|
Alveolate
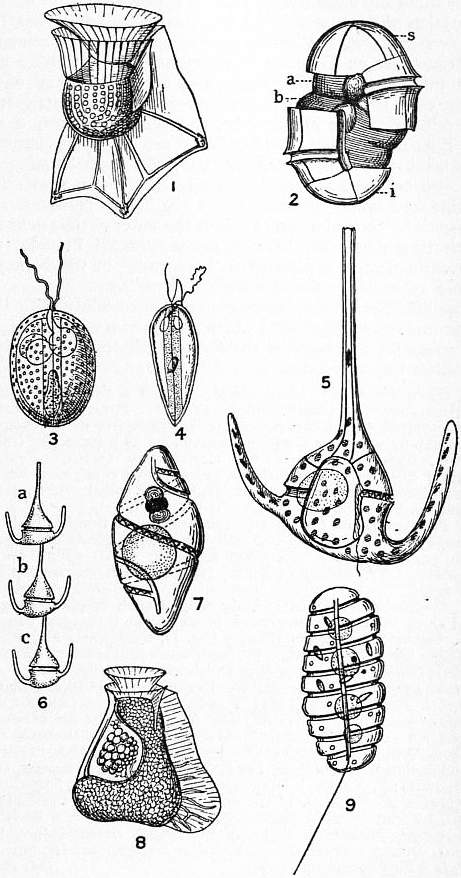
The alveolates (meaning "pitted like a honeycomb") are a group of protists, considered a major unranked clade or superphylum within Eukaryota. They are currently grouped with the Stramenopiles and Rhizaria among the protists with tubulocristate mitochondria into the SAR supergroup. Characteristics The most notable shared characteristic is the presence of cortical (near the surface) alveoli (sacs). These are flattened vesicles (sacs) arranged as a layer just under the membrane and supporting it, typically contributing to a flexible pellicle (thin skin). In armored dinoflagellates they may contain stiff plates. Alveolates have mitochondria with tubular cristae ( invaginations), and cells often have pore-like intrusions through the cell surface. The group contains free-living and parasitic organisms, predatory flagellates, and photosynthetic organisms. Almost all sequenced mitochondrial genomes of ciliates and apicomplexa are linear. The mitochondria almost all carry mtDN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAR Supergroup
SAR is a highly diverse clade of eukaryotes, often considered a supergroup, that includes stramenopiles (heterokonts), alveolates, and rhizarians. It is a node-based taxon (under the Sar name), including all descendants of the three groups' last common ancestor, and comprises most of the now-rejected Chromalveolata. Their sister group has been found to be telonemids, with which they make up the TSAR clade. Harosa is sometimes used synonymously with TSAR. Etymology The name SAR is an acronym derived from the first letters of its three constituent clades; it has been alternatively spelled RAS. The term Harosa (at the subkingdom level) has also been used, with Stramenopiles replaced by its synonym Heterokonta in this variant of the acronym. History of discovery Before the discovery of the SAR supergroup, stramenopiles and alveolates were classified in the supergroup Chromalveolata alongside haptophytes and cryptomonads, being believed to have acquired plastids th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myzozoa
Myzozoa is a grouping of specific phyla within Alveolata, that either feed through myzocytosis, or were ancestrally capable of feeding through myzocytosis. Many protist orders are included within Myzozoa. It is sometimes described as a phylum, containing the major subphyla Dinozoa and Apicomplexa, plus minor subphyla. The term Myzozoa superseded the previous term "Miozoa", by the same authority, and gave a slightly altered meaning. Phyla Within Myzozoa, there are four phyla: *Apicomplexa – parasitic protozoa that lack axonemal locomotive structures except in gametes * Dinoflagellata – mostly marine flagellates many of which have chloroplasts *Chromerida – a marine phylum of photosynthetic protozoa * Perkinsozoa The term/group Myzozoa was not considered in a resolution of protist groups by Adl et al. 2012. Strict taxonomy only considers common traits possessed by all organisms of the group. Some organisms within each of the component groups of Myzozoa have lost the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizaria
The Rhizaria are a diverse and species-rich clade of mostly unicellular eukaryotes. Except for the Chlorarachniophytes and three species in the genus '' Paulinella'' in the phylum Cercozoa, they are all non-photosynthetic, but many Foraminifera and Radiolaria have a symbiotic relationship with unicellular algae. A multicellular form, ''Guttulinopsis vulgaris'', a cellular slime mold, has been described. This group was used by Cavalier-Smith in 2002, although the term "Rhizaria" had been long used for clades within the currently recognized taxon. Being described mainly from rDNA sequences, they vary considerably in form, having no clear morphological distinctive characters ( synapomorphies), but for the most part they are amoeboids with filose, reticulose, or microtubule-supported pseudopods. In the absence of an apomorphy, the group is ill-defined, and its composition has been very fluid. Some Rhizaria possess mineral exoskeletons ( thecae or loricas), which are in diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinoflagellate
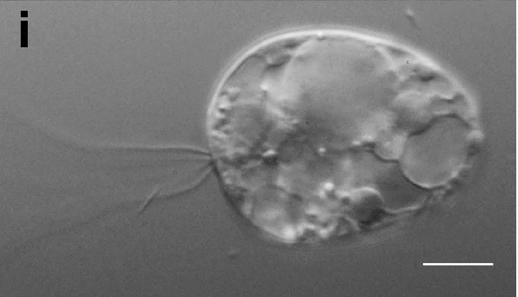
The Dinoflagellates (), also called Dinophytes, are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered protists. Dinoflagellates are mostly marine plankton, but they are also common in freshwater habitats. Their populations vary with sea surface temperature, salinity, and depth. Many dinoflagellates are photosynthetic, but a large fraction of these are in fact mixotrophic, combining photosynthesis with ingestion of prey ( phagotrophy and myzocytosis). In terms of number of species, dinoflagellates are one of the largest groups of marine eukaryotes, although substantially smaller than diatoms. Some species are endosymbionts of marine animals and play an important part in the biology of coral reefs. Other dinoflagellates are unpigmented predators on other protozoa, and a few forms are parasitic (for example, '' Oodinium'' and '' Pfiesteria''). Some dinoflagellates produce resting stages, called dinoflagellate cys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stramenopile
The stramenopiles, also called heterokonts, are protists distinguished by the presence of stiff tripartite external hairs. In most species, the hairs are attached to flagella, in some they are attached to other areas of the cellular surface, and in some they have been secondarily lost (in which case relatedness to stramenopile ancestors is evident from other shared cytological features or from genetic similarity). Stramenopiles represent one of the three major clades in the SAR supergroup, along with Alveolata and Rhizaria. Stramenopiles are eukaryotes; most are single-celled, but some are multicellular including some large seaweeds, the brown algae. The group includes a variety of algal protists, heterotrophic flagellates, opalines and closely related proteromonad flagellates (all endobionts in other organisms); the actinophryid Heliozoa, and oomycetes. The tripartite hairs characteristic of the group have been lost in some of the included taxa – for example in most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinoflagellates
The Dinoflagellates (), also called Dinophytes, are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered protists. Dinoflagellates are mostly marine plankton, but they are also common in freshwater habitats. Their populations vary with sea surface temperature, salinity, and depth. Many dinoflagellates are photosynthetic, but a large fraction of these are in fact mixotrophic, combining photosynthesis with ingestion of prey ( phagotrophy and myzocytosis). In terms of number of species, dinoflagellates are one of the largest groups of marine eukaryotes, although substantially smaller than diatoms. Some species are endosymbionts of marine animals and play an important part in the biology of coral reefs. Other dinoflagellates are unpigmented predators on other protozoa, and a few forms are parasitic (for example, '' Oodinium'' and '' Pfiesteria''). Some dinoflagellates produce resting stages, called dinoflagellate cysts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protist
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a natural group, or clade, but are a paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancestor excluding land plants, animals, and fungi. Protists were historically regarded as a separate taxonomic kingdom known as Protista or Protoctista. With the advent of phylogenetic analysis and electron microscopy studies, the use of Protista as a formal taxon was gradually abandoned. In modern classifications, protists are spread across several eukaryotic clades called supergroups, such as Archaeplastida ( photoautotrophs that includes land plants), SAR, Obazoa (which includes fungi and animals), Amoebozoa and " Excavata". Protists represent an extremely large genetic and ecological diversity in all environments, including extreme habitats. Their diversity, larger than for all other eukaryotes, has only been discovered in rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supergroup (biology)
A supergroup or super-group, in systematics, is a large group of organisms that monophyletic, share one common ancestor and have important defining characteristics. It is an informal, mostly arbitrary rank in biology, biological Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy that is often greater than phylum or kingdom (biology), kingdom, although some supergroups are also treated as phylum, phyla. Eukaryotic supergroups Since the decade of the 2000s, the Eukaryote#Phylogeny, eukaryotic tree of life (abbreviated as eToL) has been divided into 5–8 major groupings called 'supergroups'. These groupings were established after the idea that only monophyletic groups should be accepted as ranks, as an alternative to the use of paraphyletic kingdom Protista. In the early days of the eToL six traditional supergroups were considered: Amoebozoa, Opisthokonta, "Excavata", Archaeplastida, "Chromalveolata" and Rhizaria. Since then, the eToL has been rearranged profoundly, and most of these groups were found as pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryote
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of Outline of life forms, life forms alongside the two groups of prokaryotes: the Bacteria and the Archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but given their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is much larger than that of prokaryotes. The eukaryotes emerged within the archaeal Kingdom (biology), kingdom Asgard (Archaea), Promethearchaeati and its sole phylum Promethearchaeota. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among the Archaea. Eukaryotes first emerged during the Paleoproterozoic, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated cells. The leading evolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinozoa
Dinozoa is a group of microorganisms composed of dinoflagellates and perkinsids. It was initially coined in 1981 as a synonym of dinoflagellates, but in 2004 the name was repurposed for the evolutionary lineage or clade In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ... of dinoflagellates and their closest relatives, the perkinsids. References {{Alveolate-stub Alveolata taxa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrompodellid
Chrompodellids are a phylum of single-celled protists belonging to the Alveolata supergroup. It comprises two different polyphyletic groups of flagellates: the colpodellids, phagotrophic predators, and the chromerids, photosynthetic algae that live as symbionts of corals. These groups were independently discovered and described, but molecular phylogenetic analyses demonstrated that they are intermingled in a clade that is the closest relative to Apicomplexa, and they became collectively known as chrompodellids. Due to the history of their research, they are variously known in biological classification as Chromerida or Colpodellida (ICZN)/Colpodellales ( ICN). Description and life cycle Chrompodellids are a phylum of unicellular protists containing two functionally different groups: the photosynthetic "chromerids" and the predatory phagotrophic "colpodellids". Like other Alveolata, they present tubular mitochondrial cristae and highly flattened cortical alveoli with microtu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apicomplexa
The Apicomplexa (also called Apicomplexia; single: apicomplexan) are organisms of a large phylum of mainly parasitic alveolates. Most possess a unique form of organelle structure that comprises a type of non-photosynthetic plastid called an apicoplastwith an apical complex membrane. The organelle's apical shape is an adaptation that the apicomplexan applies in penetrating a host cell. The Apicomplexa are unicellular and spore-forming. Most are obligate endoparasites of animals, except '' Nephromyces'', a symbiont in marine animals, originally classified as a chytrid fungus, and the Chromerida, some of which are photosynthetic partners of corals. Motile structures such as flagella or pseudopods are present only in certain gamete stages. The Apicomplexa are a diverse group that includes organisms such as the coccidia, gregarines, piroplasms, haemogregarines, and plasmodia. Diseases caused by Apicomplexa include: * Babesiosis ('' Babesia'') * Malaria (''Plasmodium'') * Cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |