|
Alpha (investment)
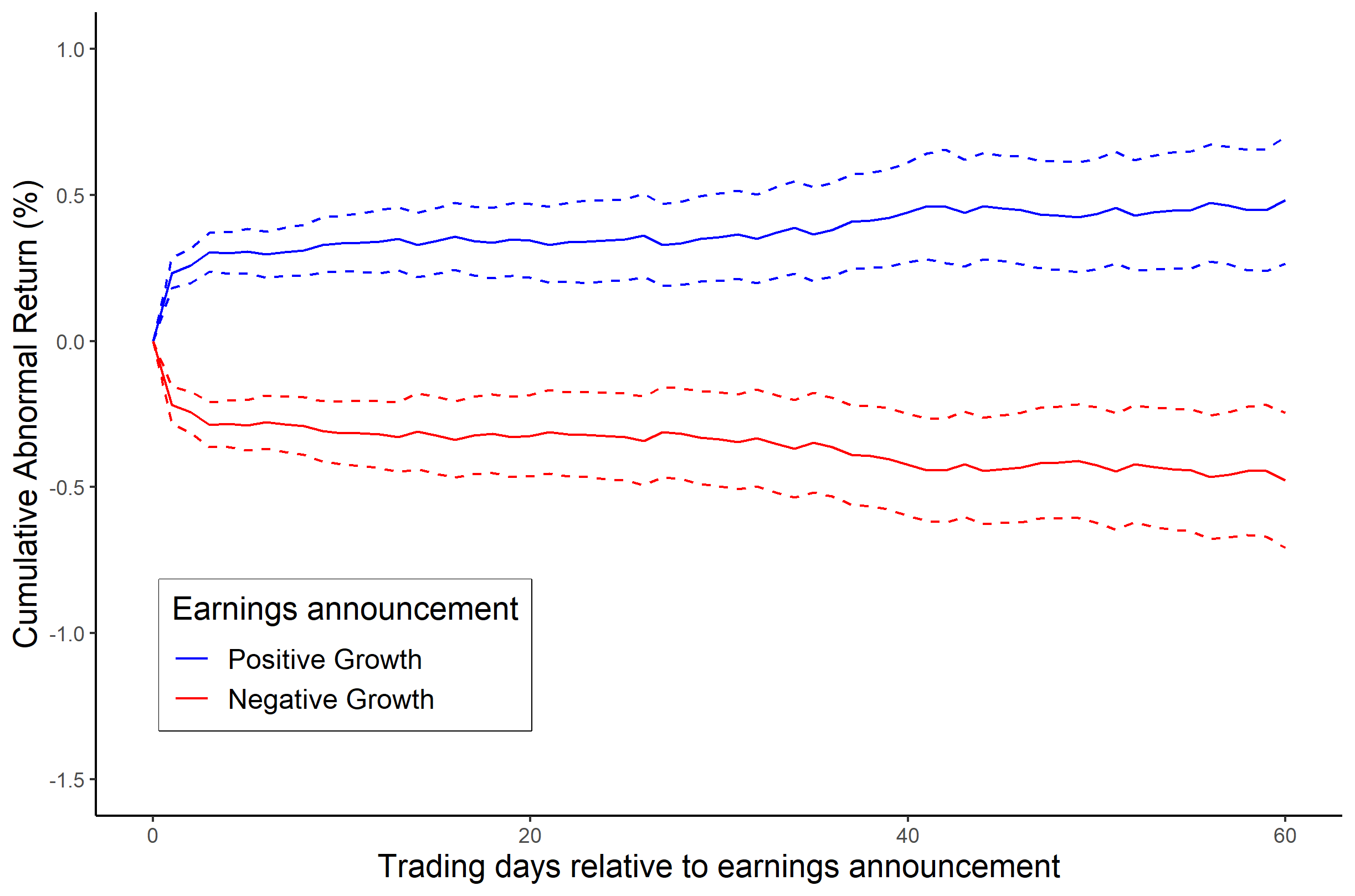
Alpha is a measure of the active return on an investment, the performance of that investment compared with a suitable stock market index, market index. An alpha of 1% means the investment's return on investment over a selected period of time was 1% better than the market during that same period; a negative alpha means the investment underperformed the market. Alpha, along with Beta (finance), beta, is one of two key coefficients in the capital asset pricing model used in modern portfolio theory and is closely related to other important quantities such as Standard deviation#Finance, standard deviation, R-squared and the Sharpe ratio#Use in finance, Sharpe ratio. In modern financial markets, where index funds are widely available for purchase, alpha is commonly used to judge the performance of mutual funds and similar investments. As these funds include various fees normally expressed in percent terms, the fund has to maintain an alpha greater than its fees in order to provide posi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Return
In finance, active return refers to the financial return, returns produced by an investment portfolio due to active management decisions made by the portfolio manager that cannot be explained by the portfolio's exposure to returns or to risks in the portfolio's investment benchmark; active return is usually the objective of active management and subject of performance attribution. In contrast, passive returns refers to returns produced by an investment portfolio due to its exposure to returns of its benchmark. Passive returns can be obtained deliberately through Passive management, passive tracking of the portfolio benchmark or obtained inadvertently through an investment process unrelated to tracking the index. Benchmark portfolios are often represented in theoretical contexts to include all investment assets - sometimes called a market portfolio in these contexts, but is in practice a subset of practically available investable assets. In those cases where the benchmark or the mark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Security Characteristic Line
Security characteristic line (SCL) is a regression line, plotting performance of a particular security or portfolio against that of the market portfolio at every point in time. The SCL is plotted on a graph where the Y-axis is the excess return on a security over the risk-free return and the X-axis is the excess return of the market in general. The slope of the SCL is the security's beta, and the intercept is its alpha. Formula :\mathrm : R_ - R_ = \alpha_i + \beta_i\, ( R_ - R_ ) + \epsilon_ where: :''α''''i'' is called the asset's alpha Alpha (uppercase , lowercase ) is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of one. Alpha is derived from the Phoenician letter ''aleph'' , whose name comes from the West Semitic word for ' ... (abnormal return) :''βi''(''R''''M'',''t'' – ''Rf'') is a nondiversifiable or systematic risk :''ε''''i'',''t'' is the non-systematic or diversifiable, non-market or idiosyncratic risk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilshire 5000
The Wilshire 5000 Total Market Index, or more simply the Wilshire 5000, is a market-capitalization-weighted index of the market value of all American stocks actively traded in the United States. As of December 31, 2023, the index contained 3,403 components. The index is intended to measure the performance of most publicly traded companies headquartered in the United States, with readily available price data (Bulletin Board/penny stocks and stocks of extremely small companies are excluded). Hence, the index includes a majority of the common stocks and REITs traded primarily through New York Stock Exchange, NASDAQ, or the American Stock Exchange. Limited partnerships and ADRs are not included. It can be tracked by following the ticker ^FTW5000. History *The Wilshire 5000 Total Market Index was established by the Wilshire Associates in 1974, naming it for the approximate number of issues it included at the time. It was renamed the "Dow Jones Wilshire 5000" in April 2004, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S&P 500
The Standard and Poor's 500, or simply the S&P 500, is a stock market index tracking the stock performance of 500 leading companies listed on stock exchanges in the United States. It is one of the most commonly followed equity indices and includes approximately 80% of the total market capitalization of U.S. public companies, with an aggregate market cap of more than $49.8 trillion as of March 31, 2025. The S&P 500 index is a Free-float weighted/ capitalization-weighted index. As of April 2025, the ten largest companies on the list of S&P 500 companies accounted for approximately 35% of the market capitalization of the index and were, in order of highest to lowest weighting: Apple (6.4%), Microsoft (6.2%), Nvidia (6.0%), Amazon.com (3.8%), Alphabet (3.6%, including both class A & C shares), Meta Platforms (2.7%), Berkshire Hathaway (2.0%), Broadcom (1.8%), Tesla (1.6%), and JPMorgan Chase (1.4%). The components that have increased their dividends in 25 consecutive ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Investopedia
Investopedia is a global financial media website headquartered in New York City. Founded in 1999, Investopedia provides investment dictionaries, advice, reviews, ratings, and comparisons of financial products, such as securities accounts. It is part of the Dotdash Meredith family of brands owned by IAC. History Founding and early history Investopedia was founded in 1999 by Cory Wagner and Cory Janssen in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. At the time, Janssen was a business student at the University of Alberta. Wagner focused on business development and research and development, while Janssen focused on marketing and sales. 2000s In April 2007, Forbes Media acquired Investopedia.com for an undisclosed amount. At the time of the acquisition, Investopedia drew about 2.5 million monthly users and provided a financial dictionary with about 5,000 terms regarding personal finance, banking and accounting. It also provided articles by financial advisers and a stock market simul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passive Management
Passive management (also called passive investing) is an investing strategy that tracks a market-weighted index or portfolio. Passive management is most common on the equity market, where index funds track a stock market index, but it is becoming more common in other investment types, including bonds, commodities and hedge funds.Burton G. Malkiel, A Random Walk Down Wall Street, W. W. Norton, 1996, There has been a substantial increase in passive investing over the last twenty years. The most popular method is to mimic the performance of an externally specified index by buying an index fund. By tracking an index, an investment portfolio typically gets good diversification, low turnover (good for keeping down internal transaction costs), and low management fees. With low fees, an investor in such a fund would have higher returns than a similar fund with similar investments but higher management fees and/or turnover/transaction costs.William F. SharpeIndexed Investing: A Pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stock Exchange
A stock exchange, securities exchange, or bourse is an exchange where stockbrokers and traders can buy and sell securities, such as shares of stock, bonds and other financial instruments. Stock exchanges may also provide facilities for the issue and redemption of such securities and instruments and capital events including the payment of income and dividends. Securities traded on a stock exchange include stock issued by listed companies, unit trusts, derivatives, pooled investment products and bonds. Stock exchanges often function as "continuous auction" markets with buyers and sellers consummating transactions via open outcry at a central location such as the floor of the exchange or by using an electronic system to process financial transactions. To be able to trade a security on a particular stock exchange, the security must be listed there. Usually, there is a central location for record keeping, but trade is increasingly less linked to a physical place as mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fair Value
In accounting, fair value is a rational and unbiased estimate of the potential market price of a good, service, or asset. The derivation takes into account such objective factors as the costs associated with production or replacement, market conditions and matters of supply and demand. Subjective factors may also be considered such as the risk characteristics, the cost of and return on capital, and individually perceived utility. Economic understanding Market price There are two schools of thought about the relation between the market price and fair value in any form of market, but especially with regard to tradable assets: * The efficient-market hypothesis asserts that, in a well organized, reasonably transparent market, the market price is generally equal to or close to the fair value, as investors react quickly to incorporate new information about relative scarcity, utility, or potential returns in their bids; see also Rational pricing. * Behavioral finance asserts t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Share Prices
A share price is the price of a single Share (finance), share of a number of saleable share capital, equity shares of a company. In layman's terms, the stock price is the highest amount someone is willing to pay for the stock, or the lowest amount that it can be bought for. Behaviour of share prices In economics and financial theory, analysts use random walk techniques to model behavior of asset prices, in particular share prices of companies publicly listed. This practice has its basis in the presumption that investors act rational investor, rationally and without biases, and that at any moment they estimate the Value (economics), value of an asset based on future expectations. Under these conditions, all existing information affects the price, which changes only when new information comes out. By definition, new information appears randomly and influences the asset price randomly. Empirical studies have demonstrated that prices do not completely follow random walks. Low serial c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efficient Market Hypothesis
The efficient-market hypothesis (EMH) is a hypothesis in financial economics that states that asset prices reflect all available information. A direct implication is that it is impossible to "beat the market" consistently on a risk-adjusted basis since market prices should only react to new information. Because the EMH is formulated in terms of risk adjustment, it only makes testable predictions when coupled with a particular model of risk. As a result, research in financial economics since at least the 1990s has focused on market anomalies, that is, deviations from specific models of risk. The idea that financial market returns are difficult to predict goes back to Bachelier, Mandelbrot, and Samuelson, but is closely associated with Eugene Fama, in part due to his influential 1970 review of the theoretical and empirical research. The EMH provides the basic logic for modern risk-based theories of asset prices, and frameworks such as consumption-based asset pricing and int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Asset Pricing Model
In finance, the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) is a model used to determine a theoretically appropriate required rate of return of an asset, to make decisions about adding assets to a Diversification (finance), well-diversified Portfolio (finance), portfolio. The model takes into account the asset's sensitivity to non-diversifiable risk (also known as systematic risk or market risk), often represented by the quantity Beta (finance), beta (β) in the financial industry, as well as the expected return of the market and the expected return of a theoretical Risk-free bond, risk-free asset. CAPM assumes a particular form of utility functions (in which only first and second Moment (mathematics), moments matter, that is risk is measured by variance, for example a quadratic utility) or alternatively asset returns whose probability distributions are completely described by the first two moments (for example, the normal distribution) and zero transaction costs (necessary for diversifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efficient-market Hypothesis
The efficient-market hypothesis (EMH) is a hypothesis in financial economics that states that asset prices reflect all available information. A direct implication is that it is impossible to "beat the market" consistently on a risk-adjusted basis since market prices should only react to new information. Because the EMH is formulated in terms of risk adjustment, it only makes testable predictions when coupled with a particular model of risk. As a result, research in financial economics since at least the 1990s has focused on market anomalies, that is, deviations from specific models of risk. The idea that financial market returns are difficult to predict goes back to Bachelier, Mandelbrot, and Samuelson, but is closely associated with Eugene Fama, in part due to his influential 1970 review of the theoretical and empirical research. The EMH provides the basic logic for modern risk-based theories of asset prices, and frameworks such as consumption-based asset pricing and int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |