|
Amaymon
In demonology, Amaymon (also Amaimon, or Amoymon) is a prince of Hell, and, according to some grimoires, the only one who has power over Asmodai. A curious characteristic of this spirit is alleged in almost all copies of the Ars Goetia in English, that during the evocation of Asmodai to visible appearance, the exorcist must stand upright with his cap or headdress removed in a show of respect, because if he does not do so, then Amaymon will deceive him and doom all of his work. According to Joseph H. Peterson, editor of "The Lesser Key of Solomon" (Weiser 2001) this is a "bizarre translation of 'si vero coopertus fuerit'" (Page 21 Footnote 57) by Scot in his "Discoverie of Witchcraft" which contains a translation by Scot of Pseudomonarchia Daemonum by Johannes Weyer. Peterson's edition includes as an appendix, a copy of Weyer's Pseudomonarchia Daemonum in the original Latin where we find (Page 242) "''Cum hujus officia exercet exorcista, fit fortis, cautus & in pedibus stans: si ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ars Goetia
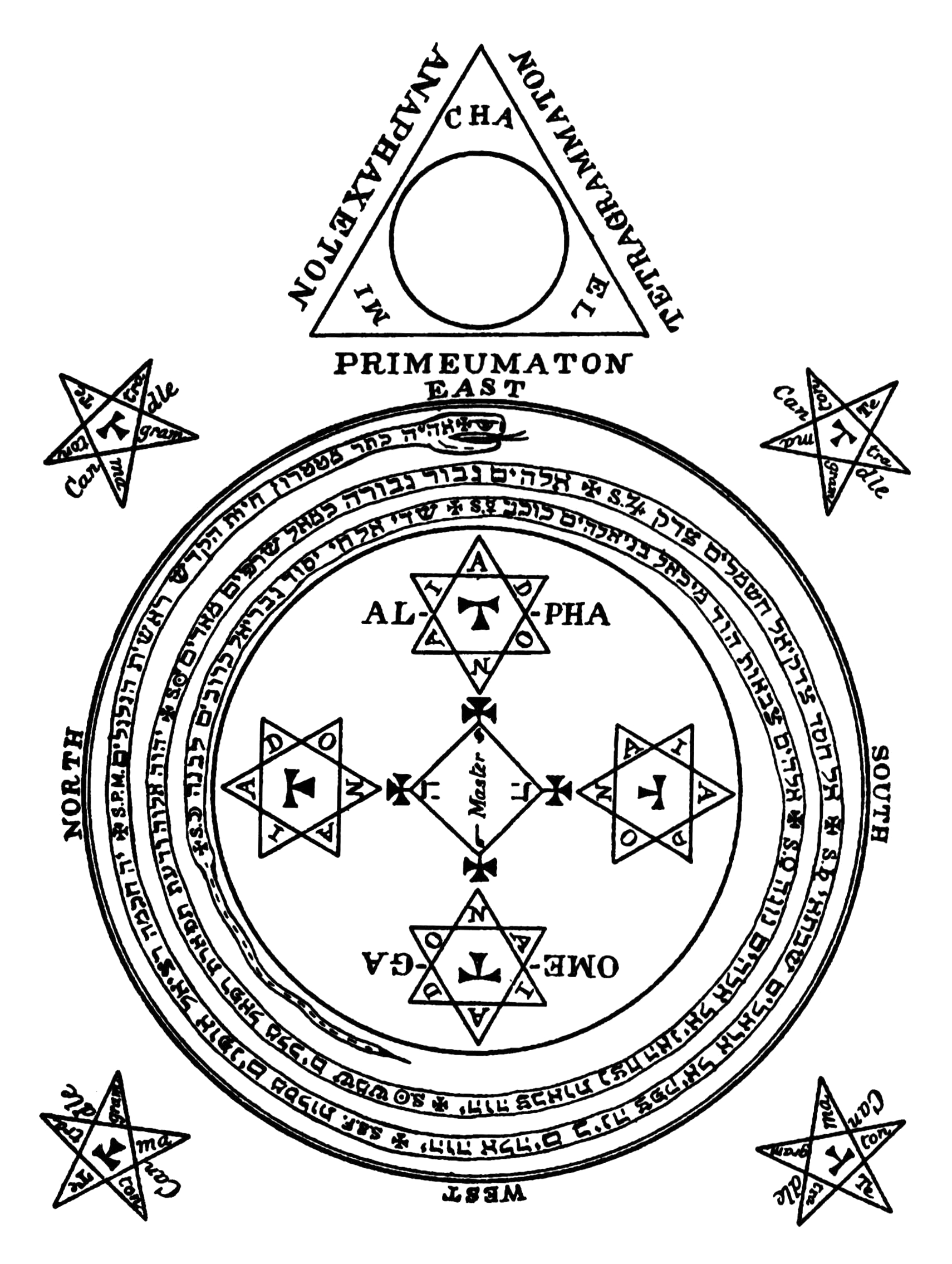
''The Lesser Key of Solomon'', also known by its Latin title ''Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis'' or simply the ''Lemegeton'', is an anonymously authored grimoire on sorcery, mysticism and magic. It was compiled in the mid-17th century from materials several centuries older... It is divided into five books: the ''Ars Goetia'', ''Ars Theurgia-Goetia'', ''Ars Paulina'', ''Ars Almadel'', and ''Ars Notoria''. It is based on the Testament of Solomon and the ring mentioned within it that he used to seal demon. Terminology The text is more properly called '', or, The little Key of Solomon''. The title most commonly used, ''The Lesser Key of Solomon'', does not in fact occur in the manuscripts. A. E. Waite, in his 1898 ''Book of Black Magic and of Pacts'' does use the terms "so-called Greater Key" and "Lesser Key" to distinguish between the Clavicula Salomonis and Lemegeton, so he may have been the one to coin it. The Latin term refers to the evocation of demons or evil spiri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Lesser Key Of Solomon
''The Lesser Key of Solomon'', also known by its Latin title ''Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis'' or simply the ''Lemegeton'', is an anonymously authored grimoire on Goetia, sorcery, mysticism and Magic (supernatural), magic. It was compiled in the mid-17th century from materials several centuries older... It is divided into five books: the ''Ars Goetia'', ''Ars Theurgia-Goetia'', ''Ars Paulina'', ''Ars Almadel'', and ''Ars Notoria''. It is based on the Testament of Solomon and the ring mentioned within it that he used to seal demon. Terminology The text is more properly called '', or, The little Key of Solomon''. The title most commonly used, ''The Lesser Key of Solomon'', does not in fact occur in the manuscripts. A. E. Waite, in his 1898 ''Book of Black Magic and of Pacts'' does use the terms "so-called Greater Key" and "Lesser Key" to distinguish between the Clavicula Salomonis and Lemegeton, so he may have been the one to coin it. The Latin term refers to the evocati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liber Officiorum Spirituum
''Liber Officiorum Spirituum'' (English: ''The Book of the Office of Spirits'')A Book of the Office of Spirits; John Porter, Trans. Frederick Hockley, Ed. Colin D. Campbell; Teitan Press, 2011.''The Book of Oberon,'' eds. Daniel Harms and Joseph Peterson, Llewllyn Publications, 2015 was a goetic grimoire and a major source for Johann Weyer's ''Pseudomonarchia Daemonum'' and the ''Ars Goetia''. The original work (if it is a single work) has not been located, but some derived texts bearing the title have been found, some in the Sloane manuscripts, some in the Folger Shakespeare Library. Each version bears many similarities to each other and to the ''Pseudomonarchia Daemonum'' and the ''Ars Goetia'', though they are far from identical.Porter, Hockley, Campbell, p.vii-xvii''The Book of Oberon,'' eds. Daniel Harms and Joseph Peterson, Llewllyn Publications, 2015, p.1-30 History Johannes Trithemius mentions two separate works (''Liber'' quoque ''Officiorum'', and ''De Officiis Spi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corson (demon)
In demonology, Corson is one of the four principal kings that have power over the seventy-two demons that are supposedly constrained by King Solomon, according to the Lesser Key of Solomon. Corson is not to be Conjuration (summoning), conjured except on great occasions. He is the king of the west according to some translations of The Lesser Key of Solomon, and king of the south according to Pseudomonarchia Daemonum. The other three demon-kings of the cardinal directions are Amaymon, Ziminiar, and Gaap (although some translations of ''The Lesser Key of Solomon'' consider Belial, Beleth, Asmodai, and Gaap to be the kings of different cardinal directions, not specifying the cardinal direction that they rule over). Other spelling *Gorson See also * Amaymon – the cardinal spirit of the east in ''The Lesser Key of Solomon'' * Gaap – the cardinal spirit of the south in ''The Lesser Key of Solomon'' * Ziminiar – the cardinal spirit of the north in ''The Lesser Key of Solomon'' So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ziminiar
In demonology, Ziminiar or Zymymar is one of the four principal kings that have power over the seventy-two demons that are supposedly constrained by King Solomon, according to the Lesser Key of Solomon. Ziminiar is not to be Conjuration (summoning), conjured except on great occasions. The other three demon-kings are Amaymon, Corson (demon), Corson, and Gaap (although some translations of ''The Lesser Key of Solomon'' consider the four kings to be Belial, Beleth, Asmodai, and Gaap, not specifying the cardinal direction that they rule over). He is the king of the north according to both The Lesser Key of Solomon and Pseudomonarchia Daemonum. See also * Amaymon – the cardinal spirit of the east in ''The Lesser Key of Solomon'' * Corson (demon), Corson – the cardinal spirit of the west in ''The Lesser Key of Solomon'' * Gaap – the cardinal spirit of the south in ''The Lesser Key of Solomon'' References Goetic demons {{occult-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asmodai
Asmodeus (; , ''Asmodaios'') or Ashmedai (; ; ; see below for other variations) is a king of demons in the legends of Solomon and the constructing of Solomon's Temple."Asmodeus" in '' The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 635. He is featured variously in Talmudic stories where he is the king of the '' shedim''. The Quran refers to a "puppet" in the Story of Solomon in Surah Ṣād verses 30-40, which is according to the '' mufassirūn'' (authorized exegetes of the Quran) referring to the demon-king Asmodeus (Sakhr). In Christianity, Asmodeus is mostly known from the deuterocanonical Book of Tobit. He is the primary antagonist and disrupts the marriages of Sarah. Peter Binsfeld classifies Asmodeus as the "demon of lust". Etymology The name ''Asmodai'' is believed to derive from the Avestan ''*aēšma-daēva'' (𐬀𐬉𐬴𐬨𐬀𐬛𐬀𐬉𐬎𐬎𐬀*, *''aēṣ̌madaēuua''), where ''aēšma'' means " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaap
Gaap (also Tap, Coap, Taob or Goap) is a demon that is described in demonological grimoires such as ''the Lesser Key of Solomon'', Johann Weyer's ''Pseudomonarchia Daemonum'', and the Munich Manual of Demonic Magic, as well as Jacques Collin de Plancy's '' Dictionnaire Infernal''. Demon These works describe Gaap as a prince in human form who incites love. The Munich Manual also says that "Taob" also provides medical care for women, transforms them to make it easier to get to a lover, renders them infertile, and rules twenty-five legions of spirits. The other sources instead describe Gaap as a president, giving him the power to teach philosophy and liberal arts, make others invisible, steal familiars from other magicians, make men stupid, and carry men between kingdoms; in addition to ruling sixty-six legions of demons. Johann Weyer also connects Gaap to necromancers, and states that he was first called upon by Noah's son Ham, along with Beleth. He was of the order of '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demonology
Demonology is the study of demons within religious belief and myth. Depending on context, it can refer to studies within theology, religious doctrine, or occultism. In many faiths, it concerns the study of a hierarchy of demons. Demons may be nonhuman separable souls, or discarnate spirits which have never inhabited a body. A sharp distinction is often drawn between these two classes, notably by the Melanesians, several African groups, and others. The Islamic jinn, for example, are not reducible to modified human souls. At the same time these classes are frequently conceived as producing identical results, e.g. diseases.van der Toorn, Becking, van der Horst (1999), ''Dictionary of Deities and Demons in The Bible'', Second Extensively Revised Edition, Entry: Demon, pp. 235-240, William B. Eerdmans Publishing Company, Prevalence of demons According to some religions, all the affairs of the universe are supposed to be under the control of spirits, each ruling a certain " elemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. The female equivalent is a princess. The English word derives, via the French word ''prince'', from the Latin noun , from (first) and (head), meaning "the first, foremost, the chief, most distinguished, noble ruler, prince". In a related sense, now not commonly used, all more or less sovereign rulers over a state, including kings, were "princes" in the language of international politics. They normally had another title, for example king or duke. Many of these were Princes of the Holy Roman Empire. Historical background The Latin word (older Latin *prīsmo-kaps, ), became the usual title of the informal leader of the Roman senate some centuries before the transition to empire, the '' princeps senatus''. Emperor Augustus establishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hell
In religion and folklore, hell is a location or state in the afterlife in which souls are subjected to punishment after death. Religions with a linear divine history sometimes depict hells as eternal destinations, such as Christianity and Islam, whereas religions with reincarnation usually depict a hell as an intermediary period between incarnations, as is the case in the Indian religions. Religions typically locate hell in another dimension or under Earth's surface. Other afterlife destinations include heaven, paradise, purgatory, limbo, and the underworld. Other religions, which do not conceive of the afterlife as a place of punishment or reward, merely describe an abode of the dead, the grave, a neutral place that is located under the surface of Earth (for example, see Kur, Hades, and Sheol). Such places are sometimes equated with the English word ''hell'', though a more correct translation would be "underworld" or "world of the dead". The ancient Mesopotamian, Greek, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grimoire
A grimoire () (also known as a book of spells, magic book, or a spellbook) is a textbook of magic, typically including instructions on how to create magical objects like talismans and amulets, how to perform magical spells, charms, and divination, and how to summon or invoke supernatural entities such as angels, spirits, deities, and demons. In many cases, the books themselves are believed to be imbued with magical powers. The only contents found in a grimoire would be information on spells, rituals, the preparation of magical tools, and lists of ingredients and their magical correspondences. In this manner, while all ''books on magic'' could be thought of as grimoires, not all ''magical books'' should be thought of as grimoires. While the term ''grimoire'' is originally European—and many Europeans throughout history, particularly ceremonial magicians and cunning folk, have used grimoires—the historian Owen Davies has noted that similar books can be found all around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exorcist
In some religions, an exorcist (from the Greek „ἐξορκιστής“) is a person who is believed to be able to cast out the devil or performs the ridding of demons or other supernatural beings who are alleged to have possessed a person, or (sometimes) a building or object. An exorcist can be a specially prepared or instructed person including: priest, a nun, a monk, a witch doctor (healer), a shaman, a psychic or a geomancer ( Feng shui - Chinese geomancy). Exorcists in various religions Christianity In Christianity, exorcisms are a rite used to cast out demons from individuals deemed possessed. In training exorcists, ecumenical collaboration between Christians of various traditions, such as the Roman Catholic, the Lutheran and the Anglican denominations has occurred, as with a May 2019 exorcists' conference in Rome. Catholicism In a Roman Catholic context, ''exorcist'' may refer to a cleric who has been ordained into the minor order of exorcist, or a pries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |