|
Altötting Half Marathon
Altötting (, , in contrast to " New Ötting"; , ) is a town in Bavaria, capital of the district Altötting of Germany. For 500 years it has been the scene of religious pilgrimages by Catholics in honor of Mary, including a visit by Pope John Paul II in 1980 and one by Pope Benedict XVI in 2006. History During the Carolingian period, there was a royal palace here. Nearby, King Carloman erected a Benedictine monastery in 876, with Werinolf as first abbot, and also built the abbey church in honour of the Apostle St. Philip. In 907 King Louis the Child gave the abbey ''in commendam'' to Burchard, the Bishop of Passau (903-915), (probably identical with Burchard, second and last abbot). In 910 the Hungarians ransacked and burnt the church and abbey. In 1228 Duke Louis I, Duke of Bavaria rebuilt these buildings and, after they were sanctified, placed them in charge of twelve Canons Regular, headed by a provost. The canons remained until the secularization of the Bavarian monaster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Our Lady Of Altötting
*
{{Disambiguation, geo ...
Our or OUR may refer to: * The possessive form of " we" Places * Our (river), in Belgium, Luxembourg, and Germany * Our, Belgium, a village in Belgium * Our, Jura, a commune in France Other uses * Office of Utilities Regulation (OUR), a government utility regulator in Jamaica * Operation Underground Railroad, a non-profit organization that helps rescue sex trafficking victims * Operation Unified Response, the United States military's response to the 2010 Haiti earthquake * Ownership, Unity and Responsibility Party, a political party in the Solomon Islands See also * Ours (other) Ours may refer to: People * Ours (singer), a French singer and songwriter. * Wes Ours (born 1977), an American football player Music * Ours (band), an American rock group Songs * Ours (song), "Ours" (song), by Taylor Swift, 2011 * "Ours", a son ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provost (religion)
A provost is a senior official in a number of Christian denomination, Christian churches. Historical development The word (Latin for 'set over', from , 'to place in front') was originally applied to any ecclesiastical ruler or dignitary. It was soon more specifically applied to the immediate subordinate to the abbot of a monastery, or to the superior of a single Monk, cell, and it was defined as such in the Rule of St Benedict. The dean (Christianity), dean () was a similarly ranked official. Chrodegang of Metz adopted this usage from the Benedictines when he introduced the monastic organization of College (canon law), canon-law colleges, especially cathedral chapter, cathedral capitular colleges. The provostship () was normally held by the archdeacon, while the office of dean was held by the archpriest. In many colleges, the temporal duties of the archdeacons made it impossible for them to fulfil those of the provostship, and the headship of the chapter thus fell to the dean. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
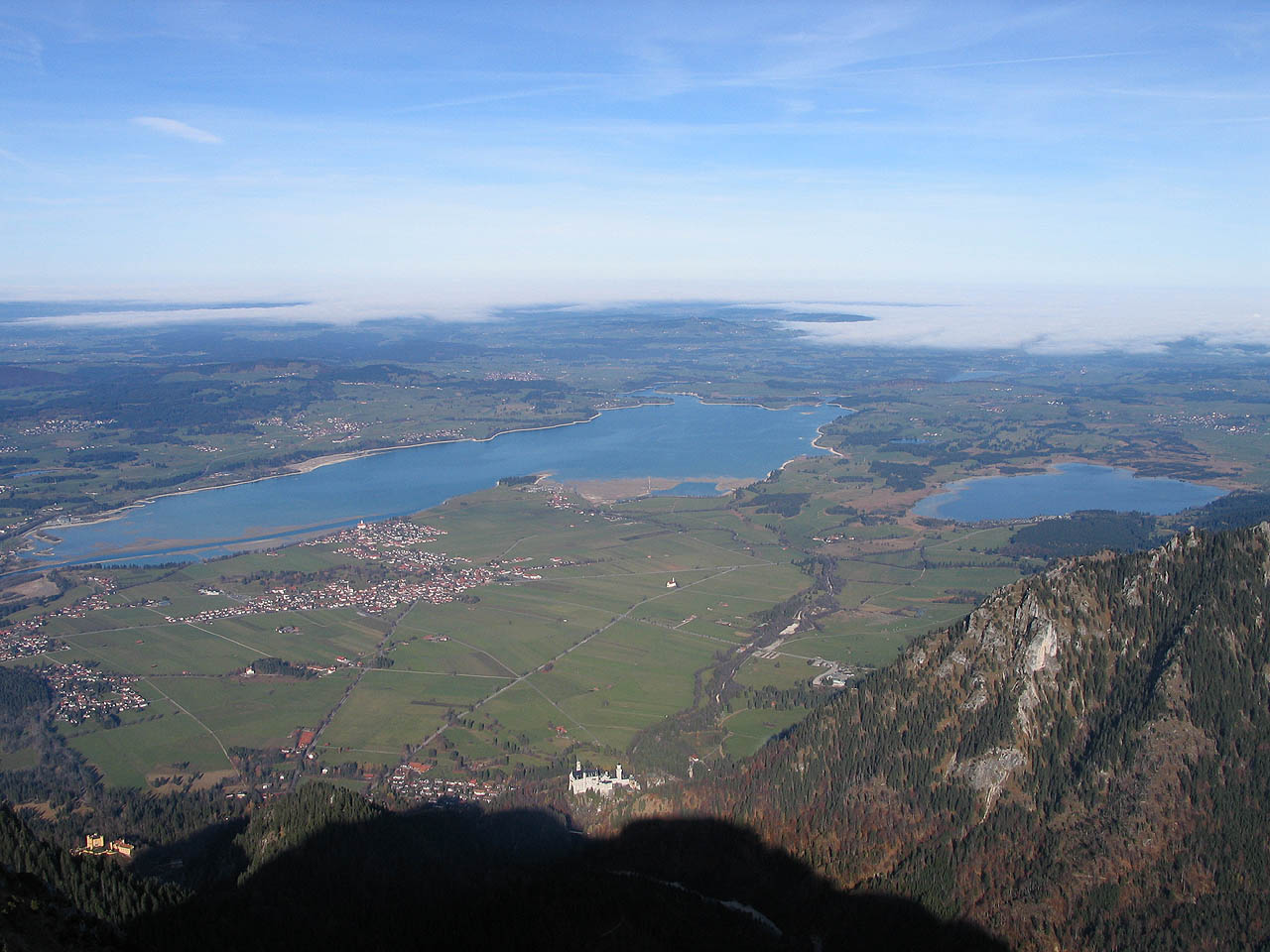
Neuschwanstein Castle
Neuschwanstein Castle (, ; ) is a 19th-century Historicism (art), historicist palace on a rugged hill of the foothills of the Alps in the very south of Germany, near the border with Austria. It is located in the Swabia (Bavaria), Swabia region of Bavaria, in the municipality of Schwangau, above the incorporated village of Hohenschwangau, which is also the location of Hohenschwangau Castle. The closest larger town is Füssen. The castle stands above the narrow gorge of the Pöllat stream, east of the Alpsee and Schwansee lakes, close to the mouth of the Lech (river), Lech into Forggensee. Despite the main residence of the Bavarian monarchs at the time—the Munich Residenz—being one of the most extensive palace complexes in the world, King Ludwig II of Bavaria felt the need to escape from the constraints he saw himself exposed to in Munich, and commissioned Neuschwanstein Castle on the remote northern edges of the Alps as a retreat but also in honour of composer Richard Wagne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig II Of Bavaria
Ludwig II (Ludwig Otto Friedrich Wilhelm; 25 August 1845 – 13 June 1886), also called the Swan King or the Fairy Tale King (), was King of Bavaria from 1864 until his death in 1886. He also held the titles of Count Palatine of the Rhine, Duke of Bavaria, Duke of Franconia, and Duke in Swabia. Outside Germany, he is at times called "the Mad King" or Mad King Ludwig. Ludwig ascended to the throne in 1864 at the age of 18. He increasingly withdrew from day-to-day affairs of state in favour of extravagant artistic and architectural projects. He commissioned the construction of lavish palaces: Neuschwanstein Castle, Linderhof Palace, and Herrenchiemsee. He was also a devoted patron of the composer Richard Wagner. Ludwig spent all his own private royal revenues (although not state funds as is commonly thought) on these projects, borrowed extensively, and defied all attempts by his ministers to restrain him. This extravagance was used against him to declare him insane, a determination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Wittelsbach
The House of Wittelsbach () is a former Bavarian dynasty, with branches that have ruled over territories including the Electorate of Bavaria, the Electoral Palatinate, the Electorate of Cologne, County of Holland, Holland, County of Zeeland, Zeeland, Sweden (with Finland under Swedish rule, Swedish-ruled Finland), Denmark, Norway, Kingdom of Hungary, Hungary, Kingdom of Bohemia, Bohemia, and Kingdom of Greece, Greece. Their ancestral lands of Bavaria and the Electoral Palatinate, Palatinate were prince-electorates, and the family had three of its members elected emperors and kings of the Holy Roman Empire. They ruled over the Kingdom of Bavaria which was created in 1805 and continued to exist until 1918. The House of Windsor, the reigning royal house of the British monarchy, are descendants of Sophia of Hanover (1630–1714), a Wittelsbach Princess of the Palatinate by birth and List of Hanoverian royal consorts, Electress of Hanover by marriage, who had inherited the success ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isabeau Of Bavaria
Isabeau of Bavaria (or Isabelle; also Elisabeth of Bavaria-Ingolstadt; c. 1370 – 24 September 1435) was Queen of France as the wife of King Charles VI of France, Charles VI from 1385 to 1422. She was born into the House of Wittelsbach as the only daughter of Duke Stephen III of Bavaria-Ingolstadt and Taddea Visconti of Milan. At age 15 or 16, Isabella was sent to France to marry the young Charles VI; the couple wed three days after their first meeting. Isabella was honored in 1389 with a lavish coronation of the French monarch, coronation ceremony and entry into Paris. In 1392, Charles suffered the first attack of what was to become a lifelong and progressive mental illness, resulting in periodic withdrawal from government. The episodes occurred with increasing frequency, leaving a court both divided by political factions and steeped in social extravagances. A 1393 masque for one of Isabeau's ladies-in-waiting—an event later known as ''Bal des Ardents''—ended in dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles VI Of France
Charles VI (3 December 136821 October 1422), nicknamed the Beloved () and in the 19th century, the Mad ( or ''le Fou''), was King of France from 1380 until his death in 1422. He is known for his mental illness and psychosis, psychotic episodes that plagued him throughout his life. Charles ascended the throne at age 11, his father Charles V of France, Charles V leaving behind a favorable military situation, marked by the reconquest of most of the English possessions in France. Charles VI was placed under the regency of his uncles: Philip II, Duke of Burgundy; Louis I, Duke of Anjou; John, Duke of Berry; and Louis II, Duke of Bourbon. He decided in 1388, aged 20, to emancipate himself. In 1392, while leading a military expedition against the Duchy of Brittany, the king had his first attack of delirium, during which he attacked his own men in the forest of Le Mans. A few months later, following the ''Bal des Ardents'' (January 1393) where he narrowly escaped death from burning, Char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blessed Virgin Mary (Roman Catholic)
The veneration of Mary in the Catholic Church encompasses various devotions which include prayer, pious acts, visual arts, poetry, and music devoted to her. Popes have encouraged it, while also taking steps to reform some manifestations of it.For example, on March 12, 1969, Pope Paul VI reduced and rearranged the number of Marian feast days in ''Sanctitas clarior''. Several of his predecessors did similarly. The Holy See has insisted on the importance of distinguishing "true from false devotion, and authentic doctrine from its deformations by excess or defect". There are significantly more titles, feasts, and venerative Marian practices among Roman Catholics than in other Western Christian traditions. The term '' hyperdulia'' indicates the special veneration due to Mary, greater than the ordinary '' dulia'' for other saints, but utterly unlike the '' latria'' due only to God. Belief in the incarnation of God the Son through Mary is the basis for calling her the Mother of Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrine
A shrine ( "case or chest for books or papers"; Old French: ''escrin'' "box or case") is a sacred space">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ...: ''escrin'' "box or case") is a sacred space dedicated to a specific deity, ancestor worship, ancestor, hero, martyr, saint, Daemon (mythology), daemon, or similar figure of respect, wherein they are venerated or worshipped. Shrines often contain Cult image, idols, relics, or other such objects associated with the figure being venerated. A shrine at which votive offerings are made is called an altar. Shrines are found in many of the world's religions, including Christianity, Islam, Hinduism, Buddhism, Chinese folk religion, Shinto, indigenous Philippine folk religions, and Germanic paganism as well as in secular and non-religious settings such as a war memorial. Shrines can be found in various settings, such as churches, temples, cemeteries, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altötting Gnadenkapelle 001
Altötting (, , in contrast to "Neuötting, New Ötting"; , ) is a Town#Germany, town in Bavaria, capital of the Altötting (district), district Altötting of Germany. For 500 years it has been the scene of religious pilgrimages by Catholics in honor of Mary, including a visit by Pope John Paul II in 1980 and one by Pope Benedict XVI in 2006. History During the Carolingian period, there was a royal palace here. Nearby, King Carloman of Bavaria, Carloman erected a Benedictine monastery in 876, with Werinolf as first abbot, and also built the abbey church in honour of the Apostle Philip the Apostle, St. Philip. In 907 King Louis the Child gave the abbey ''in commendam'' to Burchard, the Roman Catholic Diocese of Passau, Bishop of Passau (903-915), (probably identical with Burchard, second and last abbot). In 910 the Hungarians ransacked and burnt the church and abbey. In 1228 Duke Louis I, Duke of Bavaria rebuilt these buildings and, after they were sanctified, placed them in cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friary
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which may be a chapel, church, or temple, and may also serve as an oratory, or in the case of communities anything from a single building housing only one senior and two or three junior monks or nuns, to vast complexes and estates housing tens or hundreds. A monastery complex typically comprises a number of buildings which include a church, dormitory, cloister, refectory, library, balneary and infirmary and outlying granges. Depending on the location, the monastic order and the occupation of its inhabitants, the complex may also include a wide range of buildings that facilitate self-sufficiency and service to the community. These may include a hospice, a school, and a range of agricultural and manufacturing buildings such as a barn, a forge, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porter (monastery)
In a monastery, the porter is the monk (or portress for a nun) appointed to be the one who interacts with the public. It is considered an important office, as the porter is the representative of the community to the outside world. The person is stationed at the front door and responsible for greeting visitors to the monastery. The ''Rule of Saint Benedict'', in chapter 66, gives specific advice as to the qualifications of the person chosen to serve in this post.At the door of the monastery, place a sensible old man who knows how to take a message and deliver a reply, and whose age keeps him from roaming about. As soon as anyone knocks, or a poor man calls out, he replies, 'Thanks be to God' or 'Your blessing, please'; then, with all the gentleness that comes from the fear of God, he provides a prompt answer with the warmth of love. The porter needs to be someone with a gift for dealing humanely with visitors. The poor must be treated gently because they are specially loved by God ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |