|
Allenes
In organic chemistry, allenes are organic compounds in which one carbon atom has double bonds with each of its two adjacent carbon atoms (, where R is H or some organyl group). Allenes are classified as cumulated dienes. The parent compound of this class is propadiene (), which is itself also called ''allene''. A group of the structure is called allenyl, while a substituent attached to an allene is referred to as an allenic substituent (R is H or some alkyl group). In analogy to allylic and propargylic, a substituent attached to a saturated carbon α (i.e., directly adjacent) to an allene is referred to as an allenylic substituent. While allenes have two consecutive ('cumulated') double bonds, compounds with three or more cumulated double bonds are called cumulenes. History For many years, allenes were viewed as curiosities but thought to be synthetically useless and difficult to prepare and to work with.The Chemistry of the Allenes (vol. 1−3); Landor, S. R., Ed.; cademi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allene Symmetry
In organic chemistry, allenes are organic compounds in which one carbon atom has double bonds with each of its two adjacent carbon atoms (, where R is hydrogen, H or some organyl group). Allenes are classified as diene#Classes, cumulated dienes. The parent compound of this class is propadiene (), which is itself also called ''allene''. A group of the structure is called allenyl, while a substituent attached to an allene is referred to as an allenic substituent (R is H or some alkyl group). In analogy to Allyl group, allylic and Propargyl group, propargylic, a substituent attached to a saturated carbon α (i.e., directly adjacent) to an allene is referred to as an allenylic substituent. While allenes have two consecutive ('cumulated') double bonds, compounds with three or more cumulated double bonds are called cumulenes. History For many years, allenes were viewed as curiosities but thought to be synthetically useless and difficult to prepare and to work with.The Chemistry of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axial Chirality
In chemistry, axial chirality is a special case of chirality (chemistry), chirality in which a molecule contains two pairs of chemical groups in a non-planar arrangement about an axis of chirality so that the molecule is not superposable on its mirror image. The axis of chirality (or ''chiral axis'') is usually determined by a chemical bond that is constrained against free rotation either by steric hindrance of the groups, as in substituted aryl, biaryl compounds such as BINAP, or by Torsion constant#Torsional_stiffness, torsional stiffness of the bonds, as in the C=C double bonds in allenes such as glutinic acid. Axial chirality is most commonly observed in substituted biaryl compounds wherein the rotation about the aryl–aryl bond is restricted so it results in chiral atropisomers, as in various ortho-substituted biphenyls, and in binaphthyls such as BINAP. Axial chirality differs from Stereocenter, central chirality (point chirality) in that axial chirality does not require a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propadiene Structure
Propadiene () or allene () is the organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest allene, i.e. a compound with two adjacent carbon double bonds. As a constituent of MAPP gas, it has been used as a fuel for specialized welding. Production and equilibrium with methylacetylene Propadiene exists in equilibrium with methylacetylene (propyne) and the mixture is sometimes called MAPD for methylacetylene-propadiene: : for which at 270 °C or 0.1 at 5 °C. MAPD is produced as a side product, often an undesirable one, of dehydrogenation of propane to produce propene, an important feedstock in the chemical industry. MAPD interferes with the catalytic Catalysis () is the increase in reaction rate, rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst ... polymerization of propene. Occurrence in Space In 2019 it wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Hybridization
In chemistry, orbital hybridisation (or hybridization) is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new ''hybrid orbitals'' (with different energies, shapes, etc., than the component atomic orbitals) suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theory. For example, in a carbon atom which forms four single bonds, the valence-shell s orbital combines with three valence-shell p orbitals to form four equivalent sp3 mixtures in a Tetrahedral molecular geometry, tetrahedral arrangement around the carbon to bond to four different atoms. Hybrid orbitals are useful in the explanation of molecular geometry and atomic bonding properties and are symmetrically disposed in space. Usually hybrid orbitals are formed by mixing atomic orbitals of comparable energies. History and uses Chemist Linus Pauling first developed the hybridisation theory in 1931 to explain the structure of simple molecules such as methane (CH4) using atomic orbitals. Pauling pointed ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aryne
In organic chemistry, arynes and benzynes are a class of highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive chemical Chemical species, species derived from an aromatic ring by removal of two substituents. Arynes are examples of didehydroarenes (1,2-didehydroarenes in this case), although 1,3- and 1,4-didehydroarenes are also known. Arynes are examples of alkynes under high Ring strain, strain. Bonding in arynes The alkyne representation of benzyne is the most widely encountered. Arynes are usually described as having a strained triple bond (left), but resonance contributors include a cumulene form (middle) and biradical form (right): Geometric constraints on the triple bond in benzyne result in diminished overlap of in-plane p-orbitals, and thus weaker triple bond. The vibrational frequency of the triple bond in benzyne was assigned by Radziszewski to be 1846 cm−1, indicating a weaker triple bond than in unstrained alkyne with vibrational frequency of approximately 2150 cm−1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring Strain
In organic chemistry, ring strain is a type of instability that exists when bonds in a molecule form angles that are abnormal. Strain is most commonly discussed for small rings such as cyclopropanes and cyclobutanes, whose internal angles are substantially smaller than the idealized value of approximately 109°. Because of their high strain, the heat of combustion for these small rings is elevated. Ring strain results from a combination of angle strain, conformational strain or Pitzer strain (torsional eclipsing interactions), and transannular strain, also known as van der Waals strain or Prelog strain. The simplest examples of angle strain are small cycloalkanes such as cyclopropane and cyclobutane. Ring strain energy can be attributed to the energy required for the distortion of bond and bond angles in order to close a ring. Ring strain energy is believed to be the cause of accelerated rates in altering ring reactions. Its interactions with traditional bond energi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton Affinity
The proton affinity (PA, ''E''pa) of an anion or of a neutral atom or molecule is the negative of the enthalpy change in the reaction between the chemical species concerned and a proton in the gas phase: ::: A- + H+ -> HA ::: B + H+ -> BH+ These reactions are always exothermic in the gas phase, i.e. energy is released ( enthalpy is negative) when the reaction advances in the direction shown above, while the proton affinity is positive. This is the same sign convention used for electron affinity. The property related to the proton affinity is the gas-phase basicity, which is the negative of the Gibbs energy for above reactions, i.e. the gas-phase basicity includes entropic terms in contrast to the proton affinity. Acid/base chemistry The higher the proton affinity, the stronger the base and the weaker the conjugate acid ''in the gas phase''. The (reportedly) strongest known base is the ortho-diethynylbenzene dianion (''E''pa = 1843 kJ/mol), followed by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cahn–Ingold–Prelog Priority Rules
In organic chemistry, the Cahn–Ingold–Prelog (CIP) sequence rules (also the CIP priority convention; named after Robert Sidney Cahn, Christopher Kelk Ingold, and Vladimir Prelog) are a standard process to completely and unequivocally name a stereoisomer of a molecule. The purpose of the CIP system is to assign an ''R'' or ''S'' descriptor to each stereocenter and an ''E'' or ''Z'' descriptor to each double bond so that the configuration of the entire molecule can be specified uniquely by including the descriptors in its systematic name. A molecule may contain any number of stereocenters and any number of double bonds, and each usually gives rise to two possible isomers. A molecule with an integer describing the number of stereocenters will usually have stereoisomers, and diastereomers each having an associated pair of enantiomers. The CIP sequence rules contribute to the precise naming of every stereoisomer of every organic molecule with all atoms of ligancy of fewe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacobus Henricus Van 't Hoff
Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff Jr. (; 30 August 1852 – 1 March 1911) was a Dutch physical chemistry, physical chemist. A highly influential theoretical chemistry, theoretical chemist of his time, Van 't Hoff was the first winner of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. His pioneering work helped found the modern theory of chemical affinity, chemical equilibrium, chemical kinetics, and chemical thermodynamics. In his 1874 pamphlet, Van 't Hoff formulated the theory of the tetrahedral carbon atom and laid the foundations of stereochemistry. In 1875, he predicted the correct structures of allenes and cumulenes as well as their axial Chirality (chemistry), chirality. He is also widely considered one of the founders of physical chemistry as the discipline is known today. Biography The third of seven children, Van 't Hoff was born in Rotterdam, Netherlands, 30 August 1852. His father was Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff Sr., a physician, and his mother was Alida Kolff van 't Hoff. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chirality (chemistry)
In chemistry, a molecule or ion is called chiral () if it cannot be superposed on its mirror image by any combination of rotation (geometry), rotations, translation (geometry), translations, and some Conformational isomerism, conformational changes. This geometric property is called chirality (). The terms are derived from Ancient Greek (''cheir'') 'hand'; which is the canonical example of an object with this property. A chiral molecule or ion exists in two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other, called enantiomers; they are often distinguished as either "right-handed" or "left-handed" by their absolute configuration or some other criterion. The two enantiomers have the same chemical properties, except when reacting with other chiral compounds. They also have the same physics, physical properties, except that they often have opposite optical activity, optical activities. A homogeneous mixture of the two enantiomers in equal parts is said to be racemic mixture, racem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
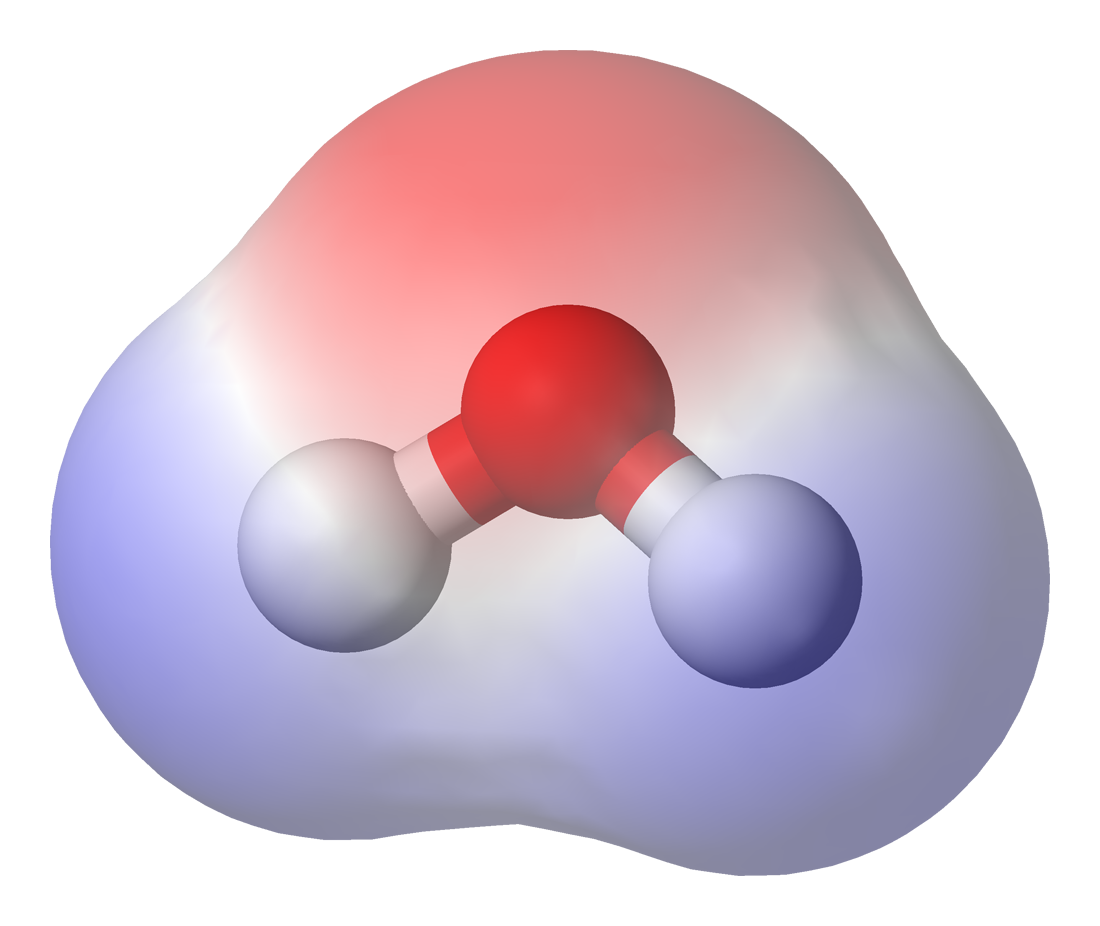
Bond Dipole Moment
In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end. Polar molecules must contain one or more polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Molecules containing polar bonds have no molecular polarity if the bond dipoles cancel each other out by symmetry. Polar molecules interact through dipole-dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Polarity underlies a number of physical properties including surface tension, solubility, and melting and boiling points. Polarity of bonds Not all atoms attract electrons with the same force. The amount of "pull" an atom exerts on its electrons is called its electronegativity. Atoms with high electronegativitiessuch as fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogenexert a greater pull on electrons than atoms with lower electronegativities such as alkali metals and alkaline e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |