|
Amandinea Punctata
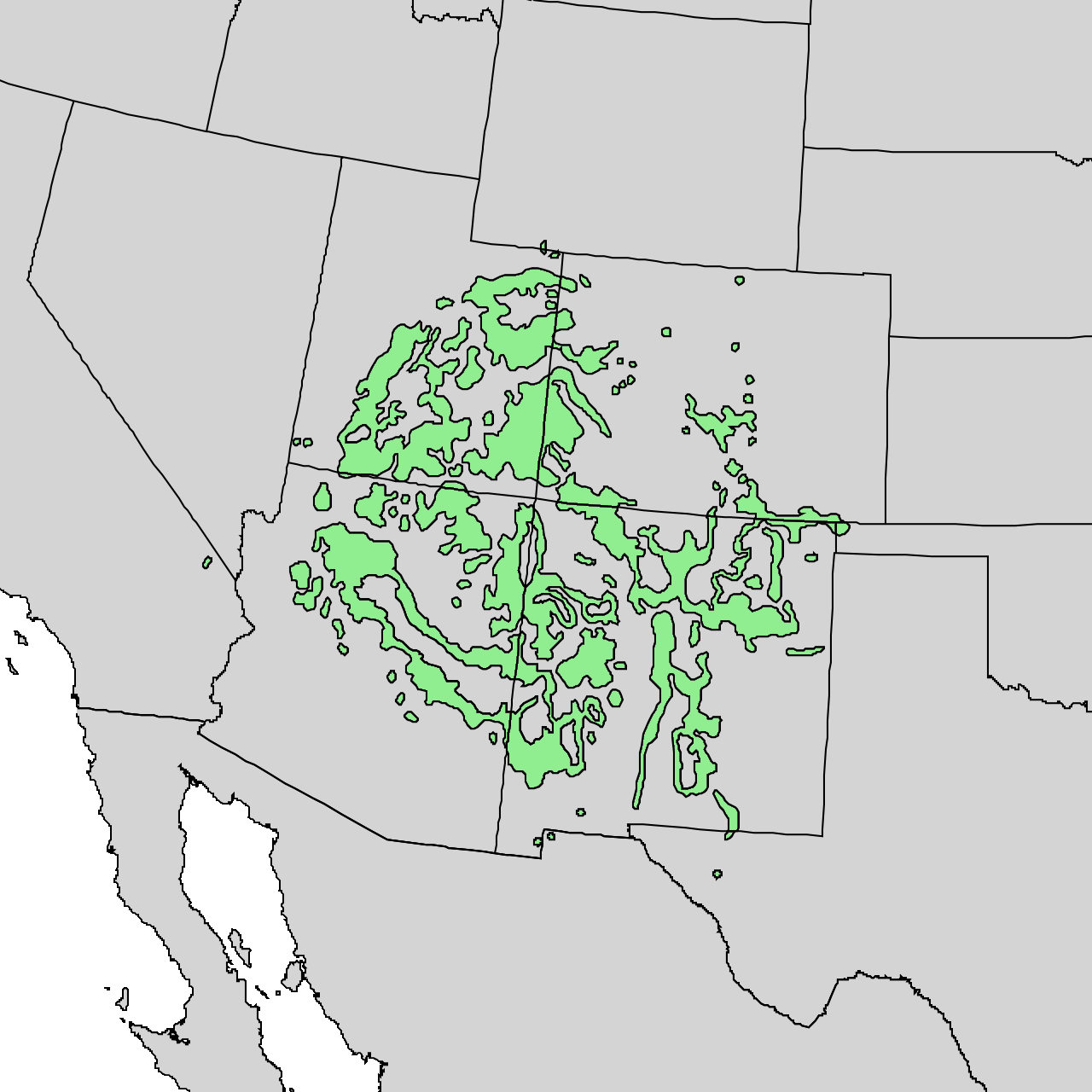
''Amandinea punctata'' (tiny button lichen) is a crustose brown to gray lichen that grows on wood and rock around the world.Amandinea punctata in the Joshua Tree National Park (California, U.S.A.) Map collection: Kerry Knudsen, Kocourková Jana; Czech University of Life Sciences Prague, Faculty of Environmental Sciences, Department of Ecology, Czech Republic; 2012 It grows on, not in the wood (epiphytic). It prefers bark that is acidic. In California, it is among the most common crustose lichens occurring on trees. Sometimes its thallus is absent, and branches may be covered in its lecideine apothecia. Because of its tolerance of low humidity, it is one of the few epiphytic lichens growing on trees in California deserts, where it commonly grows on the old, dry wood of junipers, and sometimes fallen pinyon pines and oaks, or on their dead branches. Compared to other lichens, it is tolerant of air pollutants Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinyon Pine
The pinyon or piñon pine group grows in southwestern North America, especially in New Mexico, Arizona, and Utah. The trees yield edible nuts, which are a staple food of Native Americans, and widely eaten as a snack and as an ingredient in New Mexican cuisine. The name comes from the Spanish ''pino piñonero'', a name used for both the American varieties and the stone pine common in Spain, which also produces edible nuts typical of Mediterranean cuisine. Harvesting techniques of the prehistoric American Indians are still used today to collect the pinyon seeds for personal use or for commercialization. The pinyon nut or seed is high in fats and calories. Pinyon wood, especially when burned, has a distinctive fragrance, making it a common wood to burn in chimeneas. Pinyon pine trees are also known to influence the soil in which they grow by increasing concentrations of both macronutrients and micronutrients. Some of the species are known to hybridize, the most notable ones bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichens Of Europe
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in many colors, sizes, and forms and are sometimes plant-like, but are not s. They may have tiny, leafless branches ( fruticose); flat leaf-like structures ( [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichens Described In 1796
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in many colors, sizes, and forms and are sometimes plant-like, but are not s. They may have tiny, leafless branches (); flat leaf-like structures ( [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichen Species
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in many colors, sizes, and forms and are sometimes plant-like, but are not s. They may have tiny, leafless branches ( fruticose); flat leaf-like structures ( [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amandinea
''Amandinea'' is a genus of lichenized fungi in the family Caliciaceae. Genetic studies indicates that the genus ''Amandinea'' and ''Buellia'' are the same,Scheidegger, C. 2009. Amandinea Choisy ex Scheid. & H. Mayrhofer (1993). In: C. W. Smith, A. Aptroot, B. J. Coppins, A. Fletcher, O. L. Gilbert, P. W. James and P. A. Wosley (eds.) The Lichens of Great Britain and Ireland. The British Lichen Society, Natural History Museum Publications, United Kingdom, pp. 142–144 although this is not widely accepted.Amandinea punctata in the Joshua Tree National Park (California, U.S.A.) Map collection: Kerry Knudsen, Kocourková Jana; Czech University of Life Sciences Prague, Faculty of Environmental Sciences, Department of Ecology, Czech Republic; 2012 Taxonomy The genus was originally circumscribed by Maurice Choisy in 1950, with ''Amandinea coniops'' assigned as the type species. However, the name was published invalidly because it was not accompanied by a Latin description or diagno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Dioxide
Sulfur dioxide ( IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic activity and is produced as a by-product of copper extraction and the burning of sulfur- bearing fossil fuels. Structure and bonding SO2 is a bent molecule with ''C''2v symmetry point group. A valence bond theory approach considering just ''s'' and ''p'' orbitals would describe the bonding in terms of resonance between two resonance structures. The sulfur–oxygen bond has a bond order of 1.5. There is support for this simple approach that does not invoke ''d'' orbital participation. In terms of electron-counting formalism, the sulfur atom has an oxidation state of +4 and a formal charge of +1. Occurrence Sulfur dioxide is found on Earth and exists in very small concentrations and in the atmosphere at about 1 ppm. On other p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Dioxide
Nitrogen dioxide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is one of several nitrogen oxides. is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of nitric acid, millions of tons of which are produced each year for use primarily in the production of fertilizers. At higher temperatures it is a reddish-brown gas. It can be fatal if inhaled in large quantities. Nitrogen dioxide is a paramagnetic, bent molecule with C2v molecular symmetry, point group symmetry. It is included in the NOx, NOx family of air pollution, atmospheric pollutants. Properties Nitrogen dioxide is a reddish-brown gas with a pungent, acrid odor above , becomes a yellowish-brown liquid below , and converts to the colorless dinitrogen tetroxide () below . The chemical bond, bond length between the nitrogen atom and the oxygen atom is 119.7 picometre, pm. This bond length is consistent with a bond order between one and two. Unlike ozone, O3, the ground state, ground electronic state of nitrogen dioxide is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Pollutants
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different types of air pollutants, such as gases (including ammonia, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrous oxides, methane, carbon dioxide and chlorofluorocarbons), particulates (both organic and inorganic), and biological molecules. Air pollution can cause diseases, allergies, and even death to humans; it can also cause harm to other living organisms such as animals and food crops, and may damage the natural environment (for example, climate change, ozone depletion or habitat degradation) or built environment (for example, acid rain). Air pollution can be caused by both human activities and natural phenomena. Air pollution is a significant risk factor for a number of pollution-related diseases, including respiratory infections, hear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juniper
Junipers are coniferous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Juniperus'' () of the cypress family Cupressaceae. Depending on the taxonomy, between 50 and 67 species of junipers are widely distributed throughout the Northern Hemisphere, from the Arctic, south to tropical Africa, throughout parts of western, central and southern Asia, east to eastern Tibet in the Old World, and in the mountains of Central America. The highest-known juniper forest occurs at an altitude of in southeastern Tibet and the northern Himalayas, creating one of the highest tree lines on earth. Description Junipers vary in size and shape from tall trees, tall, to columnar or low-spreading shrubs with long, trailing branches. They are evergreen with needle-like and/or scale-like leaves. They can be either monoecious or dioecious. The female seed cones are very distinctive, with fleshy, fruit-like coalescing scales which fuse together to form a berrylike structure ( galbulus), long, with one to 12 u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brian John Coppins
Brian John Coppins (born 1949) is a botanist and lichenologist, considered a world authority on crustose lichens and a leading expert on the genus '' Micarea''. Education Coppins' interest in lichens was sparked during a field trip to the Scottish island of Handa while studying at Tunbridge Wells Technical School for Boys. While still an undergraduate at the University of Hull, Coppins was the co-author, with D. W. Shimwell, of an important study of lichen dynamics in managed heathland. After receiving his B.Sc. in 1970, Coppins became a graduate student at King's College London and studied lichen ecophysiology under the supervision of Francis Rose but he changed the focus of his doctoral studies to the taxonomy of '' Micarea'' species found in Europe. Career In 1974 was appointed as an ascomycete taxonomist in the herbarium of the Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh (RBGE). He spent his career there, retiring in May 2009. He received his Ph.D. in 1982 from University College Lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apothecia
An ascocarp, or ascoma (), is the fruiting body ( sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are most commonly bowl-shaped (apothecia) but may take on a spherical or flask-like form that has a pore opening to release spores (perithecia) or no opening (cleistothecia). Classification The ascocarp is classified according to its placement (in ways not fundamental to the basic taxonomy). It is called ''epigeous'' if it grows above ground, as with the morels, while underground ascocarps, such as truffles, are termed ''hypogeous''. The structure enclosing the hymenium is divided into the types described below (apothecium, cleistothecium, etc.) and this character ''is'' important for the taxonomic classification of the fungus. Apothecia can be relatively large and fleshy, whereas the others are microscopic—about the size of flecks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |