|
Ambulator
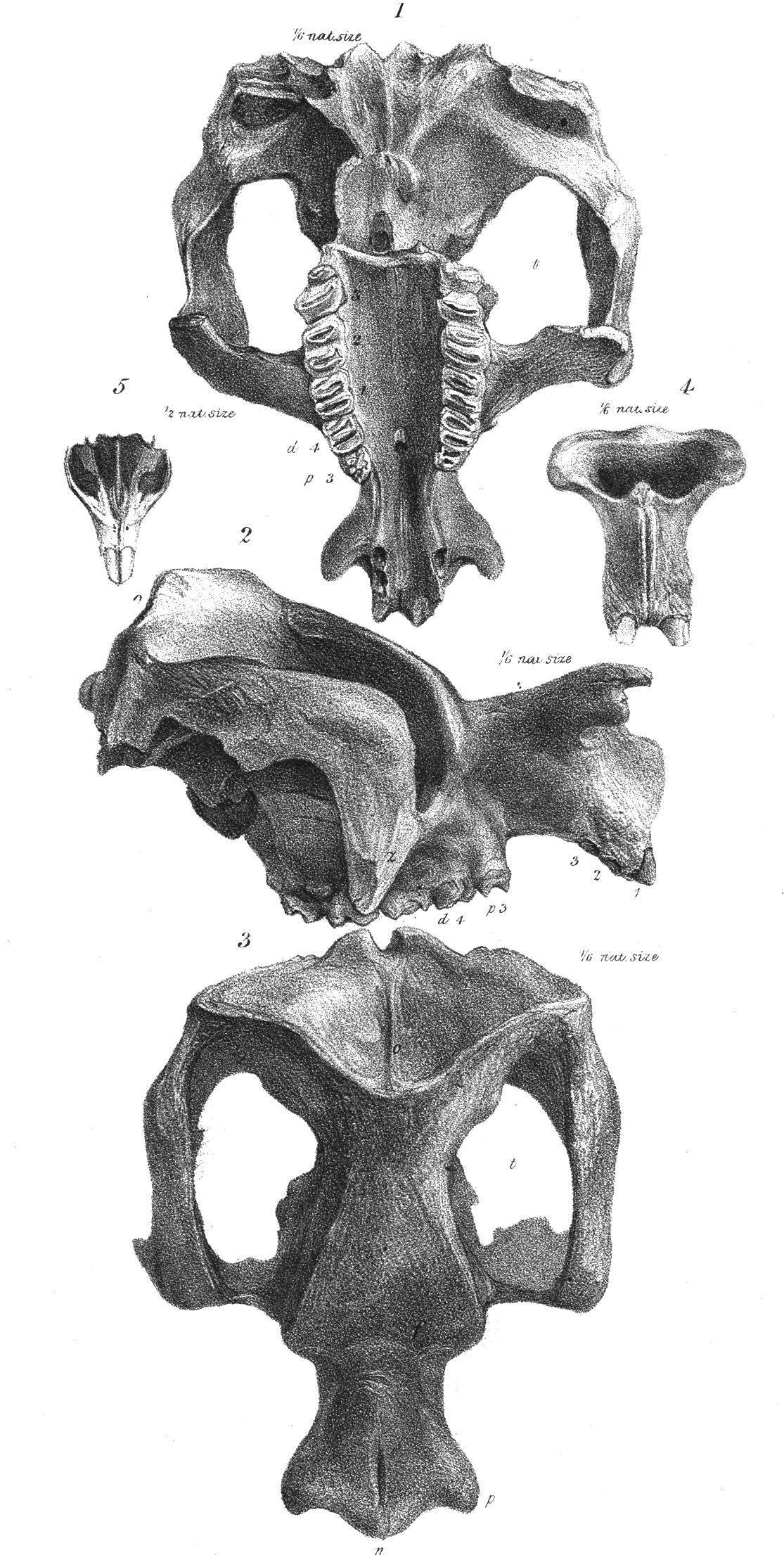
''Ambulator'' is an extinct genus of marsupials belonging to the family Diprotodontidae. It contains one species, ''A. keanei'', whose remains were found in the Pliocene-aged Tirari Formation of South Australia. ''A. keanei'' was previously included in the genus ''Zygomaturus'', but was moved to the new genus ''Ambulator'' in 2023. Features of its limbs suggest that ''Ambulator'' was better adapted to quadrupedal walking than earlier diprotodontids. References Diprotodontids Prehistoric marsupial genera Pliocene marsupials Pliocene mammals of Australia Extinct mammals of South Australia Fossil taxa described in 2023 {{Paleo-marsupial-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diprotodontids
Diprotodontidae is an extinct Family (biology), family of large herbivorous marsupials, endemic to Australia and New Guinea during the Oligocene through Pleistocene periods from 28.4 million to 40,000 years ago. Description The family primarily consisted of large quadrupedal terrestrial Browsing (herbivory), browsers, notably including the largest marsupial that ever lived, the rhino-sized ''Diprotodon.'' ''Nimbadon,'' which is often considered a basal diprotodontid, was Arboreal locomotion, arboreal. Diprotodontids were plantigrade (foot and toes flat relative to the ground). In most diprotodontids, the forelimbs were not specialised and were capable of being used for functions other than movement. Some later diprotodontids from the Pliocene onwards like ''Ambulator'' and ''Diprotodon'' developed elephant-like forelimbs specialised for walking with modified wristbones which functioned as a heel, along with the development of footpads, which means that the digits probably did no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diprotodontidae
Diprotodontidae is an extinct family of large herbivorous marsupials, endemic to Australia and New Guinea during the Oligocene through Pleistocene periods from 28.4 million to 40,000 years ago. Description The family primarily consisted of large quadrupedal terrestrial browsers, notably including the largest marsupial that ever lived, the rhino-sized '' Diprotodon.'' '' Nimbadon,'' which is often considered a basal diprotodontid, was arboreal. Diprotodontids were plantigrade (foot and toes flat relative to the ground). In most diprotodontids, the forelimbs were not specialised and were capable of being used for functions other than movement. Some later diprotodontids from the Pliocene onwards like ''Ambulator'' and ''Diprotodon'' developed elephant-like forelimbs specialised for walking with modified wristbones which functioned as a heel, along with the development of footpads, which means that the digits probably did not contact the ground, as evidenced by the lack of toes o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsupial
Marsupials are a diverse group of mammals belonging to the infraclass Marsupialia. They are natively found in Australasia, Wallacea, and the Americas. One of marsupials' unique features is their reproductive strategy: the young are born in a relatively undeveloped state and then nurtured within a pouch on their mother's abdomen. Extant marsupials encompass many species, including Kangaroo, kangaroos, Koala, koalas, Opossum, opossums, Phalangeriformes, possums, Tasmanian devil, Tasmanian devils, Wombat, wombats, Wallaby, wallabies, and Bandicoot, bandicoots. Marsupials constitute a clade stemming from the last common ancestor of extant Metatheria, which encompasses all mammals more closely related to marsupials than to Placentalia, placentals. The evolutionary split between placentals and marsupials occurred 125-160 million years ago, in the Middle Jurassic-Early Cretaceous period. Presently, close to 70% of the 334 extant marsupial species are concentrated on the Australian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygomaturus
''Zygomaturus'' is an extinct genus of giant marsupial belonging to the family Diprotodontidae which inhabited Australia from the Late Miocene to Late Pleistocene. Description It was a large animal, weighing 500 kg (1100 lbs) or over 700 kg (1544 lbs) and standing about 1.5 m (4.9 ft) tall and 2.5 m (8.2 ft) long. As in other large marsupials, the sinuses within the skull are very large, likely to reduce weight. Palaeobiology In an analysis of remains from Cuddie Springs, the carbon isotope ratios suggests that it consumed both C3 and C4 plants, with a dental microwear texture indicative of browsing. Preserved remains suggest that ''Zygomaturus'' was widely distributed over Australia during the Pleistocene. Evolution and extinction The earliest members of the genus such as ''Zygomaturus gilli'' appeared during the Late Miocene, around 8 million years ago. It is thought that the youngest species, ''Zygomaturus trilobus'' became e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch (geology), epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.33 to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago (Ma). It is the second and most recent epoch of the Neogene Period in the Cenozoic, Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Miocene Epoch and is followed by the Pleistocene Epoch. Prior to the 2009 revision of the geologic time scale, which placed the four most recent major glaciations entirely within the Pleistocene, the Pliocene also included the Gelasian Stage, which lasted from 2.59 to 1.81 Ma, and is now included in the Pleistocene. As with other older geologic periods, the Stratum, geological strata that define the start and end are well-identified but the exact dates of the start a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tirari Formation
The Dhirari (or Dirari or Tirari) were an indigenous Australian people of the state of South Australia. They are not to be confused with the Diyari people, though the Dirari/Dhirari language (now extinct) was a dialect of the Diyari language. Name Some confusion arose when, in 1904, the ethnographer A. W. Howitt confused this distinct, if small, tribe with their neighbours, the Diyari, suggesting it was a name for a horde of the latter. The German missionary Otto Siebert testified in 1936 that the Tirari's speech differed from Diyari language. Country Norman Tindale estimated their tribal lands as covering roughly . They dwelt around the eastern shore of Lake Eyre, running northwards from Muloorina to the Warburton River. Their eastern frontiers were at Killalapaninna. History of contact The Tirari were extinct by the time of Tindale's writing (1974). Their name is memorialized in the toponym denoting part of the land they occupied, Tirari Desert The Tirari Desert is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories by area, which includes some of the most arid parts of the continent, and with 1.8 million people. It is the fifth-largest of the states and territories by population. This population is the second-most highly centralised in the nation after Western Australia, with more than 77% of South Australians living in the capital Adelaide or its environs. Other population centres in the state are relatively small; Mount Gambier, the second-largest centre, has a population of 26,878. South Australia shares borders with all the other mainland states. It is bordered to the west by Western Australia, to the north by the Northern Territory, to the north-east by Queensland, to the east by New South Wales, to the south-east by Victoria (state), Victoria, and to the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Marsupial Genera
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing having spread to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. It is based on an old conception of history that without written records there could be no history. The most common conception today is that history is based on evidence, however the concept of prehistory hasn't been completely discarded. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene Marsupials
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.33 to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago (Ma). It is the second and most recent epoch of the Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Epoch and is followed by the Epoch. Prior to the 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct Mammals Of South Australia
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its last member. A taxon may become functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to reproduce and recover. As a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. Over five billion species are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryotes globally, possibly many times more if microorganisms are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, and mammoths. Through evolution, species arise through the process of speciation. Species become extinct when they are no longer able to survive in changing conditions or against superio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |