|
Ambulocetidae
Ambulocetidae is a family of early cetaceans from Pakistan. The genus ''Ambulocetus'', after which the family is named, is by far the most complete and well-known ambulocetid genus due to the excavation of an 80% complete specimen of ''Ambulocetus natans''. The other two genera in the family, '' Gandakasia'' and '' Himalayacetus'', are known only from teeth and mandibular fragments. Retaining large hindlimbs, it was once thought that they could walk on land—indeed, their name means "walking whales"—, but recent research suggests they may have been fully aquatic like modern cetaceans, though the research has some limits that cast doubt on this conclusion. Description The most basal of marine cetaceans, ambulocetids lived in shallow near-shore environments such as estuaries and bays, but were still dependent on fresh water during some stage of their life. Some of the characteristics related to sound transmission found in the lower jaws of modern whales that were absent in pak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambulocetus Nattans
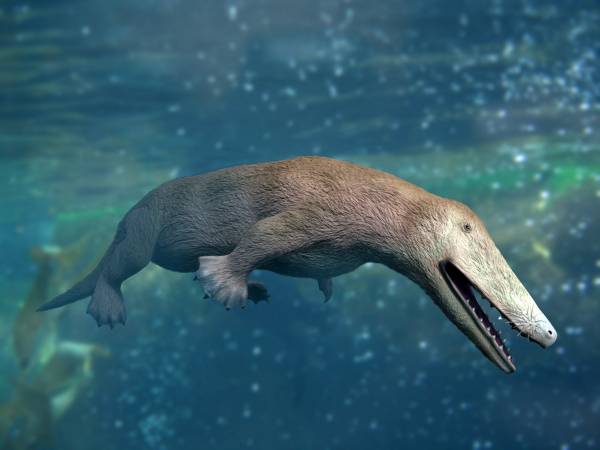
''Ambulocetus'' (Latin ''ambulare'' "to walk" + ''cetus'' "whale") is a genus of early amphibious cetacean from the Kuldana Formation in Pakistan, roughly 48 or 47 million years ago during the Early Eocene (Lutetian). It contains one species, ''Ambulocetus natans'' (Latin ''natans'' "swimming"), known solely from a near-complete skeleton. ''Ambulocetus'' is among the best-studied of Eocene cetaceans, and serves as an instrumental find in the study of cetacean evolution and their transition from land to sea, as it was the first cetacean discovered to preserve a suite of adaptations consistent with an amphibious lifestyle. ''Ambulocetus'' is classified in the group Archaeoceti—the ancient forerunners of modern cetaceans whose members span the transition from land to sea—and in the family Ambulocetidae, which includes ''Himalayacetus'' and ''Gandakasia'' (also from the Eocene of the Indian subcontinent). ''Ambulocetus'' had a narrow, streamlined body, and a long, broad snout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambulocetus
''Ambulocetus'' (Latin ''ambulare'' "to walk" + ''cetus'' "whale") is a genus of early Semiaquatic, amphibious cetacean from the Kuldana Formation in Pakistan, roughly 48 or 47 million years ago during the Early Eocene (Lutetian). It contains one species, ''Ambulocetus natans'' (Latin ''natans'' "swimming"), known solely from a near-complete skeleton. ''Ambulocetus'' is among the best-studied of Eocene cetaceans, and serves as an instrumental find in the study of evolution of cetaceans, cetacean evolution and their transition from land to sea, as it was the first cetacean discovered to preserve a suite of adaptations consistent with an amphibious lifestyle. ''Ambulocetus'' is classified in the group Archaeoceti—the ancient forerunners of modern cetaceans whose members span the transition from land to sea—and in the family (biology), family Ambulocetidae, which includes ''Himalayacetus'' and ''Gandakasia'' (also from the Eocene of the Indian subcontinent). ''Ambulocetus'' ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambulocetidae
Ambulocetidae is a family of early cetaceans from Pakistan. The genus ''Ambulocetus'', after which the family is named, is by far the most complete and well-known ambulocetid genus due to the excavation of an 80% complete specimen of ''Ambulocetus natans''. The other two genera in the family, '' Gandakasia'' and '' Himalayacetus'', are known only from teeth and mandibular fragments. Retaining large hindlimbs, it was once thought that they could walk on land—indeed, their name means "walking whales"—, but recent research suggests they may have been fully aquatic like modern cetaceans, though the research has some limits that cast doubt on this conclusion. Description The most basal of marine cetaceans, ambulocetids lived in shallow near-shore environments such as estuaries and bays, but were still dependent on fresh water during some stage of their life. Some of the characteristics related to sound transmission found in the lower jaws of modern whales that were absent in pak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeoceti
Archaeoceti ("ancient whales"), or Zeuglodontes in older literature, is an obsolete paraphyletic group of primitive cetaceans that lived from the Early Eocene to the late Oligocene (). Representing the earliest cetacean radiation, they include the initial amphibious stages in cetacean evolution, thus are the ancestors of both modern cetacean suborders, Mysticeti and Odontoceti. This initial diversification occurred in the shallow waters that separated India and Asia , resulting in some 30 species adapted to a fully oceanic life. Echolocation and filter-feeding evolved during a second radiation . All archaeocetes from the Ypresian (56–47.8 mya) and most from the Lutetian (47.8–41.3 mya) are known exclusively from Indo-Pakistan, but Bartonian (41.3–38.0 mya) and Priabonian (38.0–33.9 mya) genera are known from across Earth, including North America, Egypt, New Zealand, and Europe. Although no consensus exists regarding the mode of locomotion of which cetaceans were capabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himalayacetus
''Himalayacetus'' is an extinct genus of carnivorous aquatic mammal of the family Ambulocetidae. The holotype was found in Himachal Pradesh, India, (: paleocoordinates ) in what was the remnants of the ancient Tethys Ocean during the Early Eocene. This makes ''Himalayacetus'' the oldest archaeocete known, extending the fossil record of whales some 3.5 million years. ''Himalayacetus'' lived in the ancient coastline of the ancient Tethys Ocean before the Indian Plate had collided with the Cimmerian coast. Like ''Gandakasia'', ''Himalayacetus'' is only known from a single jaw fragment, making comparisons to other ambulocetids difficult. Description Upon its discovery, ''Himalayacetus'' was described as a pakicetid because the dentary has a small mandibular canal and a dentition similar to ''Pakicetus''. assigned ''Himalaycetus'' to the ambulocetids. Etymology ''Himalayacetus'' was named by . Its type is ''Himalayacetus subathuensis'' after the Himalayas, ''cetus'', "wha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution Of Cetaceans
The evolution of cetaceans is thought to have begun in the Indian subcontinent from even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla) 50 million years ago (mya) and to have proceeded over a period of at least 15 million years. Cetaceans are fully aquatic mammals belonging to the order Artiodactyla and branched off from other artiodactyls around 50 Year#Abbreviations yr and ya, mya. Cetaceans are thought to have evolved during the Eocene (56-34 mya), the second epoch of the present-extending Cenozoic Era. Molecular and morphological analyses suggest Cetacea share a relatively recent closest common ancestor with hippopotamus, hippopotamuses and that they are sister groups. Being mammals, they surface to breathe air; they have five finger bones (even-toed) in their fins; they nurse their young; and, despite their fully aquatic life style, they retain many skeletal features from their terrestrial ancestors.Thewissen, J. G. M., L. N. Cooper, J. C. George, and S. Bajpai. 2009. From land to wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gandakasia
''Gandakasia'' is an extinct genus of ambulocetid from Pakistan, that lived in the Eocene epoch. It probably caught its prey near rivers or streams. Just like '' Himalayacetus'', ''Gandakasia'' is only known from a single jaw fragment, making comparisons to other ambulocetids difficult. The first ambulocetid to be described, ''Gandakasia'' was not initially recognized as a cetacean. Gandakasia probably inhabited a freshwater niche similar to the pakicetid Pakicetidae ("Pakistani whales") is an extinct family of early whales that lived during the Early Eocene in Pakistan. Unlike modern cetaceans, they had well-developed limbs and were capable of walking. The species included were fox to wolf-sized. ...s. References Ambulocetidae Monotypic prehistoric cetacean genera Fossil taxa described in 1958 Extinct mammals of Asia {{paleo-whale-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cetacea
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals belonging to the order Artiodactyla that includes whales, dolphins and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively carnivorous diet. They propel themselves through the water with powerful up-and-down movements of their tail, which ends in a paddle-like fluke, using their flipper-shaped forelimbs to steer. While the majority of cetaceans live in marine environments, a small number reside solely in brackish water, brackish or fresh water. Having a cosmopolitan distribution, they can be found in some rivers and all of Earth's oceans, and many species migrate throughout vast ranges with the changing of the seasons. Cetaceans are famous for cetacean intelligence, their high intelligence, complex social behaviour, and the enormous size of some of the group's members. For example, the blue whale reaches a maximum confirmed length of and a weight of 173 tonne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene First Appearances
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''Ēṓs'', ' Dawn') and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch.See: *Letter from William Whewell to Charles Lyell dated 31 January 1831 in: * From p. 55: "The period next antecedent we shall call Eocene, from ήως, aurora, and χαινος, recens, because the extremely small proportion of living species contained in these strata, indicates what may be considered the first commencement, or ''dawn'', of the existing state of the animate creation." The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
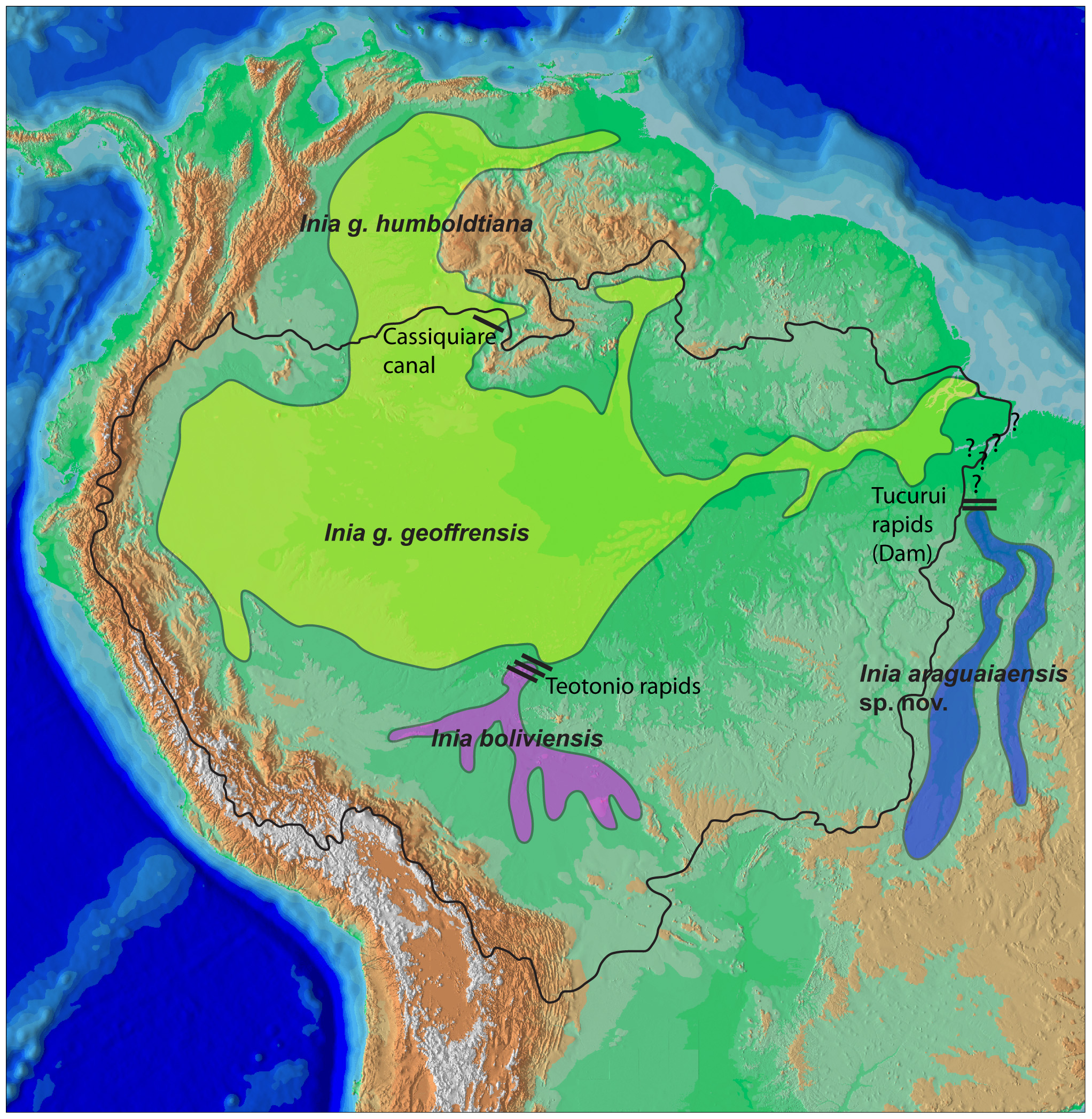
River Dolphin
River dolphins are a polyphyletic group of fully aquatic mammals that reside exclusively in freshwater or brackish water. They are an informal grouping of dolphins, which itself is a paraphyletic group within the infraorder Cetacea. Extant river dolphins are placed in two superfamilies, Platanistoidea and Inioidea. They comprise the families Platanistidae (the South Asian dolphins), the possibly extinct Lipotidae (Yangtze River dolphin), Iniidae (the Amazonian dolphins) and Pontoporiidae. There are five extant species of river dolphins. River dolphins, alongside other cetaceans, belong to the clade Artiodactyla, with even-toed ungulates, and their closest living relatives the hippopotamuses, from which they diverged about 40 million years ago. Specific types of dolphins can be pink. River dolphins are relatively small compared to other dolphins, having evolved to survive in warm, shallow water and strong river currents. They range in size from the long South Asian river dol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |