|
American Journey
''American Journey'' (originally titled ''The Unfinished Journey'') is a six-part orchestral composition by the American composer John Williams. The piece was commissioned by U.S. President Bill Clinton to accompany a multimedia presentation titled ''The Unfinished Journey'' directed by Steven Spielberg for the 2000 "Millennium" celebrations. The work premiered at the Lincoln Memorial in Washington, D.C. on New Year's Eve, 1999. Composition Structure Lasting approximately twenty-five minutes in performance, ''American Journey'' is composed in six short movements played without pause: #"Immigration and Building" #"The Country at War" #"Popular Entertainment" #"Arts and Sports" #"Civil Rights and the Women's Movement" #"Flight and Technology" Style and influences The first movement, "Immigration and Building," contains quotes from Williams' score to the 1992 film ''Far and Away''. Additionally, the style of the music would heavily anticipate his score to the 2000 film '' The Patri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orchestra
An orchestra (; ) is a large instrumental ensemble typical of classical music, which combines instruments from different families. There are typically four main sections of instruments: * String instruments, such as the violin, viola, cello, and double bass * Woodwinds, such as the flute, oboe, clarinet, bassoon, and occasional saxophone * Brass instruments, such as the French horn (commonly known as the "horn"), trumpet, trombone, cornet, and tuba, and sometimes euphonium * Percussion instruments, such as the timpani, snare drum, bass drum, cymbals, triangle, tambourine, tam-tam and mallet percussion instruments Other instruments such as the piano, harpsichord, pipe organ, and celesta may sometimes appear in a fifth keyboard section or may stand alone as soloist instruments, as may the concert harp and, for performances of some modern compositions, electronic instruments, and guitars. A full-size Western orchestra may sometimes be called a or phil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cor Anglais
The cor anglais (, or original ; plural: ''cors anglais''), or English horn (mainly North America), is a double-reed woodwind instrument in the oboe family. It is approximately one and a half times the length of an oboe, making it essentially an alto oboe in F. The cor anglais is a transposing instrument pitched in F, a perfect fifth lower than the oboe (a C instrument). This means that music for the cor anglais is written a perfect fifth higher than the instrument sounds. The fingering and playing technique used for the cor anglais are essentially the same as those of the oboe, and oboists typically double on the cor anglais when required. The cor anglais normally lacks the lowest B key found on most oboes, and so its sounding range stretches from E3 (written B) below middle C to C6 two octaves above middle C. Some versions being made today have a Low B key to extend the range down one more note to sounding E3. Description and timbre The pear-shaped bell (called Liebesfuß ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cymbal
A cymbal is a common percussion instrument. Often used in pairs, cymbals consist of thin, normally round plates of various alloys. The majority of cymbals are of indefinite pitch, although small disc-shaped cymbals based on ancient designs sound a definite note (such as crotales). Cymbals are used in many ensembles ranging from the orchestra, percussion ensembles, jazz bands, heavy metal bands, and marching groups. Drum kits usually incorporate at least a crash, ride, or crash/ride, and a pair of hi-hat cymbals. A player of cymbals is known as a cymbalist. Etymology and names The word cymbal is derived from the Latin , which is the latinisation , which in turn derives . In orchestral scores, cymbals may be indicated by the French ; German , , , or ; Italian or ; and Spanish . Many of these derive from the word for plates. History Cymbals have existed since ancient times. Representations of cymbals may be found in reliefs and paintings from Armenian Highlands (7t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubular Bells
Tubular bells (also known as chimes) are musical instruments in the Percussion instrument, percussion family. Their sound resembles that of church bells, carillons, or a bell tower; the original tubular bells were made to duplicate the sound of church bells within an ensemble. Each bell (instrument), bell is a metal tube, in diameter, tuned by altering its length. Its standard range is C4–F5, though many professional instruments reach G5. Tubular bells are often replaced by studio chimes, which are smaller and usually less expensive instruments. Studio chimes are similar in appearance to tubular bells, but each bell has a smaller diameter than the corresponding bell on tubular bells. Tubular bells are sometimes struck on the top edge of the tube with a rawhide (textile), rawhide- or plastic-headed hammer. Often, a sustain pedal will be attached to allow extended ringing of the bells. They can also be bowed at the bottom of the tube to produce a very loud, very high-pitche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bass Drum
The bass drum is a large drum that produces a note of low definite or indefinite pitch. The instrument is typically cylindrical, with the drum's diameter usually greater than its depth, with a struck head at both ends of the cylinder. The heads may be made of calfskin or plastic and there is normally a means of adjusting the tension, either by threaded taps or by strings. Bass drums are built in a variety of sizes, but size does not dictate the volume produced by the drum. The pitch and the sound can vary much with different sizes,Norman Del Mar, Del Mar, Norman (1981). ''Anatomy of the Orchestra''. . but the size is also chosen based on convenience and aesthetics. Bass drums are percussion instruments that vary in size and are used in several musical genres. Three major types of bass drums can be distinguished. * The type usually seen or heard in orchestral, ensemble or concert band music is the orchestral, or concert bass drum (in Italian: gran cassa, gran tamburo). It is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percussion Instrument
A percussion instrument is a musical instrument that is sounded by being struck or scraped by a percussion mallet, beater including attached or enclosed beaters or Rattle (percussion beater), rattles struck, scraped or rubbed by hand or struck against another similar instrument. Excluding Zoomusicology, zoomusicological instruments and the human voice, the percussion family is believed to include the oldest musical instruments.''The Oxford Companion to Music'', 10th edition, p.775, In spite of being a very common term to designate instruments, and to relate them to their players, the percussionists, percussion is not a systematic classificatory category of instruments, as described by the scientific field of organology. It is shown below that percussion instruments may belong to the organological classes of idiophone, membranophone, aerophone and String instrument, chordophone. The percussion section of an orchestra most commonly contains instruments such as the timpani, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timpani
Timpani (; ) or kettledrums (also informally called timps) are musical instruments in the percussion instrument, percussion family. A type of drum categorised as a hemispherical drum, they consist of a Membranophone, membrane called a drumhead, head stretched over a large bowl traditionally made of copper. Thus timpani are an example of kettledrums, also known as vessel drums and semispherical drums, whose body is similar to a section of a sphere whose cut conforms the head. Most modern timpani are ''pedal timpani'' and can be tuned quickly and accurately to specific pitches by skilled players through the use of a movable foot-pedal. They are played by striking the head with a specialized Beater (percussion), beater called a ''timpani stick'' or ''timpani mallet''. Timpani evolved from military drums to become a staple of the European classical music, classical orchestra by the last third of the 18th century. Today, they are used in many types of Musical ensemble, ensembles, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuba
The tuba (; ) is the largest and lowest-pitched musical instrument in the brass instrument, brass family. As with all brass instruments, the sound is produced by lip vibrationa buzzinto a mouthpiece (brass), mouthpiece. It first appeared in the mid-19th century, making it one of the newer instruments in the modern orchestra and concert band, and largely replaced the ophicleide. ''Tuba'' is Latin for "trumpet". A person who plays the tuba is called a tubaist, a tubist, or simply a tuba player. In a British Brass band (British style), brass band or military band, they are known as bass players. History Prussian Patent No. 19 was granted to Wilhelm Friedrich Wieprecht and Johann Gottfried Moritz on 12 September 1835 for a "bass tuba" in F1. The original Wieprecht and Moritz instrument used five valves of the Brass instrument valve#Double-piston valve, Berlinerpumpen type that was the forerunner of the modern piston valve. The first tenor tuba was invented in 1838 by Moritz's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trombone
The trombone (, Italian, French: ''trombone'') is a musical instrument in the Brass instrument, brass family. As with all brass instruments, sound is produced when the player's lips vibrate inside a mouthpiece, causing the Standing wave, air column inside the instrument to vibrate. Nearly all trombones use a telescoping slide mechanism to alter the Pitch (music), pitch instead of the brass instrument valve, valves used by other brass instruments. The valve trombone is an exception, using three valves similar to those on a trumpet, and the superbone has valves and a slide. The word "trombone" derives from Italian ''tromba'' (trumpet) and ''-one'' (a suffix meaning "large"), so the name means "large trumpet". The trombone has a predominantly cylindrical bore like the trumpet, in contrast to the more conical brass instruments like the cornet, the flugelhorn, the Baritone horn, baritone, and the euphonium. The most frequently encountered trombones are the tenor trombone and bass tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
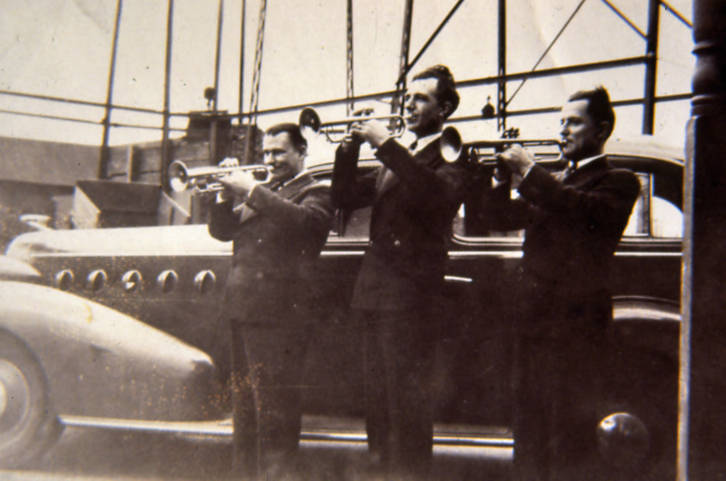
Trumpet
The trumpet is a brass instrument commonly used in classical and jazz musical ensemble, ensembles. The trumpet group ranges from the piccolo trumpet—with the highest Register (music), register in the brass family—to the bass trumpet, pitched one octave below the standard B or C trumpet. Trumpet-like instruments have historically been used as signaling devices in battle or hunting, with examples dating back to the 2nd Millenium BC. They began to be used as musical instruments only in the late 14th or early 15th century. Trumpets are used in art music styles, appearing in orchestras, concert bands, chamber music groups, and jazz ensembles. They are also common in popular music and are generally included in school bands. Sound is produced by vibrating the lips in a mouthpiece, which starts a standing wave in the air column of the instrument. Since the late 15th century, trumpets have primarily been constructed of brass tubing, usually bent twice into a rounded rectangular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Horn
The French horn (since the 1930s known simply as the horn in professional music circles) is a brass instrument made of tubing wrapped into a coil with a flared bell. The double horn in F/B (technically a variety of German horn) is the horn most often used by players in professional orchestras and bands, although the descant and triple horn have become increasingly popular. A musician who plays a horn is known as a list of horn players, horn player or hornist. Pitch is controlled through the combination of the following factors: speed of air through the instrument (controlled by the player's lungs and thoracic diaphragm); diameter and tension of lip aperture (by the player's lip muscles—the embouchure) in the mouthpiece; plus, in a modern horn, the operation of Brass instrument valve, valves by the left hand, which route the air into extra sections of tubing. Most horns have lever-operated rotary valves, but some, especially older horns, use piston valves (similar to a trumpet's) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contrabassoon
The contrabassoon, also known as the double bassoon, is a larger version of the bassoon, sounding an octave lower. Its technique is similar to its smaller cousin, with a few notable differences. Differences from the bassoon The Reed (mouthpiece), reed is considerably larger than the bassoon's, at in total length (and in width) compared with for most bassoon reeds. The large blades allow ample vibration that produces the low register of the instrument. The contrabassoon reed is similar to an average bassoon's in that scraping the reed affects both the Intonation (music), intonation and response of the instrument. Contrabassoons feature a slightly simplified version of bassoon keywork, though all open toneholes on bassoon have necessarily been replaced with keys and pads due to the physical distances. In the lower Register (music), register, its Fingering (music), fingerings are nearly identical to bassoon. However, the octave mechanism used to play in the middle register wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |