beginning of the Paleocene and killed off 75% of species, most famously the non-avian dinosaurs. The end of the epoch was marked by the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), which was a major climatic event wherein about 2,500–4,500 gigatons of carbon were released into the atmosphere and ocean systems, causing a spike in global temperatures and ocean acidification. In the Paleocene, the continents of the Northern Hemisphere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmodraco
''Kosmodraco'' is a genus of large bodied choristodere from the Paleocene of North America. Originally described as a species of the closely related ''Simoedosaurus'', it was found to represent a distinct genus in 2022. Multiple fossil skulls show a relatively short and robust snout and a skull that is considerably wider behind the eyes. Two species are currently recognized, ''K. dakotensis'' and ''K. magnicornis''. History and naming The first specimen now known to belong to ''Kosmodraco'' was discovered in 1964 and 1968 in the Polecat Bench Formation (Wyoming). These two skulls, alongside others from Montana's Bear Creek, were reported on briefly by Sigogneau-Russell and Donald in 1978, who regarded them as evidence for the presence of the Eurasian genus ''Simoedosaurus'' in North America. However, at the time, these four specimens, although thought to be diagnostic at a genus level, were still unprepared and not assigned to a species. They were subsequently stored in the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
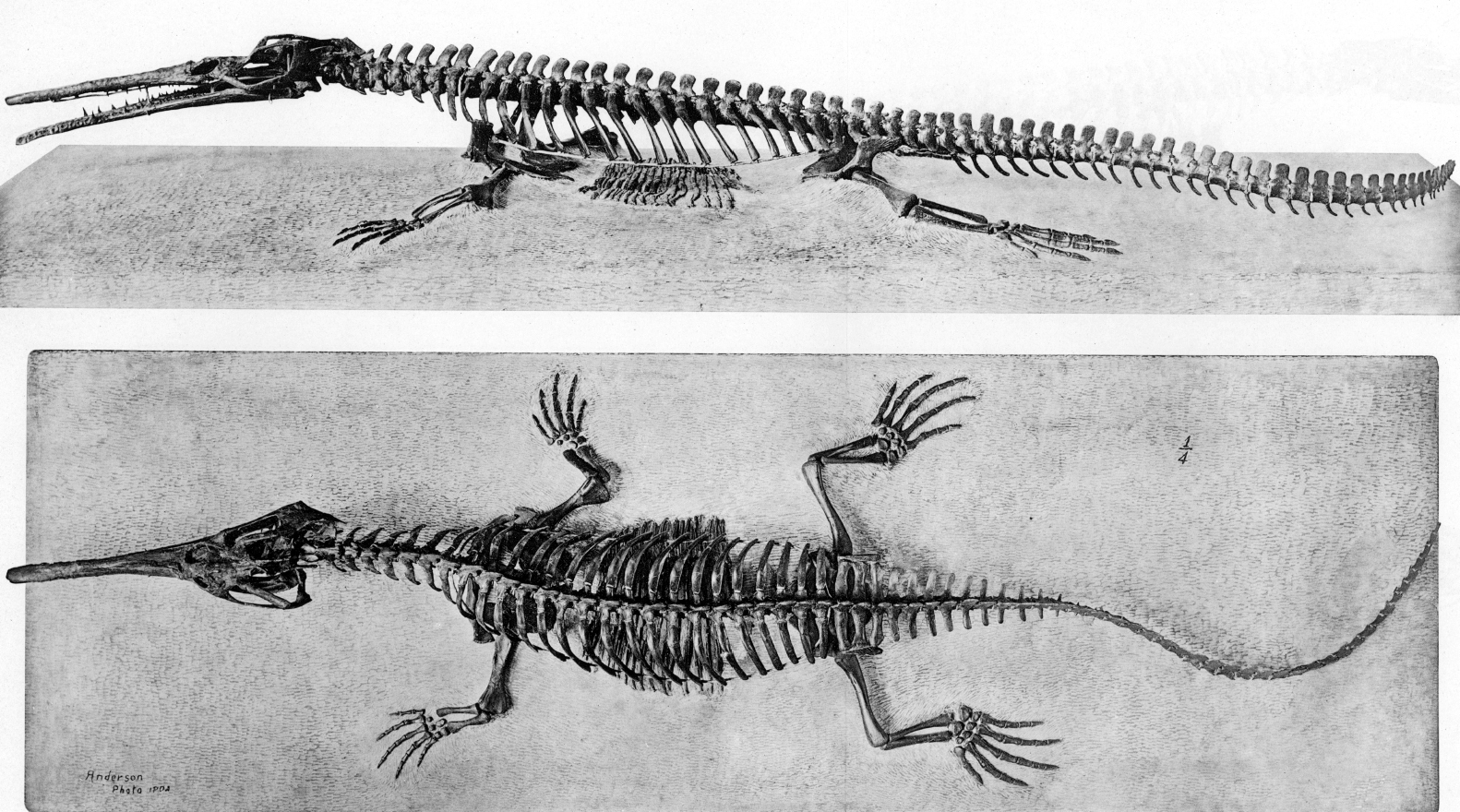
Champsosaurus
''Champsosaurus'' is an extinct genus of crocodile-like choristodere reptile, known from the Late Cretaceous and early Paleogene periods of North America and Europe (Campanian–Paleocene). The name ''Champsosaurus'' is thought to come from , () said in an Ancient Greek source to be an Egyptian word for "crocodiles", and , () Greek for "lizard". The morphology of ''Champsosaurus'' resembles that of gharials, with a long, elongated snout. It was native to freshwater environments where it likely preyed on fish, similar to living gharials. History of research ''Champsosaurus'' was the first member of the Choristodera to be described. ''Champsosaurus'' was named by Edward Drinker Cope in 1876, from isolated vertebrae found in Late Cretaceous strata of the Judith River Formation on the banks of the Judith River in Fergus County, Montana. Cope designated ''C. annectens'' as the type species rather than the first named ''C. profundus'' due to the larger number of vertebrae he attribu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choristodera
Choristodera (from the Greek χωριστός ''chōristos'' + δέρη ''dérē'', 'separated neck') is an extinct order of semiaquatic diapsid reptiles that ranged from the Middle Jurassic, or possibly Triassic, to the Miocene (168 to 20 or possibly 11.6 million years ago). Choristoderes are morphologically diverse, with the best known members being the crocodile-like neochoristoderes such as '' Champsosaurus''. Other choristoderans had lizard-like or long necked morphologies. Choristoderes appear to have been confined to the Northern Hemisphere, having been found in North America, Asia, and Europe, and possibly also North Africa. Choristoderes are generally thought to be derived neodiapsids that are close relatives or members of Sauria. History of discovery Choristodera was erected in 1876, originally as a suborder of Rhynchocephalia by Edward Drinker Cope to contain '' Champsosaurus,'' which was described from Late Cretaceous strata of Montana by Cope in the same paper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sturgeon
Sturgeon (from Old English ultimately from Proto-Indo-European language, Proto-Indo-European *''str̥(Hx)yón''-) is the common name for the 27 species of fish belonging to the family Acipenseridae. The earliest sturgeon fossils date to the Late Cretaceous, and are descended from other, earlier Acipenseriformes, acipenseriform fish, which date back to the Early Jurassic period, some 174 to 201 million years ago. They are one of two living families of the Acipenseriformes alongside paddlefish (Polyodontidae). The family is grouped into five genera: ''Acipenser'', ''Huso'', ''Scaphirhynchus,'' ''Sinosturio'', and ''Pseudoscaphirhynchus''. Two species (''Adriatic sturgeon, H. naccarii'' and ''Dabry's sturgeon, S. dabryanus'') may be extinct in the wild, and one (''Syr Darya sturgeon, P. fedtschenkoi'') may be entirely extinct. Sturgeons are native to subtropical, temperate and sub-Arctic rivers, lakes and coastlines of Eurasia and North America. A Maastrichtian-age fossil found i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acipenser
''Acipenser'' is a genus of sturgeons, containing three species native to freshwater and estuarine systems of eastern North America and Europe. It is the type genus of the family Acipenseridae and the order Acipenseriformes. Taxonomy Prior to 2025, ''Acipenser'' contained almost all species in the Acipenseridae outside of ''Huso'' and the "shovelnose" sturgeons (''Scaphirhynchus'' and '' Pseudoscaphirhynchus''). However, such a placement is now known to be paraphyletic with respect to the other genera, and these species have since been split into ''Huso'' and '' Sinosturio''. ''Acipenser'' in the strict sense ('' sensu stricto'') has been redefined with only 3 species. This is an ancient genus, with phylogenetic evidence suggesting that it is the most basal sturgeon genus, having diverged from other sturgeons during the Early Cretaceous period. Several fossil species known as far back as the Late Cretaceous, with the fossils of two species ('' A. praeparatorum'' and '' A. a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amia? Hesperia
''Amia''? ''hesperia'' is an extinct species of ray-finned fish in the bowfin family, Amiidae. The species is known from fossils found in the early Eocene deposits of northern Washington in the United States and southeastern British Columbia. The species is one of eight fish species identified in the Eocene Okanagan Highlands paleofauna. The species has been suggested to possibly belong to either ''Amia'' or the extinct genus ''Cyclurus''. More recent studies have affirmed it as a basal member of ''Amia''. Distribution and paleoenvironment ''Amia''? ''hesperia'' fossils have been recovered from two locations in the Eocene Okanagan Highlands, the Allenby Formation of the Princeton, British Columbia region and as isolated scales from the Klondike Mountain Formation in northern Ferry County, Washington. Both sites represent upland lake systems that were surrounded by a warm temperate ecosystem with nearby volcanism. The highlands likely had a mesic upper microthermal to low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vidalamiinae
The Amiidae are a family of basal (phylogenetics), basal ray-finned fishes. The bowfin and the eyespot bowfin (''Amia ocellicauda'') are the only two species to survive today, although additional species in all four subfamilies of Amiidae are known from Jurassic, Cretaceous, and Eocene fossils. Bowfins are now found throughout eastern North America, typically in slow-moving backwaters, canals, and ox-bow lakes. When the oxygen level is low (as often happens in still waters), the bowfin can rise to the surface and gulp air into its swim bladder, which is lined with blood vessels and can serve as a primitive lung. Amiidae is a monophyletic group that has numerous synapomorphic characters. Amiidae were widespread and particularly rich in species during the Eocene era. During this era, they appeared to be confined almost exclusively to fresh water. Taxonomy The family is divided into five subfamilies, with 16 genera *Amiidae **Subfamily Amiinae (latest Cretaceous -Present) ***Genu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |