|
Alumina
Aluminium oxide (or aluminium(III) oxide) is a chemical compound of aluminium and oxygen with the chemical formula . It is the most commonly occurring of several aluminium oxides, and specifically identified as aluminium oxide. It is commonly called alumina and may also be called aloxide, aloxite, ALOX or alundum in various forms and applications and alumina is refined from bauxite. It occurs naturally in its crystalline polymorphic phase α-Al2O3 as the mineral corundum, varieties of which form the precious gemstones ruby and sapphire,which have an alumina content approaching 100%. Al2O3 is used as feedstock to produce aluminium metal, as an abrasive owing to its hardness, and as a refractory material owing to its high melting point. Natural occurrence Corundum is the most common naturally occurring crystalline form of aluminium oxide. Rubies and sapphires are gem-quality forms of corundum, which owe their characteristic colours to trace impurities. Rubies are given their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has a great affinity towards oxygen, passivation (chemistry), forming a protective layer of aluminium oxide, oxide on the surface when exposed to air. It visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, magnetism, nonmagnetic, and ductility, ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al, which is highly abundant, making aluminium the abundance of the chemical elements, 12th-most abundant element in the universe. The radioactive decay, radioactivity of aluminium-26, 26Al leads to it being used in radiometric dating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bauxite
Bauxite () is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)), and diaspore (α-AlO(OH)), Mixture, mixed with the two iron oxides goethite (FeO(OH)) and haematite (), the aluminium Clay minerals, clay mineral kaolinite () and small amounts of anatase () and ilmenite ( or ). Bauxite appears dull in Lustre (mineralogy), luster and is reddish-brown, white, or tan. In 1821, the French people, French geologist Pierre Berthier discovered bauxite near the village of Les Baux-de-Provence, Les Baux in Provence, southern France. Formation Numerous classification schemes have been proposed for bauxite but, , there was no consensus. Vadász (1951) distinguished Laterite, lateritic bauxites (silicate bauxites) from karst bauxite ores (carbonate bauxites): * The carbonate bauxites occur predominantly in Europe, Guyana, Suriname, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractory
In materials science, a refractory (or refractory material) is a material that is resistant to decomposition by heat or chemical attack and that retains its strength and rigidity at high temperatures. They are inorganic, non-metallic compounds that may be porous or non-porous, and their crystallinity varies widely: they may be crystalline, polycrystalline, amorphous, or composite. They are typically composed of oxides, carbides or nitrides of the following elements: silicon, aluminium, magnesium, calcium, boron, chromium and zirconium. Many refractories are ceramics, but some such as graphite are not, and some ceramics such as clay pottery are not considered refractory. Refractories are distinguished from the '' refractory metals'', which are elemental metals and their alloys that have high melting temperatures. Refractories are defined by ASTM C71 as "non-metallic materials having those chemical and physical properties that make them applicable for structures, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium Hydroxide
Aluminium hydroxide, , is found as the mineral gibbsite (also known as hydrargillite) and its three much rarer polymorphs: bayerite, doyleite, and nordstrandite. Aluminium hydroxide is amphoteric, i.e., it has both basic and acidic properties. Closely related are aluminium oxide hydroxide, AlO(OH), and aluminium oxide or alumina (), the latter of which is also amphoteric. These compounds together are the major components of the aluminium ore bauxite. Aluminium hydroxide also forms a gelatinous precipitate in water. Structure is built up of double layers of hydroxyl groups with aluminium ions occupying two-thirds of the octahedral holes between the two layers. Four polymorphs are recognized. All feature layers of octahedral aluminium hydroxide units, with hydrogen bonds between the layers. The polymorphs differ in terms of the stacking of the layers. All forms of crystals are hexagonal : * gibbsite is also known as γ- or α- * bayerite is also known as α- or ''β ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sapphire
Sapphire is a precious gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum, consisting of aluminium oxide () with trace amounts of elements such as iron, titanium, cobalt, lead, chromium, vanadium, magnesium, boron, and silicon. The name ''sapphire'' is derived from the Latin word ', itself from the Greek language, Greek word (), which referred to lapis lazuli. It is typically blue, but natural "fancy" sapphires also occur in yellow, purple, orange, and green colors; "parti sapphires" show two or more colors. Red corundum stones also occur, but are called ruby, rubies rather than sapphires. Pink-colored corundum may be classified either as ruby or sapphire depending on the locale. Commonly, natural sapphires are cut and polished into gemstones and worn in jewellery, jewelry. They also may be created synthetically in laboratories for industrial or decorative purposes in large boule (crystal), crystal boules. Because of the remarkable hardness of sapphires 9 on the Mohs scale of miner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abrasive
An abrasive is a material, often a mineral, that is used to shape or finish a workpiece through rubbing which leads to part of the workpiece being worn away by friction. While finishing a material often means polishing it to gain a smooth, reflective surface, the process can also involve roughening as in satin, matte or beaded finishes. In short, the ceramics which are used to cut, grind and polish other softer materials are known as abrasives. Abrasives are extremely commonplace and are used very extensively in a wide variety of industrial, domestic, and technological applications. This gives rise to a large variation in the physical and chemical composition of abrasives as well as the shape of the abrasive. Some common uses for abrasives include grinding, polishing, buffing, honing, cutting, drilling, sharpening, lapping, and sanding (see abrasive machining). (For simplicity, "mineral" in this article will be used loosely to refer to both minerals and mineral-like substances ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corundum
Corundum is a crystalline form of aluminium oxide () typically containing traces of iron, titanium, vanadium, and chromium. It is a rock (geology), rock-forming mineral. It is a naturally transparency and translucency, transparent material, but can have different colors depending on the presence of transition metal impurities in its crystalline structure. Corundum has two primary gemstone, gem varieties: ruby and sapphire. Rubies are red due to the presence of chromium, and sapphires exhibit a range of colors depending on what transition metal is present. A rare type of sapphire, Sapphire#Padparadscha, padparadscha sapphire, is pink-orange. The name "corundum" is derived from the Tamil language, Tamil-Dravidian languages, Dravidian word ''kurundam'' (ruby-sapphire) (appearing in Sanskrit as ''kuruvinda''). Because of corundum's hardness (pure corundum is defined to have 9.0 on the Mohs scale), it can scratch almost all other minerals. Emery (rock), Emery, a variety of corundum w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium Sulfide
Aluminium sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula Al2 S3. This colorless species has an interesting structural chemistry, existing in several forms. The material is sensitive to moisture, hydrolyzing to hydrated aluminium oxides/hydroxides. This can begin when the sulfide is exposed to the atmosphere. The hydrolysis reaction generates gaseous hydrogen sulfide (H2S). Crystal structure More than six crystalline forms of aluminium sulfide are known and only some are listed below. Most of them have rather similar, wurtzite-like structures, and differ by the arrangement of lattice vacancies, which form ordered or disordered sublattices. The β and γ phases are obtained by annealing the most stable α-Al2S3 phase at several hundred degrees Celsius. Compressing aluminium sulfide to 2–65 bar results in the δ phase where vacancies are arranged in a superlattice of tetragonal symmetry. Unlike Al2O3, in which the Al(III) centers occupy octahedral holes, the more expanded fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
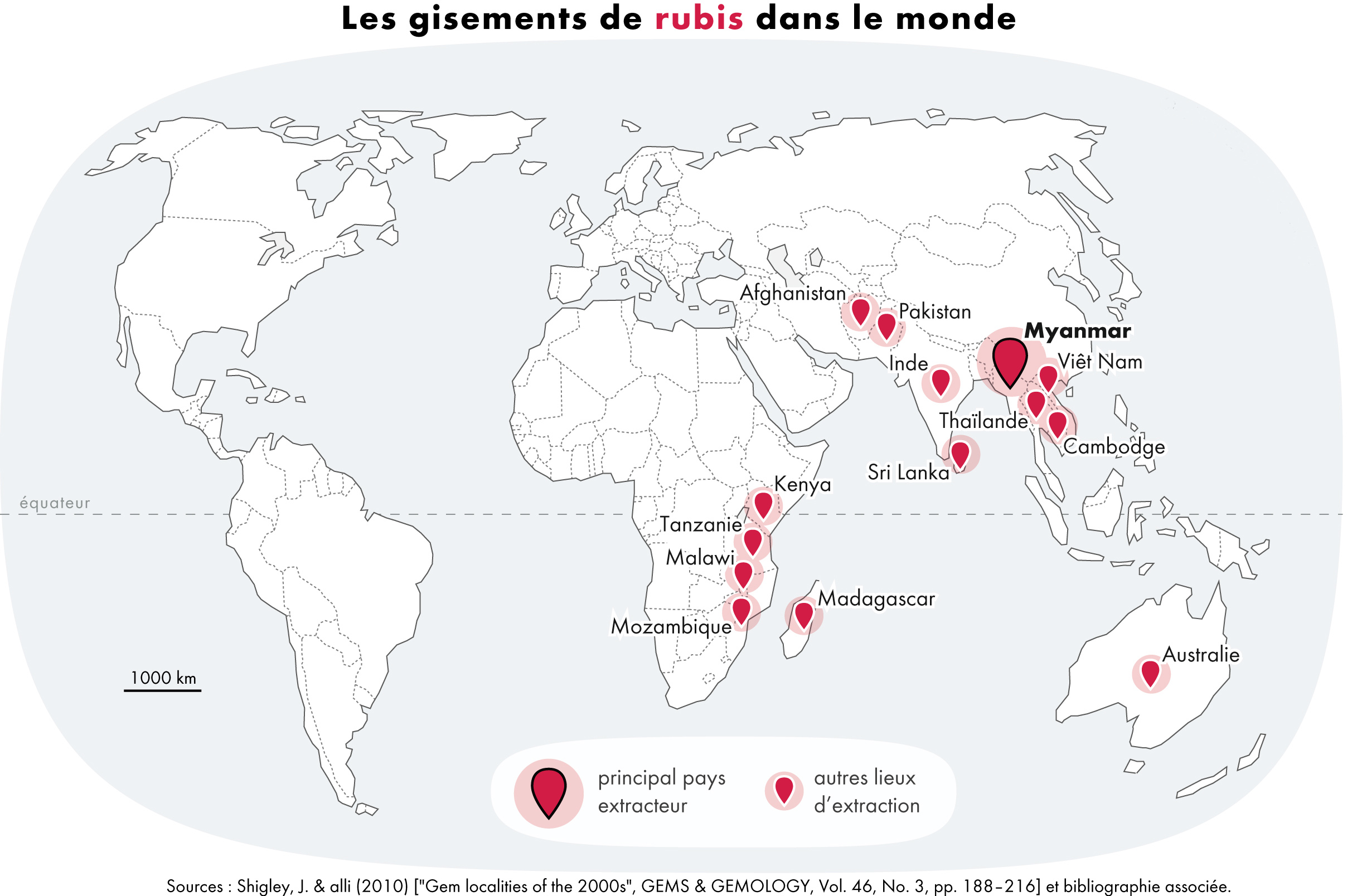
Ruby
Ruby is a pinkish-red-to-blood-red-colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum ( aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapphires; given that the rest of the corundum species are called as such, rubies are sometimes referred to as "red sapphires". Ruby is one of the traditional cardinal gems, alongside amethyst, sapphire, emerald, and diamond. The word ''ruby'' comes from ''ruber'', Latin for red. The color of a ruby is due to the presence of chromium. Some gemstones that are popularly or historically called rubies, such as the Black Prince's Ruby in the British Imperial State Crown, are actually spinels. These were once known as "Balas rubies". The quality of a ruby is determined by its color, cut, and clarity, which, along with carat weight, affect its value. The brightest and most valuable shade of red, called blood-red or pigeon blood, commands a lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boron Trioxide
Boron trioxide or diboron trioxide is the oxide of boron with the formula . It is a colorless transparent solid, almost always glassy (amorphous), which can be crystallized only with great difficulty. It is also called boric oxide or boria. It has many important industrial applications, chiefly in ceramics as a flux for glazes and enamels and in the production of glasses. Structure Boron trioxide has three known forms, one amorphous and two crystalline. Amorphous form The amorphous form (g-) is by far the most common. It is thought to be composed of boroxol rings which are six-membered rings composed of alternating 3-coordinate boron and 2-coordinate oxygen. Because of the difficulty of building disordered models at the correct density with many boroxol rings, this view was initially controversial, but such models have recently been constructed and exhibit properties in excellent agreement with experiment. It is now recognized, from experimental and theoretical studies, that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Minerals'; p. 1. In the series ''Geology: Landforms, Minerals, and Rocks''. Rosen Publishing Group. The Geology, geological definition of mineral normally excludes compounds that occur only in living organisms. However, some minerals are often biogenic (such as calcite) or organic compounds in the sense of chemistry (such as mellite). Moreover, living organisms often synthesize inorganic minerals (such as hydroxylapatite) that also occur in rocks. The concept of mineral is distinct from rock (geology), rock, which is any bulk solid geologic material that is relatively homogeneous at a large enough scale. A rock may consist of one type of mineral or may be an aggregate (geology), aggregate of two or more different types of minerals, spaci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |